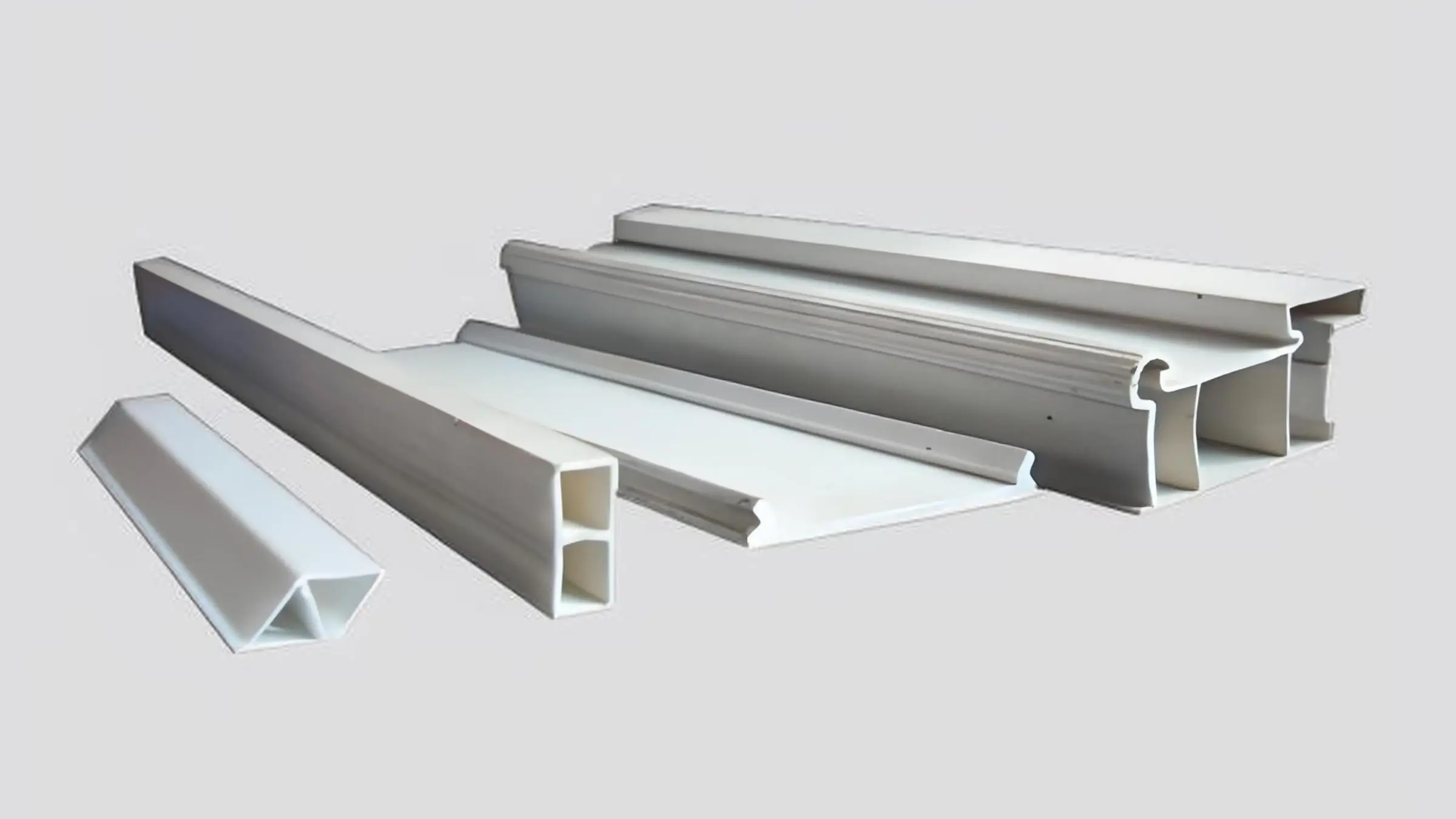
Produsen Profil PVC Khusus
Di Uplastechkami mengkhususkan diri dalam menyediakan profil PVC khusus yang disesuaikan untuk memenuhi kebutuhan unik setiap klien.
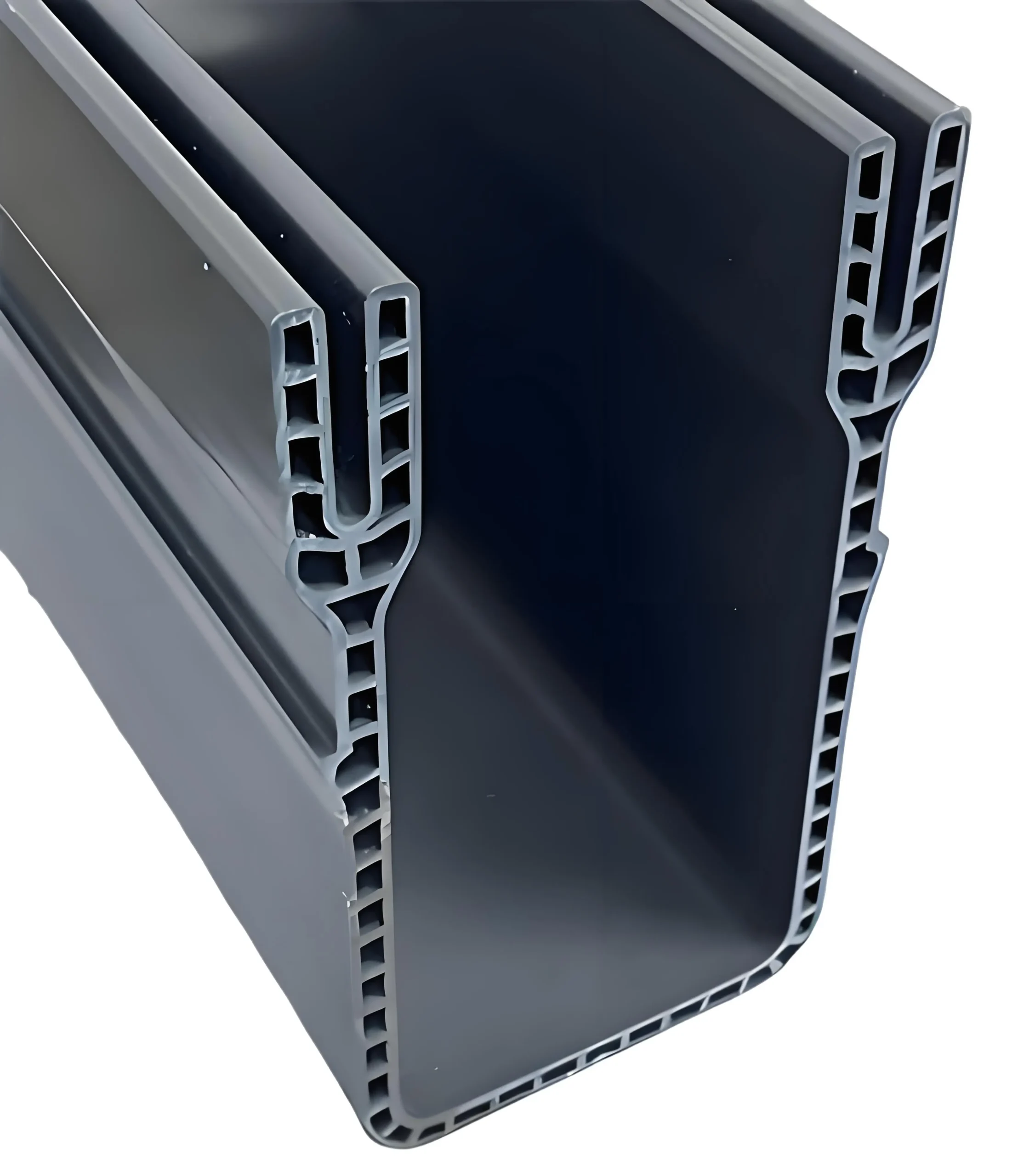

