真空成形と 射出成形1 are two widely used plastic manufacturing processes2. While both are employed to create plastic parts, they differ significantly in their methods, applications, and suitability for different projects. Understanding the differences between these two processes is crucial for making informed decisions about which one to use for your specific needs.
Vacuum forming heats a plastic sheet and uses a vacuum to shape it over a mold, ideal for larger, simpler parts. Injection molding injects molten plastic into a mold, best for small, detailed, high-volume parts.
Choosing between vacuum forming and injection molding depends on factors like part complexity, production volume, and budget. Delve deeper to explore how each process works and which one suits your project.
Vacuum forming is generally cheaper for low volumes.真
Vacuum forming has lower tooling costs and faster setup times, making it more cost-effective for small production runs.
Injection molding is only suitable for small parts.偽
While injection molding excels in producing small, intricate parts, it can also be used for larger components, though it may be less cost-effective.
What is Vacuum Forming and Injection Molding?
明確な定義
- 真空成形3 (Thermoforming): A manufacturing process where a thermoplastic sheet is heated to a pliable temperature, stretched over a single-surface mold (male or female), and shaped using vacuum pressure. The vacuum pulls the sheet against the mold, forming a hollow, thin-walled part. It is often referred to as thermoforming, a broader category that includes other forming techniques.

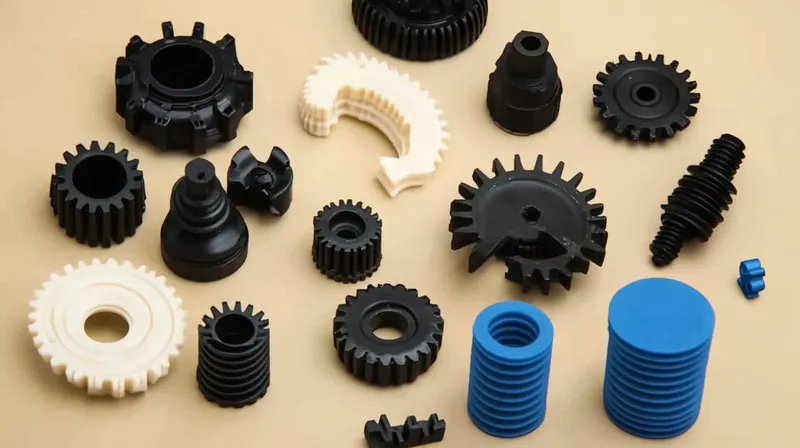
- 射出成形: A process where plastic pellets are melted and injected under high pressure into a double-sided mold cavity. The material cools and solidifies, forming a precise, solid part that is ejected from the mold. It is widely used for producing complex, high-volume parts with tight tolerances.

分類
-
プロセスによって: Vacuum forming is a subset of thermoforming, relying on heat and vacuum pressure. Injection molding is a distinct process involving high-pressure injection of molten material.
-
材料別: Both primarily use 熱可塑性プラスチック4 (e.g., ABS, PVC). Injection molding also supports thermosets, rubber, liquid silicone rubber (LSR), and metal injection molding (MIM).

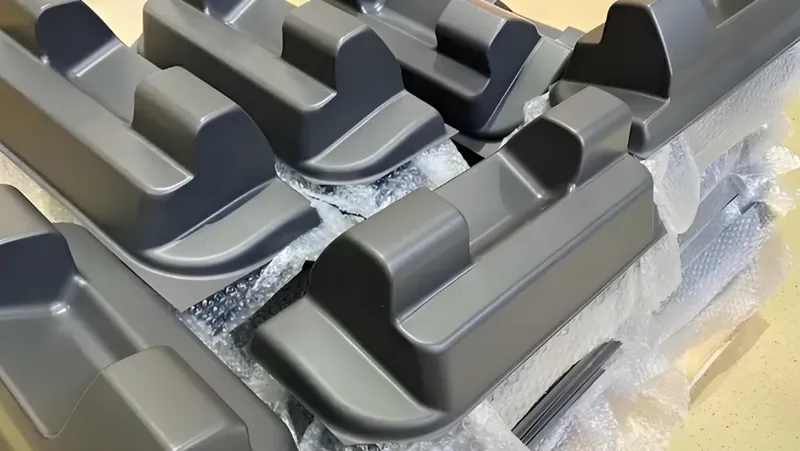
- アプリケーション別: Vacuum forming is suited for large, shallow parts with simpler geometries, such as packaging or automotive interiors. Injection molding excels in small, intricate parts like medical devices or consumer electronics components.
Vacuum forming is limited to thermoplastics.真
Vacuum forming primarily uses thermoplastics due to their ability to be heated and reshaped.
Injection molding can only use plastics.偽
Injection molding can also process thermosets, rubber, and even metals through metal injection molding (MIM).
When to Use Vacuum Forming vs. Injection Molding?
代表的なアプリケーション・シナリオ
- 真空成形: Commonly used in industries requiring large, lightweight parts with moderate detail, including:

