Heavy gauge thermoforming is a versatile manufacturing process that produces durable, large-scale plastic parts by heating thick plastic sheets and molding them into specific shapes. This method is widely adopted across various industries due to its cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and ability to create complex geometries. In this article, we will explore the industries that commonly use heavy gauge thermoformed parts, their applications, and the advantages of this process.
Heavy gauge thermoforming is essential in industries like medical, automotive, aerospace, and packaging, producing durable parts like enclosures, panels, and trays, offering cost-effective solutions1 for medium to large components.
Understanding the applications and benefits of Termoformowanie o dużej grubości2 can help industries make informed decisions about their manufacturing processes. This article will delve into the industries that rely on this technology, the advantages it offers, and the technical aspects of the process.
Heavy gauge thermoforming is only used for small, intricate parts.Fałsz
Heavy gauge thermoforming is specifically designed for large, durable parts, unlike thin gauge thermoforming, which is used for smaller, disposable items.
Heavy gauge thermoforming reduces tooling costs compared to injection molding.Prawda
The process uses simpler, less expensive molds, making it ideal for prototyping and medium production runs.
What Industries Use Heavy Gauge Thermoformed Parts?
Heavy gauge thermoformed parts are integral to industries requiring robust, large-scale components3. The process’s ability to handle thick plastic sheets makes it suitable for applications where strength and durability are paramount.
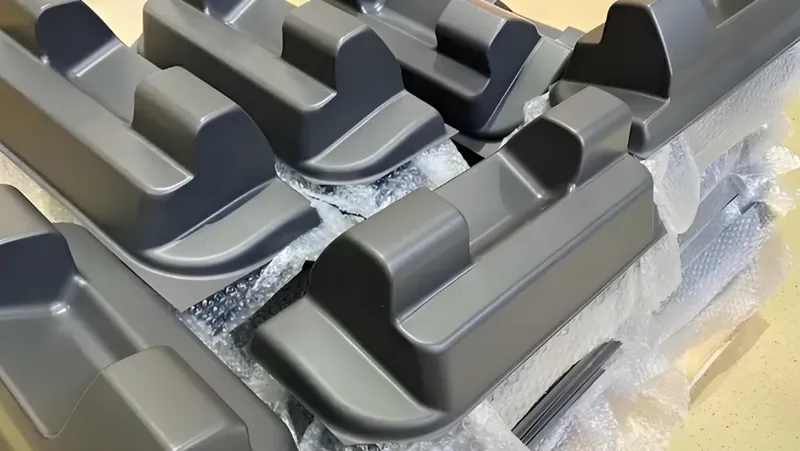

Industries such as medical, automotive, aerospace, defense, packaging, agriculture, transportation, recreational, industrial, and high-tech sectors commonly use heavy gauge thermoformed parts4 for their durability and cost-effectiveness5.
| Przemysł | Zastosowania |
|---|---|
| Medyczny | Enclosures for devices, surgical trays, transfer packaging, medical carts |
| Motoryzacja | Interior panels, exterior trim, under-the-hood parts, after-market accessories |
| Lotnictwo i kosmonautyka | Interior panels, seating components, structural assemblies |
| Defense | Protective packaging, equipment cases |
| Opakowanie | Custom pallets, industrial trays, commercial packaging |
| Rolnictwo | Machinery parts, protective covers |
| Transport | Interior components for trains and trucks, seating |
| Recreational | Sports equipment, playground structures |
| Przemysłowy | Custom machinery parts, enclosures |
| High-Tech | Electronics housings, advanced technology components |
These industries leverage heavy gauge thermoforming for its ability to produce large parts with good structural integrity at a lower cost than alternative methods.
Przemysł medyczny
In the medical field, heavy gauge thermoforming is used to create enclosures for medical devices, surgical trays, and transfer packaging. The process allows for the production of lightweight yet durable components that meet stringent hygiene and safety standards. Companies like Wilbert Plastic Services highlight its use in medical carts and enclosures (Wilbert Plastic Services).
Przemysł motoryzacyjny
The automotive sector benefits from heavy gauge thermoforming for interior panels, exterior trim, and under-the-hood components. This process is particularly advantageous for electric vehicles, where weight reduction is crucial. Plastics Technology discusses its growing role in automotive applications (Plastics Technology).