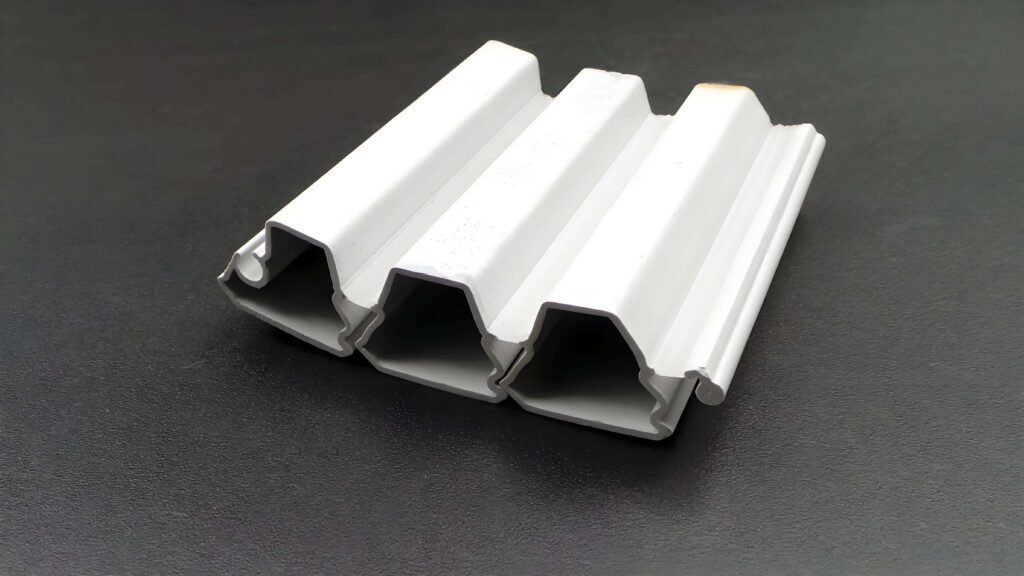
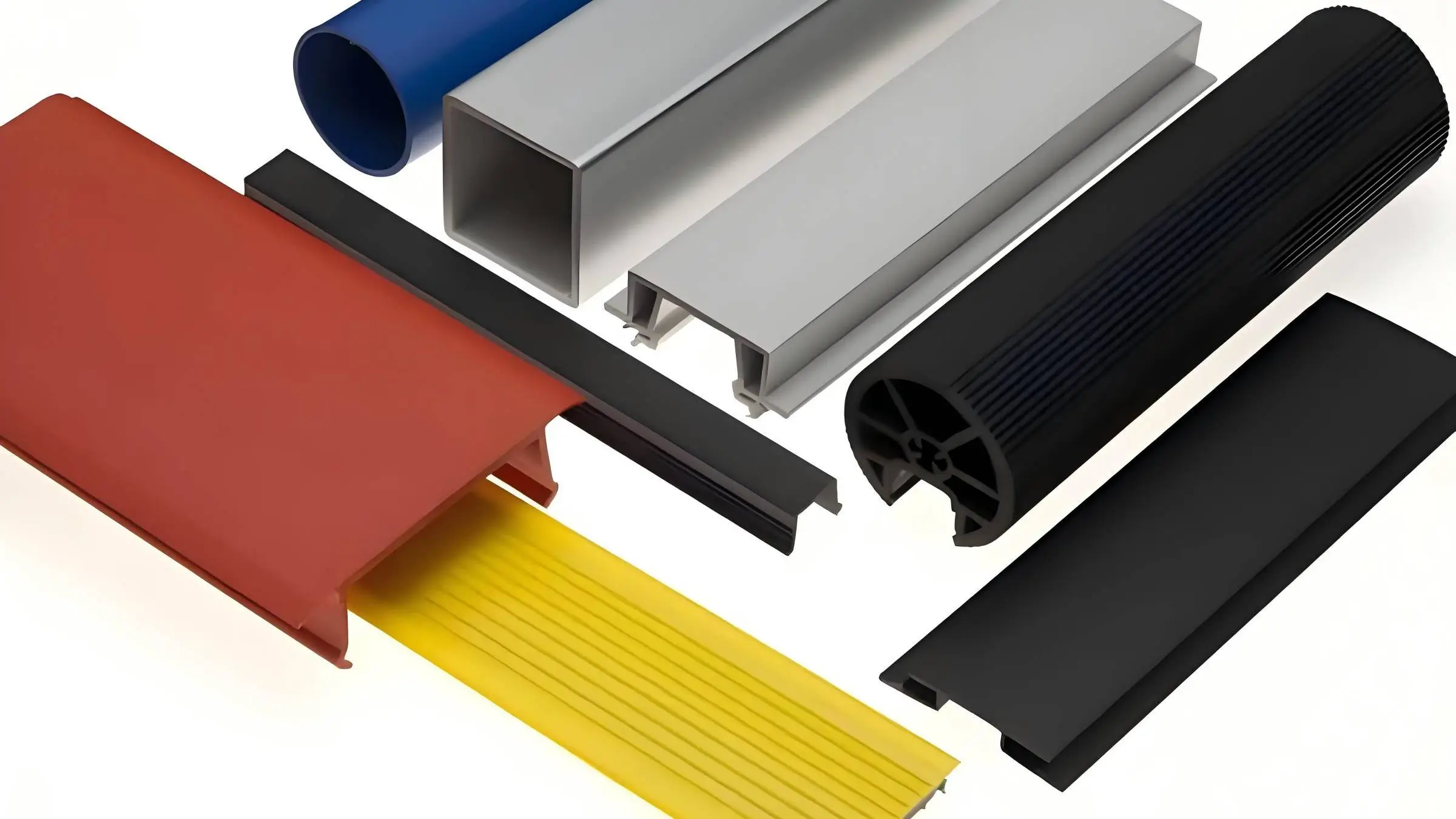
Saluran Drainase PVC
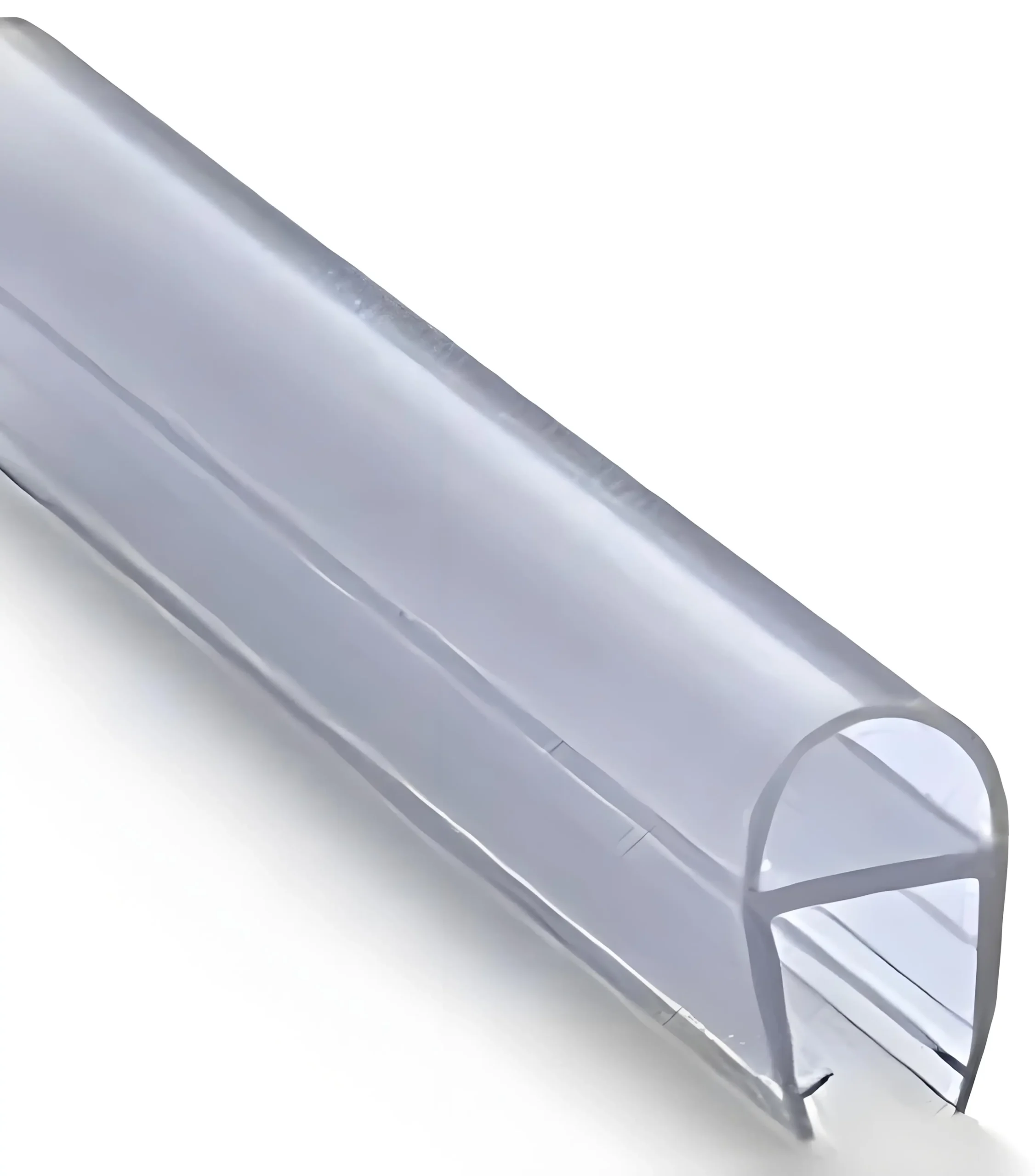