- パッケージング: Blister packs, clamshells, and trays.
- 自動車: Interior panels, dashboards, and trim.
- メディカルだ: Device housings and trays.
- Consumer Products: Appliance covers, display stands.
- 射出成形: Preferred for high-precision, complex parts across various sectors, such as:
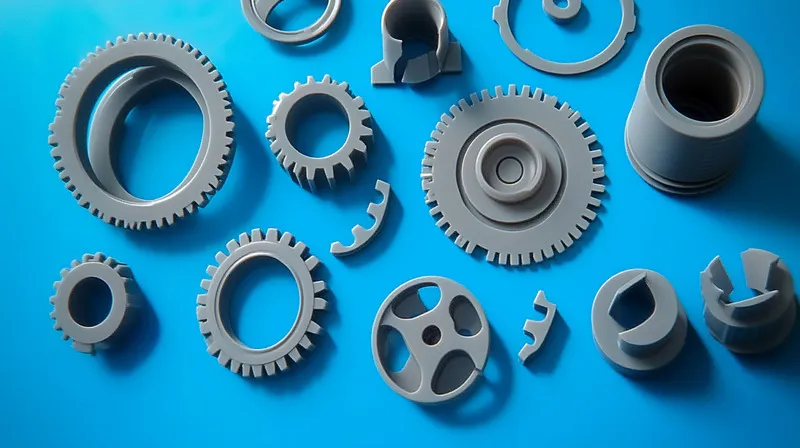

- 自動車: Gears, connectors, and engine components.
- メディカルだ: Syringes, surgical instruments, and diagnostic equipment.
- コンシューマー・エレクトロニクス Phone cases, keyboard keys, and remote controls.
- 産業用だ: Valves, fittings, and tool components.
長所と短所の比較
The following table summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of each process:
| アスペクト | 真空成形 | 射出成形 |
|---|---|---|
| 長所 | - Lower tooling costs - Faster setup - Suitable for large parts - Ideal for prototyping and short runs |
- 高い生産率 - Excellent detail and finish - Consistent quality - Wide material range |
| 短所 | - Limited to simpler geometries - Less detail - Variable wall thickness - Not for high volumes |
- High initial tooling costs - Longer setup times - Higher waste (with cold runners) - Not economical for low volumes |
Vacuum forming is better for prototyping.真
Due to its lower tooling costs and faster setup, vacuum forming is often preferred for prototyping and short production runs.
Injection molding cannot produce large parts.偽
While less common, injection molding can produce large parts, but it may require specialized equipment and higher costs.
How Do the Processes Work?
プロセス全体のワークフロー
-
真空成形:
-
暖房: A thermoplastic sheet is placed in an oven and heated until soft and pliable.
-
成形する: The sheet is stretched over a mold (male for inner dimensions, female for outer dimensions) using mechanical or air pressure.
-