Aerospace and Defense
Aerospace and defense industries use heavy gauge thermoformed parts for interior panels, seating components, and protective packaging. The process’s ability to create large, lightweight parts makes it ideal for these sectors, where performance and safety are critical (Tru-Form Plastics).
Heavy gauge thermoforming is widely used in the aerospace industry.Prawda
The process is favored for its ability to produce large, lightweight components that meet the stringent requirements of aerospace applications.
Heavy gauge thermoforming is unsuitable for high-volume production.Prawda
While cost-effective for medium runs, it may not be the best choice for very high-volume production compared to processes like injection molding.
What are the Advantages of Heavy Gauge Thermoforming?
Heavy gauge thermoforming offers several benefits that make it a preferred choice for many industries. Understanding these advantages can help manufacturers decide when to use this process over others.
Heavy gauge thermoforming provides niższe koszty oprzyrządowania6, faster production times7, and the ability to create large, durable parts, making it ideal for prototyping and medium-volume production.

Niższe koszty oprzyrządowania
One of the primary advantages of heavy gauge thermoforming is its lower tooling costs compared to processes like injection molding. The molds used are simpler and less expensive, making it an attractive option for prototyping and medium production runs.
Faster Production Times
The process allows for quicker prototyping and production, as the molds can be made and adjusted more rapidly than those for injection molding. This speed is beneficial for industries needing to bring products to market quickly.

Versatility in Part Size and Complexity
Heavy gauge thermoforming can produce large parts, up to 72” x 108”, with moderate complexity. Techniques like twin-sheet forming enable the creation of hollow or double-walled parts, expanding its application range.
Heavy gauge thermoforming can produce parts with high precision and intricate details.Fałsz
While it can achieve moderate complexity, it is not as precise as injection molding for intricate designs.
Heavy gauge thermoforming is more cost-effective for large parts than injection molding.Prawda
The lower tooling costs and ability to handle large sheets make it more economical for big components.
What are the Steps in the Heavy Gauge Thermoforming Process?
Understanding the technical aspects of heavy gauge thermoforming is crucial for professionals looking to optimize their manufacturing processes. This section breaks down the key steps involved.
The heavy gauge thermoforming process includes wybór materiału8, tooling design9, heating, forming, cooling, trimming, and finishing, each critical to achieving the desired part quality.

Wybór materiału
Choose a thermoplastic sheet based on the application’s requirements, such as impact resistance or chemical compatibility. Common materials include PVC, PETG, ABS, Polycarbonate, and Kydex.
Projektowanie narzędzi
Design a mold, typically made from aluminum, to shape the heated sheet. The mold can be male or female, depending on the part’s design.
Ogrzewanie
Heat the plastic sheet to its forming temperature, which varies by material (e.g., 300–350°F for ABS). Uniform heating is essential to prevent thinning and ensure consistent part quality.
Formowanie
Place the heated sheet over or into the mold and apply vacuum or pressure to shape it. Techniques like vacuum forming, pressure forming, or twin-sheet forming are used based on the part’s complexity.
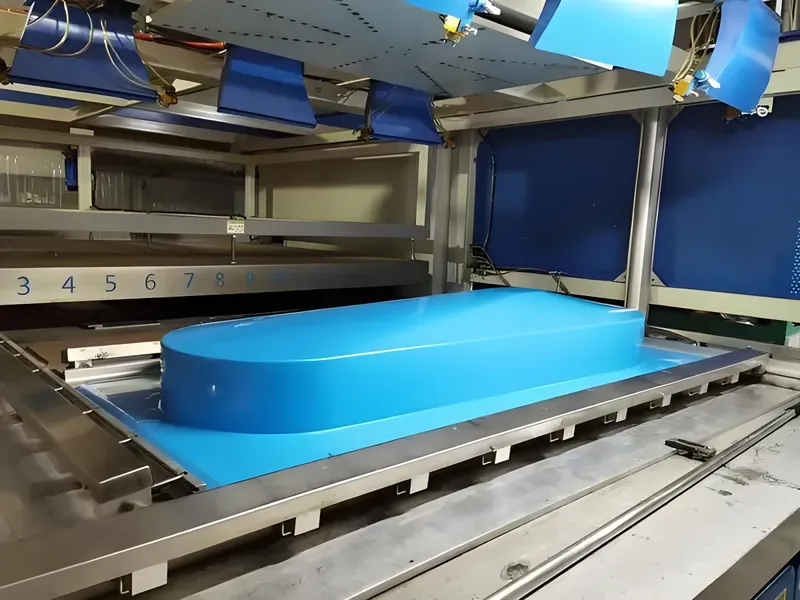
Chłodzenie
Cool the formed part using fans or water mist to solidify the shape. The cooling rate affects the part’s dimensional stability and surface finish.
Przycinanie
Remove excess material using precision tools like 5-axis CNC machines to achieve tight tolerances, often as precise as ±0.010”.
Wykończenie
Apply surface treatments or assemble the part with other components as needed for the final product.
Uniform heating is critical in heavy gauge thermoforming.Prawda
Even heating prevents thinning and ensures the sheet forms correctly without defects.
Heavy gauge thermoforming can achieve the same precision as injection molding.Fałsz
While it offers good precision, it typically cannot match the intricate detail and tight tolerances of injection molding.
How to Choose Between Heavy Gauge Thermoforming and Other Processes?
Selecting the right manufacturing process is crucial for optimizing cost, quality, and production efficiency. This section provides a guide to help decide when to use heavy gauge thermoforming.
Choose heavy gauge thermoforming for large parts, medium wielkość produkcji10, and when lower koszty oprzyrządowania11 and faster lead times are priorities.