Profil Transparan PVC
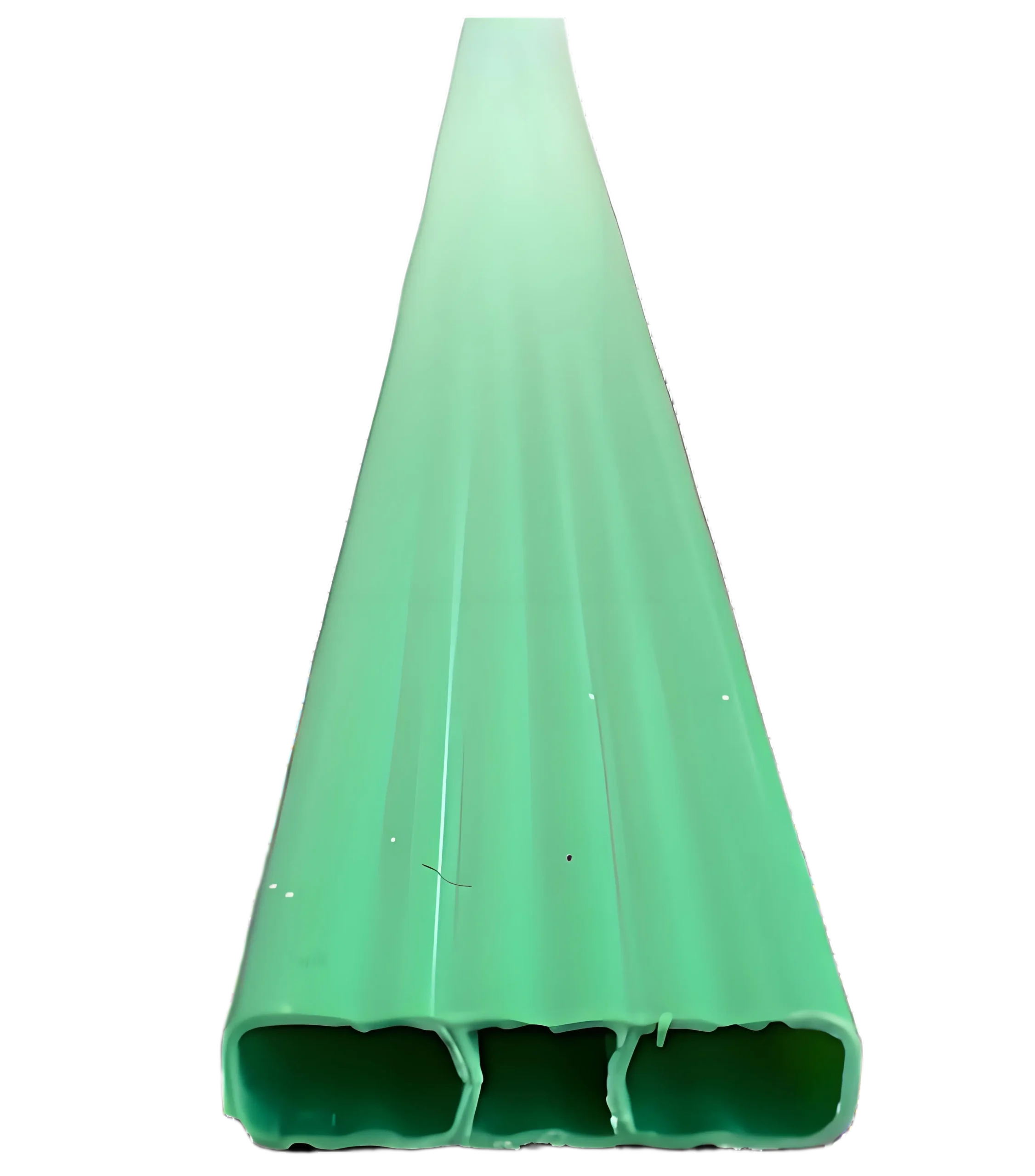

Profil Berongga PVC
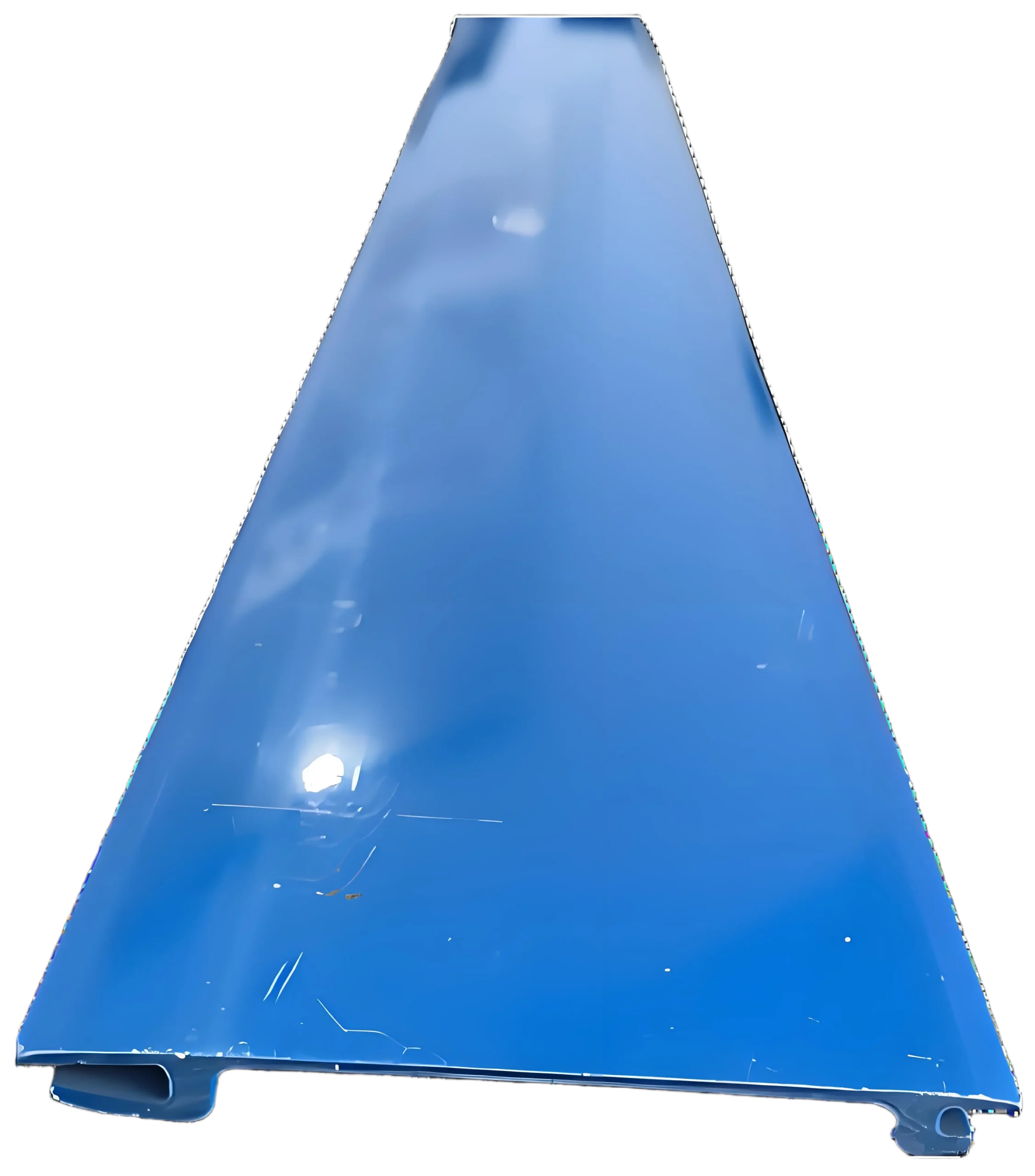

Profil Penutup Alur PVC
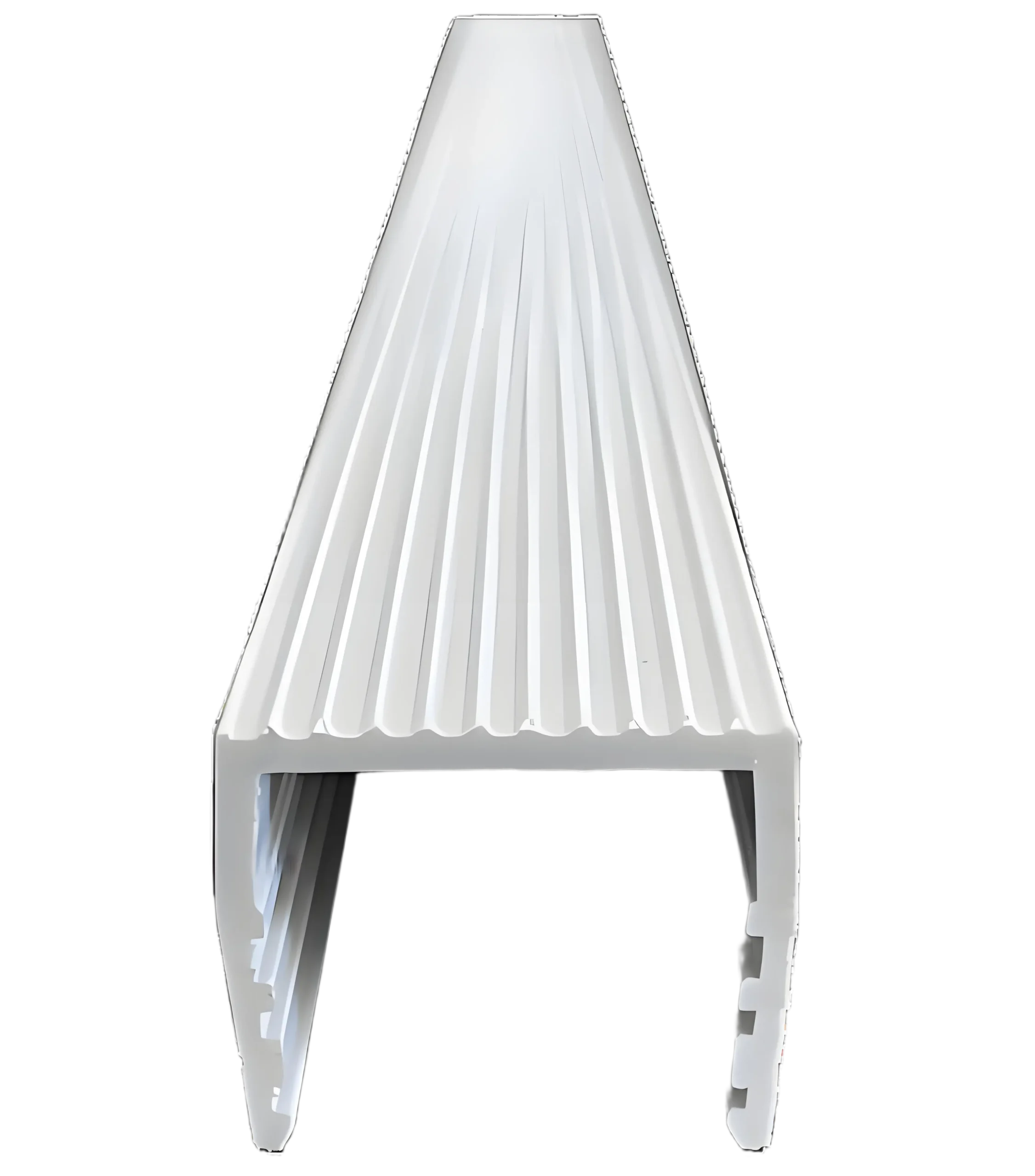

Profil Dasar PVC
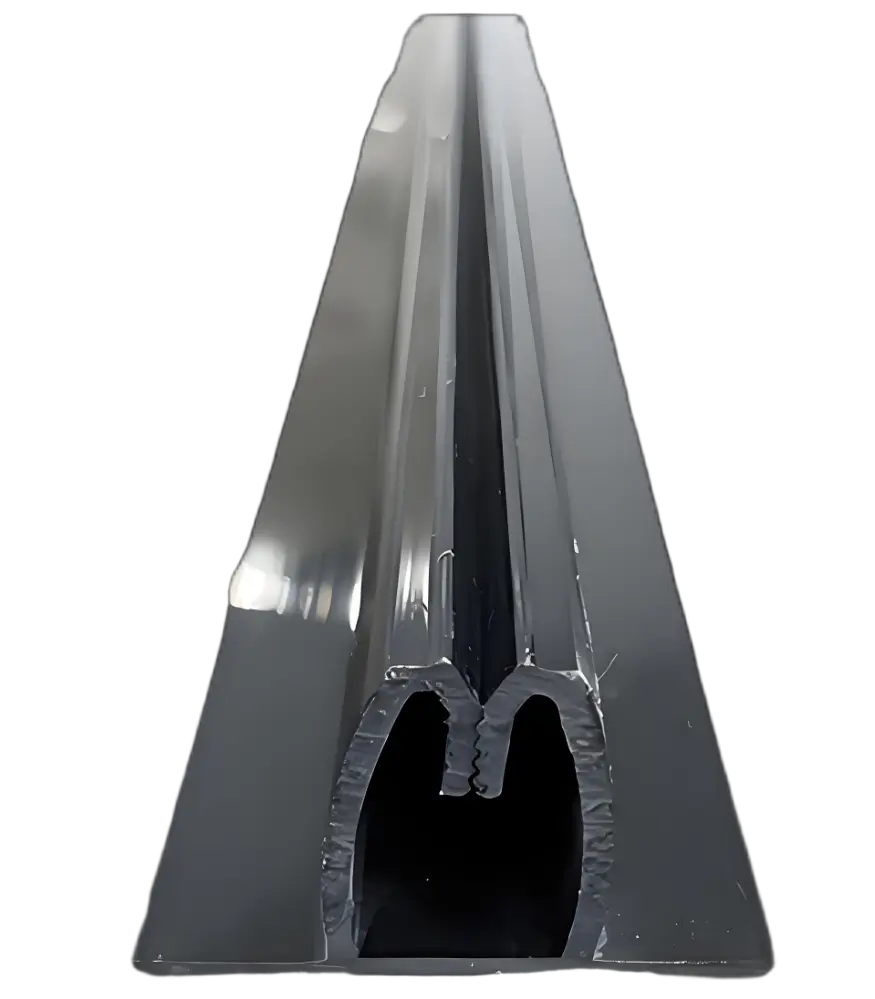

Profil Pallet PVC
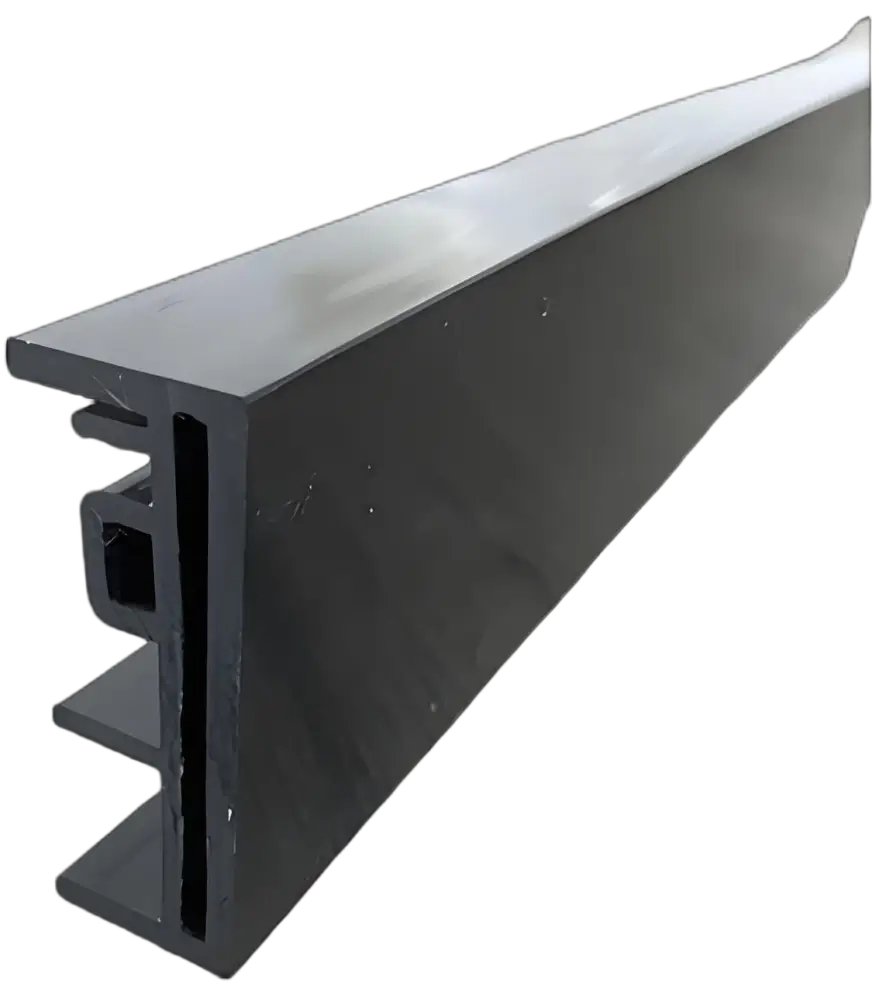

Profil Bingkai PVC
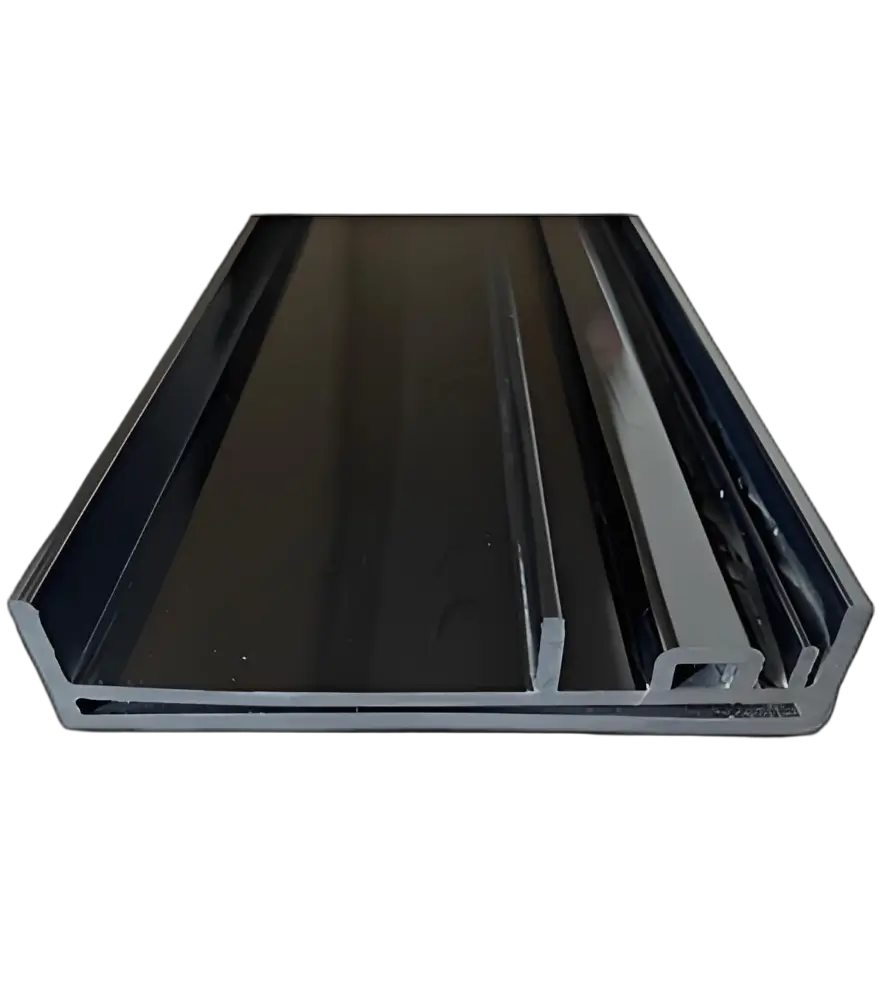

Profil Rakitan PVC
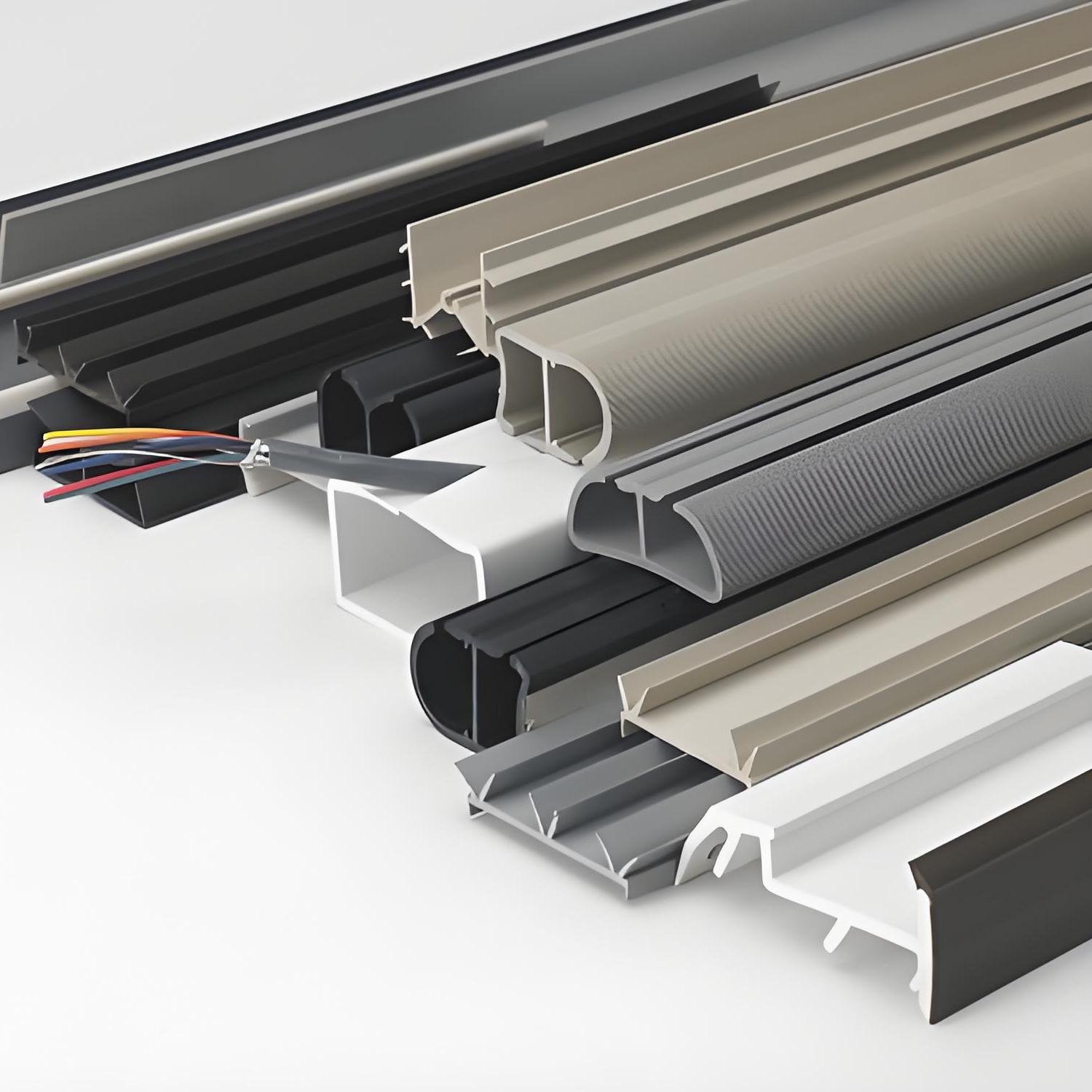

Panduan untuk Pembuatan Profil Ekstrusi PVC Khusus
Apa yang dimaksud dengan Profil PVC?
Profil PVC, juga dikenal sebagai ekstrusi PVC, adalah bentuk khusus yang terbuat dari polivinil klorida (PVC), bahan plastik serbaguna dan banyak digunakan. Profil ini dibuat melalui proses manufaktur yang disebut ekstrusi plastik, di mana resin PVC dipanaskan, dilelehkan, dan dipaksa melalui cetakan untuk membentuknya menjadi bentuk yang kontinu. Profil yang dihasilkan dapat berupa bentuk sederhana, seperti tabung dan batang, atau bentuk yang lebih kompleks seperti trim dekoratif dan komponen fungsional. Profil PVC umumnya digunakan di berbagai industri, termasuk konstruksi, otomotif, furnitur, dan bidang medis.
