Die design is a cornerstone of the plastic extrusion process, directly shaping molten plastic into precise profiles while ensuring quality and efficiency. This blog explores the multifaceted role of die design, providing a comprehensive guide for both newcomers and seasoned professionals in the field.
Die design in plastic extrusion shapes molten plastic into desired profiles, ensuring uniform thickness and reducing defects, crucial for product quality and production efficiency.
By mastering die design1, manufacturers can optimize material use, enhance product consistency, and streamline production. Dive into the details below to understand how die design influences every stage of plastic extrusion.
Die design is crucial for product quality in plastic extrusion.True
A well-designed die ensures uniform thickness and reduces defects, directly impacting the final product's quality.
Die design only affects the shape of the extruded product.False
Die design also influences production efficiency, material waste, and the ability to handle different plastics, making it a multifaceted component in extrusion.
- 1. What is Die Design in Plastic Extrusion?
- 2. How Does Die Design Impact Plastic Extrusion Applications?
- 3. What Are the Key Steps and Parameters in Die Design for Plastic Extrusion?
- 4. What Should You Consider When Designing a Die for Plastic Extrusion?
- 5. How Does Die Design Integrate with Other Technologies in Plastic Extrusion?
- 6. Conclusion
What is Die Design in Plastic Extrusion?
Die design in plastic extrusion refers to the creation of a specialized tool—commonly called an extrusion die2 or shaping die—that molds molten plastic into a specific cross-sectional profile as it exits the extruder. The die operates on the core principle of managing uniform flow and pressure, ensuring consistent dimensions while compensating for phenomena like extrudate swell3 (the tendency of plastic to expand after leaving the die).

Classification of Dies
Dies can be categorized based on process, materials, and applications:
-
By Process: Sheet dies, film dies, pipe dies, profile dies, and coextrusion dies.
-
By Materials: Designed for plastics such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), or polyvinyl chloride (PVC).

- By Applications: Employed in construction (e.g., window frames), packaging (e.g., films), and plumbing (e.g., pipes).
| Classification Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| By Process | Sheet dies, film dies, pipe dies, profile dies, coextrusion dies |
| By Materials | Polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polyvinyl chloride (PVC) |
| By Applications | Construction (window frames), packaging (films), plumbing (pipes) |
How Does Die Design Impact Plastic Extrusion Applications?
Die design adapts to specific industry needs and product requirements, influencing the extrusion process’s versatility.

Typical Application Scenarios
-
Sheet Dies: Produce flat plastic sheets for packaging trays or construction panels.
-
Film Dies: Create thin films for shopping bags and food wraps.
-
Pipe Dies: Form pipes for plumbing and irrigation systems.
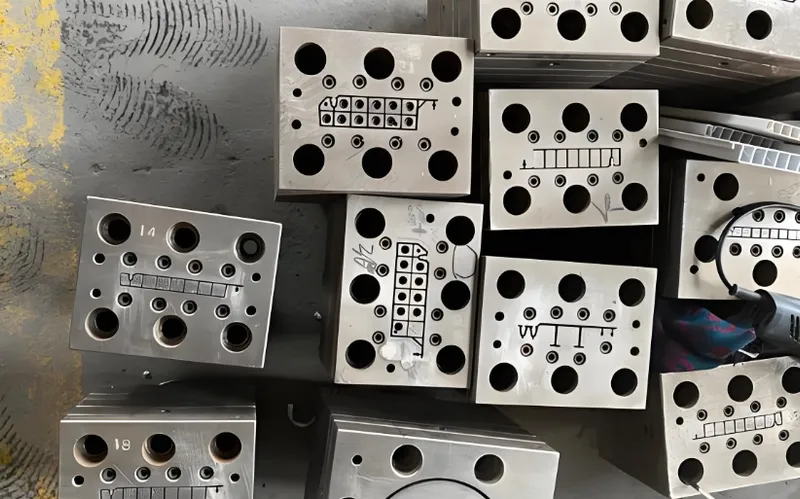

-
Profile Dies: Shape complex profiles like window frames or decorative moldings.
-
Coextrusion Dies: Enable multi-layered products, such as barrier films for food packaging.
Pros and Cons Compared to Other Technologies
-
Advantages: Enables continuous production, minimizes material waste, and supports a wide range of shapes.
-
Disadvantages: Less effective for extremely thin or thick sections, involves higher initial tooling costs, and may lead to defects if not optimized.
Die design enables continuous production in plastic extrusion.True
Unlike batch processes, extrusion with a well-designed die allows for uninterrupted manufacturing, ideal for long profiles.
Die design is always more cost-effective than other molding techniques.False
While efficient for certain applications, die design can have higher initial tooling costs compared to simpler molding methods.
What Are the Key Steps and Parameters in Die Design for Plastic Extrusion?
Die design is integral to the plastic extrusion workflow, with specific steps and parameters ensuring success.
Process Workflow Breakdown
- Feeding: Plastic pellets are introduced into the extruder.

-
Melting: Pellets are melted in the extruder barrel under controlled heat.
-
Pressurizing: Molten plastic is pressurized to ensure consistent flow.
-
Die Shaping: The die molds the plastic, with critical parameters like land length (the straight section of the die) and flow channel design affecting output.
-
Cooling: The extruded product solidifies in a cooling system.
-
Post-Processing: The product is cut, coiled, or further refined.