Rozmiar i złożoność części
Heavy gauge thermoforming is ideal for large parts with moderate complexity. If the part is small or requires intricate details, injection molding might be more suitable.
Wielkość produkcji
For low to medium production volumes (hundreds to thousands of units), heavy gauge thermoforming is cost-effective. High-volume production may benefit more from injection molding due to economies of scale.

Lead Time and Tooling Costs
If quick prototyping and lower initial costs are important, heavy gauge thermoforming is advantageous. Injection molding requires more time and investment in mold design and manufacturing.
Heavy gauge thermoforming is always the best choice for plastic part production.Fałsz
It is best suited for specific applications, such as large parts and medium volumes, but may not be ideal for all scenarios.
Heavy gauge thermoforming offers faster prototyping than injection molding.Prawda
The simpler tooling and quicker setup allow for rapid prototyping and adjustments.
Wnioski
Heavy gauge thermoforming is a versatile and Efektywny kosztowo proces produkcji12 used across various industries, including medical, automotive, aerospace, and more. Its ability to produce large, durable parts13 with lower tooling costs and faster production times makes it an attractive option for many applications. By understanding the industries that use this process, its advantages, and the technical steps involved, manufacturers can make informed decisions about when to leverage heavy gauge thermoforming for their projects.
-
Learn about the cost-effective solutions offered by heavy gauge thermoforming and how they benefit industries by checking this link. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand the significance and applications of heavy gauge thermoforming in different sectors. ↩
-
Discover the industries that depend on robust components and the reasons behind their choices, enhancing your understanding of market needs. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand the significance and applications of heavy gauge thermoformed parts across various industries. ↩
-
This resource will provide insights into how durability and cost-effectiveness influence manufacturing choices, especially in thermoforming. ↩
-
Exploring this resource will provide insights into how lower tooling costs can enhance manufacturing efficiency and reduce expenses. ↩
-
This link will help you understand the significance of faster production times in meeting market demands and improving competitiveness. ↩
-
Learn about the critical factors in material selection for thermoforming to enhance product quality and performance. ↩
-
Discover best practices in tooling design that can lead to improved efficiency and part quality in thermoforming processes. ↩
-
This resource will provide insights on how production volumes influence the choice of manufacturing processes, helping you make informed decisions. ↩
-
Learn about the various factors that impact tooling costs, which is crucial for budgeting and planning in manufacturing. ↩
-
Discover insights on cost-effective manufacturing processes that can optimize production and reduce expenses in various industries. ↩
-
Learn about the production of durable parts and the technologies involved, which can help improve product quality and longevity. ↩