Proses pembuatan profil PVC dimulai dengan ekstrusi resin PVC. Pertama, pelet PVC dipanaskan hingga meleleh, dan bahan cair kemudian dipaksa melalui cetakan (die) yang membentuknya menjadi profil yang diinginkan. Saat bahan keluar dari cetakan, bahan tersebut didinginkan dan dipotong menjadi panjang tertentu. Selama proses ini, aditif fungsional tambahan seperti pewarna, penstabil, dan pelumas dapat dimasukkan untuk memodifikasi sifat material, seperti fleksibilitas, warna, atau ketahanan terhadap sinar UV. proses ekstrusi memastikan bahwa profil PVC dapat diproduksi dalam volume besar dan dengan biaya yang relatif rendah, menjadikannya teknik manufaktur yang disukai di banyak industri.
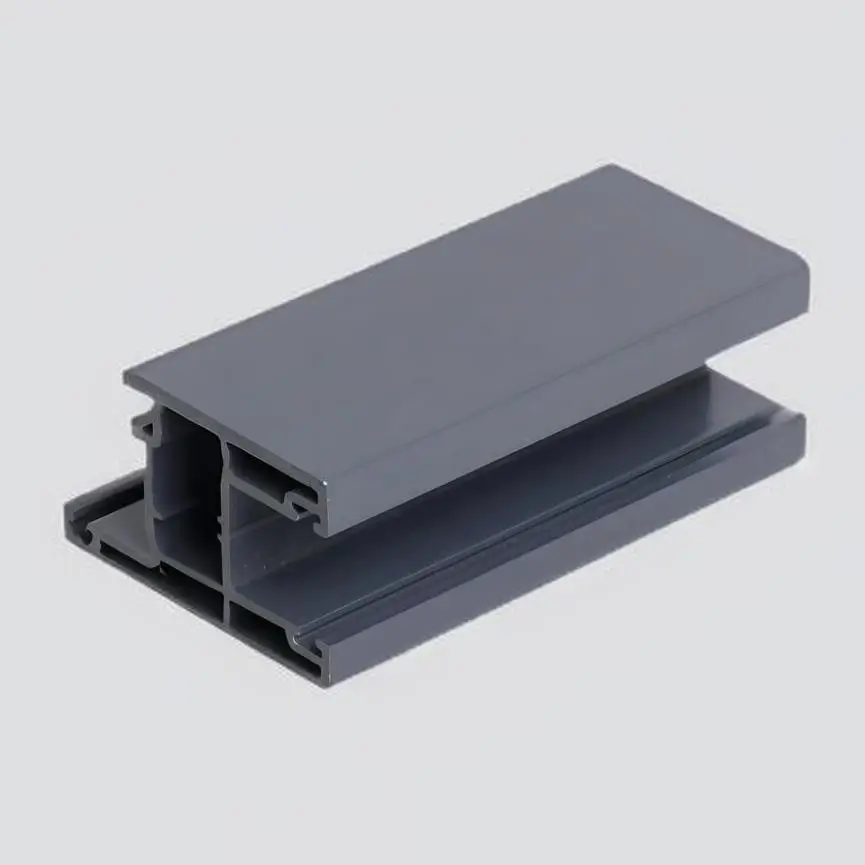

Mengapa Menggunakan PVC untuk Profil?
PVC (Polivinil Klorida) telah menjadi salah satu bahan yang paling banyak digunakan dalam pembuatan profil, berkat berbagai kelebihannya. Kombinasi daya tahan, efektivitas biaya, dan keserbagunaan membuatnya menjadi bahan pilihan untuk berbagai industri. Di bawah ini adalah pandangan mendalam tentang alasan mengapa PVC ideal untuk profil, terutama dalam aplikasi ekstrusi:
1. Daya Tahan dan Umur Panjang:
Profil PVC sangat tahan lama dan tahan terhadap kerusakan, termasuk goresan, retakan, dan pudar. Tidak seperti kayu atau logam, PVC tidak melengkung, berkarat, atau rusak saat terkena kondisi cuaca ekstrem, menjadikannya pilihan yang sangat baik untuk aplikasi di dalam dan luar ruangan. Umurnya yang panjang memastikan bahwa produk seperti kusen jendela, pintu, dan pipa dapat bertahan selama beberapa dekade dengan degradasi minimal, bahkan di lingkungan yang keras.
2. Efektivitas Biaya:
Profil PVC relatif murah dibandingkan dengan bahan alternatif seperti aluminium atau kayu. Mereka membutuhkan investasi yang lebih sedikit baik dalam biaya material maupun pemasangan, yang menjadikannya pilihan yang hemat biaya untuk produksi skala besar. Selain itu, masa pakai yang lama dan persyaratan perawatan yang rendah berarti bahwa pengguna menghemat uang dari waktu ke waktu untuk penggantian dan pemeliharaan.