-
真空アプリケーション5: A vacuum is applied to pull the sheet tightly against the mold, forming the shape.
-
冷却: The sheet cools on the mold to set the shape.
- 仕上げ: The part is removed, trimmed (manually or via CNC), and may be sanded, painted, or stenciled.
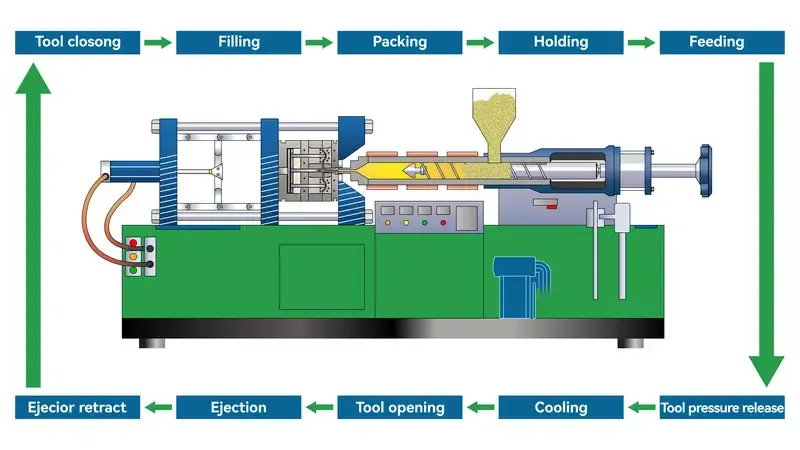
- 射出成形:
-
材料の準備6: Plastic pellets are fed into a hopper and melted in a heated barrel.
- Injection: The molten plastic is injected into a closed mold under high pressure.
-
冷却: The mold is cooled to solidify the plastic.
-
Ejection: The mold opens, and the part is ejected using pins or other mechanisms.
-
Secondary Operations: Parts may be trimmed, assembled, or finished (e.g., painting, silk-screening).
素材適合性の説明
- 真空成形: Limited to thermoplastics that can be heated and stretched without degrading. Common materials include:
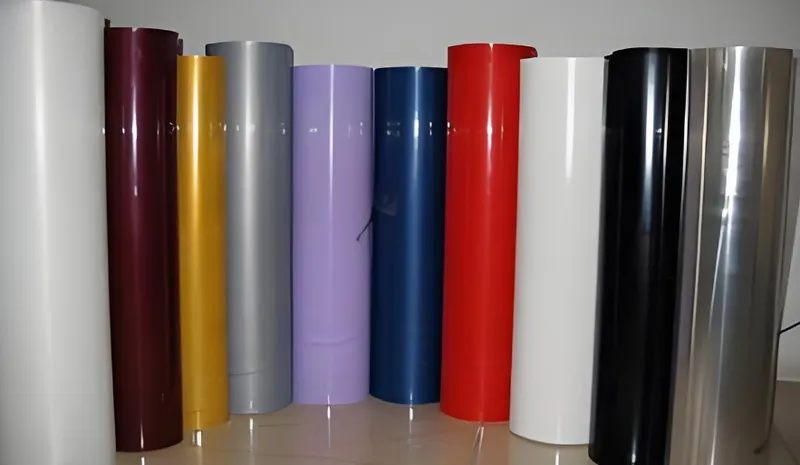

- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Durable and versatile.
- Acrylic: Transparent and impact-resistant.
- Polycarbonate: Strong and heat-resistant.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): Flexible and chemical-resistant.
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): Clear and food-safe.
- Material choice affects part strength, clarity, and cost.
- 射出成形: Supports a broader range of materials, offering greater flexibility:

- 熱可塑性プラスチック: ABS, polypropylene, polyethylene, polystyrene, PVC.
- Thermosets: Epoxy, phenolic (for heat-resistant parts).
- Rubber and LSR: For flexible or medical-grade parts.
- Glass-Filled Polymers: For enhanced strength.
- Specialty Plastics: Fireproof, food-safe, or biocompatible grades.
- Metals (MIM): For high-strength, small components.
- Material selection depends on part requirements for strength, flexibility, or environmental resistance.
Vacuum forming can use the same materials as injection molding.偽
While both processes use thermoplastics, injection molding supports a wider range of materials, including thermosets and metals.
Material choice impacts part properties in both processes.真
The selected material directly influences the strength, flexibility, and other properties of the final part.
What are the Design Considerations for Each Process?
デザイン・チェックリスト

- Avoid deep draws or complex undercuts due to single-direction shaping.
- Aim for uniform wall thickness to prevent thinning during stretching.
- ベリファイ 材料適合性8 with heating and forming processes.
- 射出成形用:
- Design for easy ejection using ejector pins or stripper plates.