Material Compatibility
Dies must be tailored to the plastic’s properties:
-
High-Viscosity Plastics4 (e.g., PVC): Require wider die channels for smooth flow.
-
Low-Viscosity Plastics (e.g., PE): Demand precise channel designs to control flow.
-
Temperature-Sensitive Plastics (e.g., Polystyrene): Need accurate temperature regulation.
-
Extrudate Swell-Prone Materials (e.g., PP): Require adjusted exit dimensions to account for expansion.
Die design must account for material properties to prevent defects.True
Different plastics behave uniquely, necessitating tailored die designs to avoid issues like uneven cooling or extrudate swell.
All plastics can be extruded using the same die design.False
Each plastic has distinct flow and thermal properties, requiring specific die adjustments for optimal performance.
What Should You Consider When Designing a Die for Plastic Extrusion?
Effective die design hinges on practical considerations and decision-making tools.
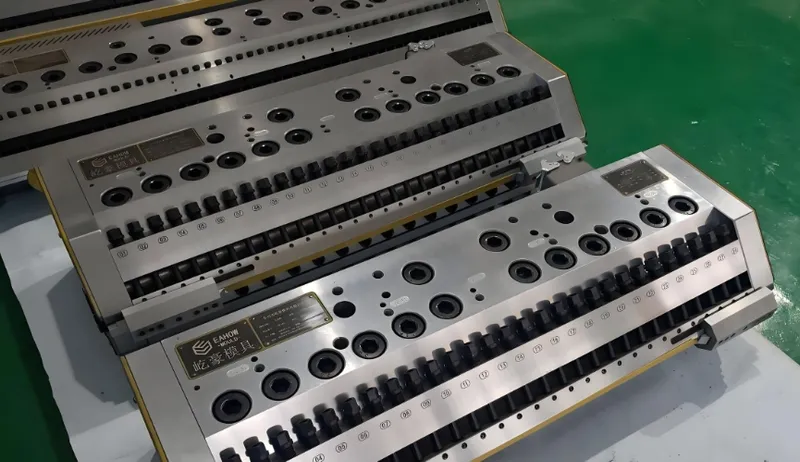

Design Checklist
-
Die Geometry5: Aligns with the target product shape.
-
Land Length: Optimized for cooling and flow stability.
-
Uniform Flow Channels: Prevents imbalances that cause defects.
-
Extrudate Swell Compensation: Adjusts exit dimensions accordingly.
-
Temperature Control6: Incorporates heating/cooling channels.
-
Maintenance Access: Simplifies cleaning and upkeep.
Process Selection Decision-Making
-
Product Complexity: Use standard dies for simple shapes, custom dies for intricate profiles.
-
Material Type: Match die design to viscosity and thermal properties.
-
Production Volume: Opt for durable dies for high-volume runs, simpler designs for low-volume.
-
Cost vs. Quality Trade-off7: Balance initial investment with long-term performance.
A design checklist ensures die design meets process limitations.True
By following a checklist, manufacturers can address key factors like geometry and temperature control, enhancing operability.
Die design is a one-size-fits-all process for all extrusion applications.False
Die design must be tailored to specific product requirements, material properties, and production volumes.
How Does Die Design Integrate with Other Technologies in Plastic Extrusion?
Die design doesn’t operate in isolation—it connects to a broader technological ecosystem.

Related Technology Navigation
-
Upstream Technologies:
-
Extruder Design: Affects melt quality and pressure entering the die.
-
Material Selection: Influences die design based on plastic properties.
-
-
Downstream Technologies:
-
Cooling Systems: Solidify the die-shaped product.
-
Post-Extrusion Processing: Includes cutting, coiling, or additional shaping.
-
Quality Control: Verifies die performance against specifications.
-
Conclusion
Die design is a linchpin in plastic extrusion, determining product shape, quality, and production efficiency. This blog has covered its foundational concepts, practical applications, technical intricacies, design tools, and connections to related technologies. Whether you’re producing pipes, films, or profiles, a well-crafted die is key to success.
Die design is a critical factor in the success of plastic extrusion processes.True
It directly affects product quality, production efficiency, and material usage, making it indispensable in manufacturing.
Die design is only relevant for complex extrusion profiles.False
Even simple profiles require well-designed dies to ensure uniform flow and prevent defects.
-
Understanding die design is crucial for optimizing the plastic extrusion process, ensuring quality and efficiency in production. ↩
-
Exploring the mechanics of an extrusion die can enhance your knowledge of plastic shaping and improve production techniques. ↩
-
Learning about extrudate swell helps in managing product quality and preventing defects during the extrusion process. ↩
-
Learning about high-viscosity plastics can help in selecting the right materials for specific applications in extrusion. ↩
-
Understanding die geometry is crucial for achieving the desired product shape and quality in plastic extrusion processes. ↩
-
Temperature control is vital for maintaining product quality and consistency; explore its impact on die design. ↩
-
Balancing cost and quality is essential for optimizing die design; learn more about making informed decisions. ↩