3. Persyaratan Perawatan yang Rendah:
Salah satu manfaat utama dari profil PVC adalah perawatannya yang rendah. Tidak seperti kayu, yang membutuhkan pengecatan dan penyegelan secara berkala, atau logam yang dapat berkarat, PVC tidak memerlukan perawatan rutin. PVC mudah dibersihkan-hanya dengan sabun dan air biasanya sudah cukup-dan tidak menarik hama seperti kayu. Hal ini menjadikannya pilihan yang menarik bagi industri yang ingin mengurangi biaya operasional dan waktu perawatan.
4. Tahan terhadap cuaca:
Profil PVC sangat tahan terhadap berbagai faktor lingkungan, termasuk radiasi UV, suhu ekstrem, kelembapan, dan paparan air. Ketahanan ini membuatnya ideal untuk aplikasi luar ruangan, seperti jendela, pintu, dan pagar, di mana mereka tidak akan rusak seiring waktu. Proses ekstrusi memungkinkan PVC dibentuk menjadi profil kompleks yang mempertahankan integritasnya meskipun terpapar dalam waktu lama.
5. Keserbagunaan dalam Desain:
Proses ekstrusi memungkinkan PVC dicetak menjadi berbagai macam bentuk, ukuran, dan warna yang tak terbatas, memberikan fleksibilitas kepada produsen untuk menghasilkan profil khusus yang memenuhi kebutuhan desain tertentu. Baik untuk aplikasi arsitektur, komponen otomotif, atau penggunaan industri, kemampuan beradaptasi PVC memastikannya dapat memenuhi beragam persyaratan di berbagai sektor. Ini juga dapat dikombinasikan dengan bahan lain untuk meningkatkan kinerja dalam aplikasi tertentu.
6. Efisiensi Energi dan Isolasi:
Profil PVC secara alami bersifat insulasi, yang dapat meningkatkan efisiensi energi dalam bangunan. Ketika digunakan pada kusen jendela dan pintu, profil ini membantu mencegah perpindahan panas, menjaga suhu dalam ruangan tetap stabil dan mengurangi kebutuhan akan pemanas atau pendingin. Hal ini menjadikan PVC sebagai komponen utama dalam desain hemat energi, berkontribusi pada biaya energi yang lebih rendah dan lingkungan yang lebih berkelanjutan.
7. Tahan Bahan Kimia dan Api:
Profil PVC tahan terhadap banyak bahan kimia, termasuk asam, basa, minyak, dan pelarut. Ketahanan ini membuatnya cocok untuk digunakan di lingkungan yang sering terpapar bahan kimia, seperti di lingkungan industri, laboratorium, atau medis. Selain itu, PVC dapat memadamkan diri sendiri dan tidak mengeluarkan asap beracun saat terkena api, menjadikannya pilihan yang lebih aman dalam aplikasi yang sensitif terhadap api.
8. Pengurangan Kebisingan:
Kemampuan profil PVC untuk menyerap gelombang suara membuatnya efektif dalam mengurangi kebisingan di lingkungan tertentu. Kualitas ini sangat berharga dalam aplikasi seperti gedung perkantoran, kompleks perumahan, atau kendaraan rekreasi, di mana pengendalian kebisingan sangat penting. Sifat peredam suara PVC membantu menciptakan ruang yang lebih nyaman dan lebih tenang.
9. Daur Ulang dan Dampak Lingkungan:
PVC adalah bahan yang sangat mudah didaur ulang, yang membantu mengurangi dampak lingkungan. Profil PVC bekas dapat digunakan kembali untuk membuat produk baru, sehingga berkontribusi terhadap keberlanjutan. Selain itu, karena PVC tahan lama dan awet, produk yang terbuat dari bahan ini lebih jarang diganti, sehingga mengurangi limbah dan melestarikan sumber daya.
10. Keselamatan Kebakaran:
Profil PVC dapat memadamkan dirinya sendiri, yang berarti bahwa profil tersebut akan berhenti terbakar setelah sumber api eksternal dihilangkan. Sifat ini menambahkan lapisan ekstra keselamatan kebakaran, terutama dalam konstruksi bangunan dan aplikasi yang mengutamakan ketahanan terhadap api. Tidak seperti beberapa bahan lainnya, profil PVC tidak mengeluarkan asap berbahaya atau beracun saat terkena api, sehingga meningkatkan keamanan bagi pengguna dan penghuni.
Apa Saja Jenis Profil PVC yang Berbeda?
Profil PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) adalah komponen plastik cetakan yang terbuat dari polimer sintetis yang dikenal dengan daya tahan, ketahanan terhadap faktor lingkungan, dan keserbagunaannya. Profil PVC banyak digunakan dalam konstruksi, manufaktur, dan industri lainnya karena sifatnya yang ringan, rendah perawatan, dan hemat biaya. Profil ini tersedia dalam berbagai jenis, masing-masing dirancang untuk aplikasi tertentu, dan dapat diproduksi melalui ekstrusi plastik, sebuah proses yang membentuk PVC menjadi profil khusus untuk penggunaan yang berbeda.
Jenis Umum Profil PVC:

1. Profil PVC (uPVC) yang kaku:
Aplikasi: Kusen jendela dan pintu, kelongsong, atap.
Keuntungan: Kaku dan tahan lama, menawarkan ketahanan benturan yang sangat baik dan tahan terhadap cuaca. Profil uPVC sangat tahan terhadap penuaan dan korosi, sehingga ideal untuk aplikasi perumahan dan komersial.
2. Profil PVC Fleksibel (fPVC):
Aplikasi: Pipa medis, suku cadang otomotif, perpipaan industri.
Keuntungan: Fleksibel, mudah dibengkokkan tanpa kehilangan bentuk. Fleksibilitas ini membuatnya ideal untuk aplikasi dinamis seperti selang dan seal.
3. Profil PVC-U:
Aplikasi: Mirip dengan PVC kaku, umumnya digunakan dalam sistem pipa, bingkai jendela, dan bahan konstruksi.
Keuntungan: Dikenal karena kekakuan dan ketahanan benturannya, serta tahan terhadap bahan kimia, sehingga cocok untuk lingkungan yang keras.
4. Profil PVC Plastisisasi (PVC-P):
Aplikasi: Segel, trim, weatherstripping.
Keuntungan: Lebih fleksibel dan tahan benturan daripada PVC yang tidak diplastisisasi, menawarkan kemudahan pemasangan dan penggunaan dalam aplikasi yang membutuhkan tingkat fleksibilitas tertentu.
5. Profil PVC Berorientasi (PVC-O):
Aplikasi: Pipa bertekanan, sistem air, sistem gas.
Keuntungan: Kekuatan dan fleksibilitas yang ditingkatkan, sangat baik untuk digunakan dalam aplikasi bertekanan tinggi, seperti pipa air.
6. Profil PVC Terklorinasi (PVC-C):
Aplikasi: Perpipaan industri, sistem transportasi bahan kimia, alat kelengkapan.
Keuntungan: Sangat tahan terhadap bahan kimia, korosi, dan panas. Ideal untuk lingkungan yang menuntut daya tahan dan ketahanan terhadap bahan kimia.
7. Profil PVC yang dimodifikasi (PVC-M):
Aplikasi: Kusen jendela, kelongsong, profil pintu.
Keuntungan: Menawarkan ketangguhan dan fleksibilitas yang lebih baik dibandingkan PVC standar. Profil ini ideal untuk aplikasi luar ruangan, karena menawarkan ketahanan UV dan benturan.
8. Profil PVC yang Dimodifikasi Akrilik (PVC-A):
Aplikasi: Aplikasi eksterior seperti profil jendela dan pintu.
Keuntungan: Tahan benturan tinggi, tahan UV, dan fleksibel. PVC yang dimodifikasi dengan akrilik menawarkan penampilan estetika yang mirip dengan bahan kelas atas.
9. Profil PVC berfluorinasi (PVC-F):
Aplikasi: Pipa, alat kelengkapan, dan pelapis industri.
Keuntungan: Ketahanan yang sangat baik terhadap berbagai macam bahan kimia, abrasi, dan suhu tinggi.
10. Profil PVC yang Dimodifikasi Silikon (PVC-S):
Aplikasi: Segel jendela, gasket, segel otomotif.
Keuntungan: Fleksibilitas tinggi, tahan terhadap sinar UV, dan tahan terhadap benturan.
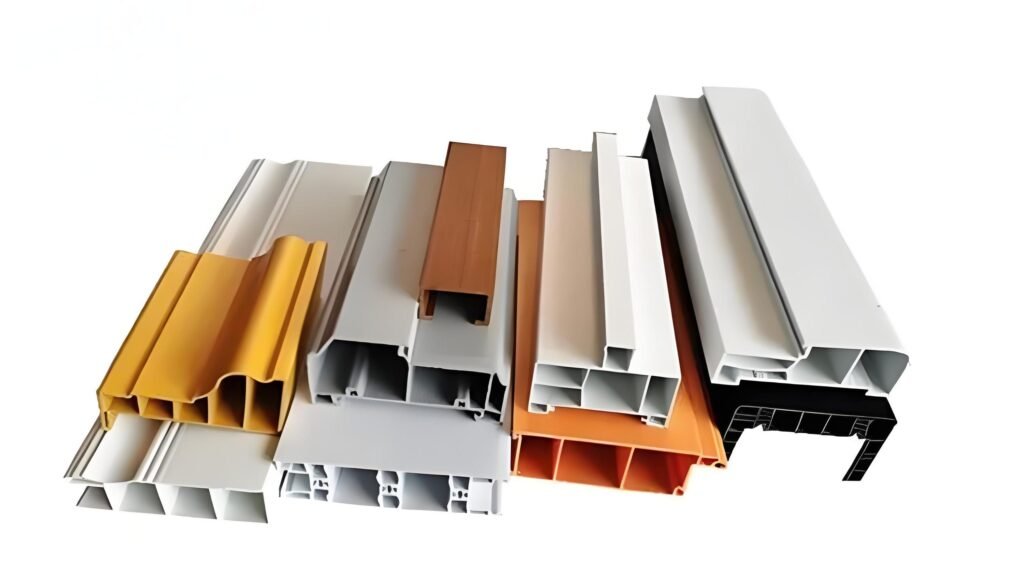
Profil PVC Khusus:
Selain profil standar yang tercantum di atas, PVC juga dapat diekstrusi menjadi berbagai profil khusus yang disesuaikan untuk kebutuhan tertentu:
1. Lembar Profil PVC: Digunakan untuk atap, pelapis dinding, dan panel dekoratif, menawarkan ketahanan terhadap UV dan sifat insulasi.
2. Panel PVC: Umumnya digunakan untuk dinding dan plafon pada bangunan perumahan dan komersial, yang dikenal karena kemudahan pemasangan dan perawatannya.
3. Profil Pintu dan Jendela PVC: Dirancang untuk memenuhi kebutuhan spesifik pintu dan jendela, profil ini dapat disesuaikan untuk meningkatkan insulasi, keamanan, dan estetika.
4. Profil Pelapis Dinding dan Trim PVC: Memberikan tampilan akhir yang bersih pada eksterior bangunan dengan manfaat tambahan berupa perawatan yang mudah dan hemat energi.
5. Bentuk Beton PVC: Dapat digunakan kembali dan tahan lama, formulir ini digunakan untuk membentuk beton dalam konstruksi, mempromosikan keberlanjutan.
Apa Karakteristik Utama dari Profil PVC?
Profil PVC (Polivinil Klorida), yang diproduksi melalui ekstrusi plastik, menawarkan banyak keuntungan, sehingga menjadi pilihan populer di berbagai industri seperti konstruksi, otomotif, dan manufaktur. Proses ekstrusi plastik memungkinkan PVC dicetak menjadi profil dengan berbagai bentuk, ukuran, dan hasil akhir, sehingga sangat serbaguna untuk berbagai aplikasi. Di bawah ini adalah ikhtisar karakteristik utama profil PVC, termasuk atribut kinerja dan manfaatnya.
1. Daya tahan:
(1) Tahan Lama: Profil PVC dikenal karena daya tahannya yang luar biasa. Bahannya tahan aus, goresan, retak, dan pudar, sehingga menjadikannya pilihan yang dapat diandalkan untuk aplikasi di dalam dan luar ruangan. Sebagai contoh, bingkai jendela yang terbuat dari PVC dapat menahan pembukaan dan penutupan berulang kali selama bertahun-tahun tanpa kerusakan yang berarti.
② Tahan terhadap Kerusakan Fisik: Profil PVC kuat dan tahan terhadap benturan, guncangan, dan abrasi. Hal ini membuatnya cocok untuk area dengan lalu lintas tinggi dan aplikasi yang sering ditangani.
2. Tahan terhadap cuaca:
(1) Tahan terhadap sinar UV: Profil PVC sangat tahan terhadap radiasi ultraviolet (UV), yang membantu mencegah degradasi, perubahan warna, dan kerapuhan saat terkena sinar matahari. Hal ini membuatnya ideal untuk aplikasi luar ruangan seperti kusen jendela, pintu, dan pagar, di mana paparan sinar UV dalam jangka panjang adalah hal yang umum.
② Tahan Panas: Profil PVC dapat bekerja dengan baik dalam kisaran suhu yang luas. Profil ini tidak menjadi rapuh dalam cuaca dingin dan tidak melunak dalam suhu tinggi, sehingga cocok untuk daerah dengan iklim ekstrem.
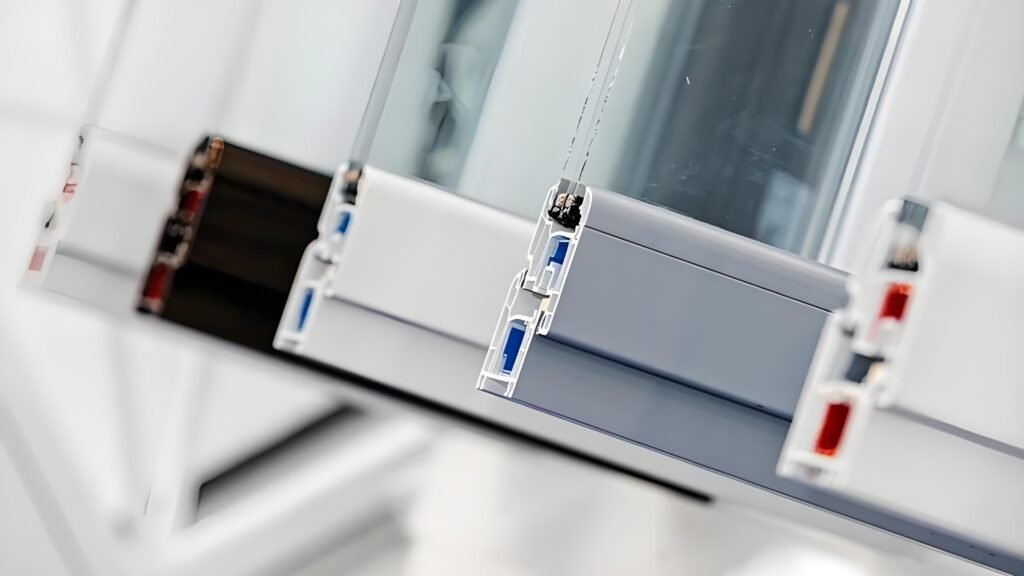


3. Perawatan Rendah:
① Mudah Dibersihkan: Tidak seperti bahan seperti kayu, yang membutuhkan perawatan rutin, profil PVC membutuhkan perawatan minimal. Pembersihan dengan sabun dan air umumnya cukup untuk mempertahankan penampilannya. Selain itu, PVC tidak mudah berjamur, berjamur, atau tumbuhnya bakteri, sehingga mengurangi kebutuhan perawatan.
② Tidak Perlu Pengecatan: Profil PVC mempertahankan warna dan tampilannya dari waktu ke waktu, sehingga tidak perlu dicat ulang, yang sering kali diperlukan untuk profil kayu atau logam.
4. Ketahanan Kimia dan Korosi:
(1) Ketahanan terhadap bahan kimia: Profil PVC tahan terhadap berbagai macam bahan kimia, termasuk asam, alkali, dan pelarut umum. Hal ini membuatnya cocok untuk lingkungan industri yang sering terpapar bahan kimia.
② Ketahanan Korosi: PVC tidak menimbulkan korosi seperti logam, memastikan bahwa profil mempertahankan integritas strukturalnya di lingkungan yang terpapar kelembapan, air asin, atau zat korosif lainnya.
5. Efisiensi Energi:
(1) Isolasi Termal: Profil PVC menawarkan insulasi termal yang sangat baik, yang membantu mengurangi kehilangan panas dan konsumsi energi. Sebagai contoh, bingkai jendela PVC berkontribusi pada bangunan hemat energi dengan mengurangi perpindahan panas antara di dalam dan di luar ruangan, sehingga menurunkan biaya pemanasan dan pendinginan.
② Isolasi Listrik: PVC juga menyediakan isolasi listrik, sehingga cocok untuk digunakan pada saluran listrik dan aplikasi lain yang memerlukan perlindungan dari arus listrik.
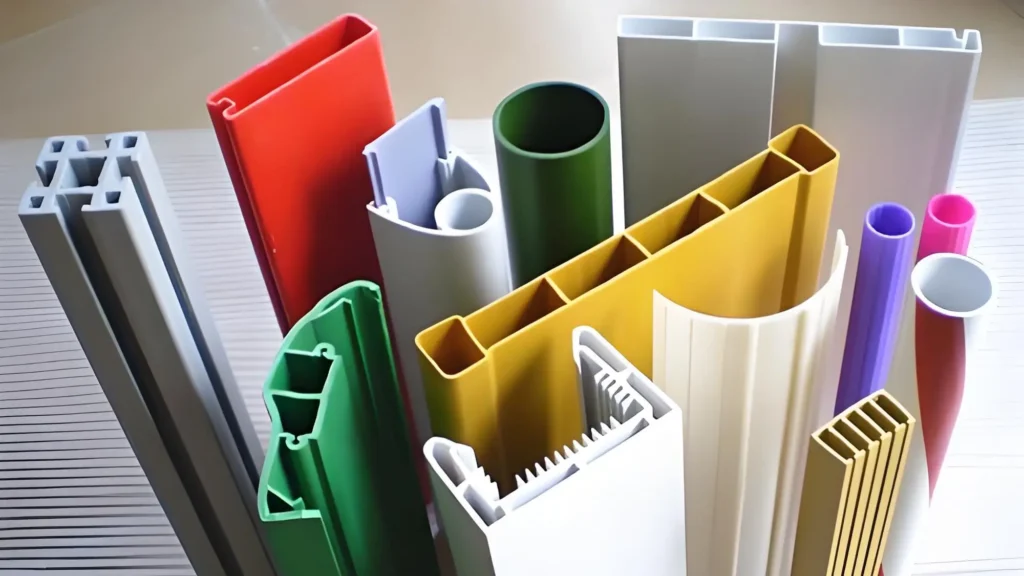