- Incorporate proper gating (e.g., edge or pin gates) to minimize visible marks.
- Ensure uniform cooling to avoid warping or sink marks.
- Optimize the flow path to prevent air traps or incomplete filling.
プロセス選択の意思決定
The following table provides a decision-making framework for choosing between vacuum forming and injection molding:
| Criteria | 真空成形 | 射出成形 |
|---|---|---|
| 部品サイズ | Large, shallow parts | Small to medium, complex parts |
| 生産量 | Low to medium (250–2,500 units/year) | High (thousands to millions) |
| Tooling Budget | Lower cost, simpler molds | Higher cost, complex molds |
| 部品の複雑さ | Simple geometries, no undercuts | Intricate designs, undercuts, threads |
| マテリアル・ニーズ | Thermoplastics only | Thermoplastics, thermosets, metals |
Decision Tree Prompt:

-
How complex is your part?
- Simple, shallow (vacuum forming).
- Detailed, intricate (injection molding).
-
What is your budget for tooling?
- Limited (vacuum forming).
- Higher (injection molding).
-
Do you need specific materials?
- Thermoplastics only (either process).
- Thermosets or metals (injection molding).
真空成形は大量生産に最適です。偽
Vacuum forming is better suited for low to medium production volumes due to its slower cycle times and simpler tooling.
Injection molding requires more design considerations than vacuum forming.真
Injection molding involves more complex design requirements, such as gating, cooling, and ejection, to ensure part quality.
関連技術とは?
関連技術ナビゲーション
- 上流技術:
- Material Science: Development of advanced thermoplastics, thermosets, and specialty plastics.
- Mold Design Software: CAD/CAM tools for creating precise molds.

-
川下技術:
- Assembly Techniques: Joining parts via adhesives, welding, or fasteners.
- Surface Finishing: Painting, silk-screening, or coating for aesthetics and durability.
- Integration: Combining with CNC machining or 3D printing for hybrid manufacturing.
-
関連プロセス
- ブロー成形: For hollow parts like bottles and containers.
- 回転成形: For large, hollow parts like tanks and playground equipment.
- Compression Molding: For thermoset materials like automotive composites.
- 3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing): For prototyping or low-volume, complex parts.
Vacuum forming and injection molding are the only plastic manufacturing processes.偽
There are several other processes, such as blow molding, rotational molding, and 3D printing, each with unique applications.
結論
Vacuum forming and injection molding are both valuable plastic manufacturing processes, each with its own strengths and ideal use cases. Vacuum forming is cost-effective for large, simple parts and low to medium production volumes, while injection molding excels in producing small, complex parts with high precision and consistency for large-scale production.
When deciding between the two, consider factors such as part size, complexity, production volume, budget, and material requirements. By understanding the differences and applications of each process, you can make an informed choice that best suits your project's needs.
-
Discover the intricacies of injection molding, its benefits, and why it's ideal for detailed parts in high volumes. ↩
-
Learn about various plastic manufacturing processes to make informed decisions for your production needs. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand the intricacies of Vacuum Forming and its applications in various industries. ↩
-
Learn about thermoplastics, their properties, and how they are utilized in different manufacturing processes. ↩
-
Understanding Vacuum Application is crucial for mastering vacuum forming techniques and achieving high-quality results. ↩
-
Learning about Material Preparation is essential for optimizing the injection molding process and ensuring product quality. ↩
-
Understanding draft angles is crucial for successful part removal in vacuum forming, ensuring efficiency and quality in production. ↩
-
Learning about material compatibility ensures that the right materials are used for optimal results in both forming processes. ↩
-
Exploring production volume helps in selecting the right manufacturing process, optimizing costs and efficiency for your project. ↩