6. Tahan Api:
Sifat Tahan Api yang melekat: Profil PVC dapat memadamkan diri sendiri dan tidak mengeluarkan asap beracun saat terkena api. Sifat ini membuatnya lebih aman dibandingkan dengan bahan lain, terutama di bangunan atau lingkungan yang mengutamakan keselamatan kebakaran.
7. Keserbagunaan dalam Desain dan Kustomisasi:
(1) Bentuk dan Ukuran Khusus: Salah satu manfaat utama profil PVC adalah keserbagunaannya. Melalui ekstrusi plastik, PVC dapat dibentuk menjadi berbagai macam bentuk, ukuran, dan hasil akhir, sehingga memungkinkan penyesuaian sesuai dengan kebutuhan aplikasi tertentu. Hal ini sangat penting untuk industri seperti konstruksi, di mana profil harus sesuai dengan pengukuran yang tepat atau persyaratan estetika.
Stabilitas Warna: Profil PVC mempertahankan warnanya dari waktu ke waktu, sehingga ideal untuk aplikasi yang mengutamakan penampilan, seperti trim dekoratif, furnitur, dan papan nama.
8. Ringan:
Kemudahan Penanganan dan Pemasangan: Terlepas dari kekuatan dan daya tahannya, profil PVC relatif ringan dibandingkan dengan bahan seperti logam atau kayu. Karakteristik ini membuatnya mudah diangkut, ditangani, dan dipasang, sehingga mengurangi biaya tenaga kerja dan waktu pemasangan.
9. Efektivitas Biaya:
Produksi yang Terjangkau: Profil PVC relatif murah untuk diproduksi dibandingkan dengan logam dan alternatif lainnya, menjadikannya solusi yang hemat biaya untuk banyak aplikasi. Umurnya yang panjang dan biaya perawatan yang rendah semakin meningkatkan nilainya, menjadikannya pilihan populer dalam proyek konstruksi dan manufaktur berskala besar.
10. Daur Ulang dan Keberlanjutan:
① Dapat didaur ulang: Profil PVC dapat didaur ulang, yang membantu mengurangi dampak lingkungan. Banyak produsen yang berfokus pada penggunaan bahan PVC daur ulang untuk produksi profil, yang berkontribusi pada proses manufaktur yang lebih berkelanjutan.
② Dampak Lingkungan: Profil PVC hemat energi dalam produksinya, membutuhkan lebih sedikit energi dibandingkan dengan beberapa bahan lain seperti aluminium. Hal ini mengurangi jejak karbonnya, menjadikannya pilihan yang lebih ramah lingkungan.
11. Isolasi Akustik:
Pengurangan Kebisingan: Profil PVC memberikan tingkat isolasi suara tertentu, sehingga bermanfaat untuk digunakan dalam aplikasi seperti kusen jendela dan pintu di bangunan tempat tinggal atau perkantoran. Sifat ini membantu mengurangi transmisi kebisingan, meningkatkan lingkungan akustik.
Cara Membuat Profil PVC: Panduan Langkah-demi-Langkah
Memproduksi profil PVC adalah proses yang sangat terkontrol yang melibatkan transformasi bahan PVC mentah menjadi bentuk dan ukuran khusus menggunakan teknologi ekstrusi plastik. Panduan langkah demi langkah ini memandu Anda melalui seluruh proses, mulai dari persiapan bahan hingga pengemasan akhir.


1. Persiapan Bahan Baku:
Langkah pertama dalam proses pembuatan profil PVC adalah memilih dan menyiapkan bahan baku.
① Pemilihan Resin PVC: Resin PVC berkualitas tinggi dipilih berdasarkan tujuan penggunaan profil. Misalnya, untuk profil jendela, resin PVC yang kaku dengan ketahanan benturan dan ketahanan terhadap cuaca yang baik lebih disukai. Resin PVC biasanya diklasifikasikan berdasarkan metode polimerisasi dan berat molekulnya.
Penggabungan Aditif: Berbagai bahan aditif dicampur dengan resin PVC untuk menyempurnakan sifat-sifatnya. Ini mungkin termasuk:
- Stabilisator (stabilisator kalsium-seng sekarang lebih umum digunakan karena masalah lingkungan).
- Pemlastis (untuk meningkatkan fleksibilitas, meskipun minimal pada profil yang kaku seperti yang digunakan untuk konstruksi).
- Pelumas (untuk mengurangi gesekan pemrosesan).
- Pengubah Dampak (untuk meningkatkan ketangguhan).
- Pigmen (untuk pewarnaan).
- Bahan baku ini dicampur secara menyeluruh untuk memastikan komposisi seragam yang mendukung karakteristik profil yang diinginkan.
2. Pencampuran dan Peracikan:
Setelah bahan baku disiapkan, bahan baku tersebut mengalami pencampuran dan peracikan.
① Pencampuran: Resin PVC dan aditif dicampur dalam mixer berkecepatan tinggi pada suhu yang terkendali (100-120 ° C) untuk memastikan distribusi yang seragam. Langkah ini sangat penting untuk mencapai sifat mekanik yang diinginkan pada produk akhir.
② Peracikan: Campuran yang tercampur kemudian diracik menggunakan mesin khusus, memastikan bahwa bahan dipanaskan dan dicampur untuk mencapai lelehan yang homogen. Langkah ini membantu memastikan bahwa resin PVC meleleh dengan baik dan aditif didistribusikan secara merata.

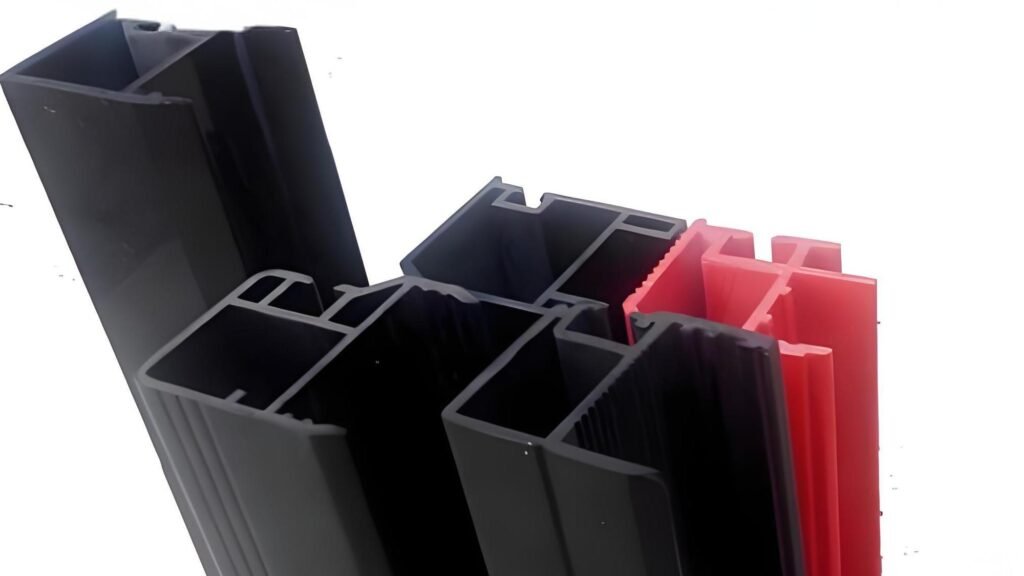
3. Proses Ekstrusi:
Setelah pencampuran, senyawa yang telah disiapkan dimasukkan ke dalam mesin ekstrusi, di mana senyawa tersebut dilelehkan dan dibentuk ke dalam profil yang diinginkan.
(1) Pengaturan Extruder: Senyawa PVC dimasukkan ke dalam ekstruder, yang terdiri dari hopper, sekrup yang berputar, dan cetakan. Rotasi sekrup menggerakkan bahan melalui laras yang dipanaskan, di mana bahan tersebut dilelehkan dan dicampur. Pengekstrusi sekrup kembar sering digunakan karena memberikan pencampuran yang lebih baik dan dapat menangani formulasi yang lebih kompleks.
② Parameter Ekstrusi: Suhu dikontrol secara hati-hati di sepanjang laras ekstruder. Zona umpan dijaga pada suhu sekitar 160-180 ° C, sedangkan zona cetakan dapat mencapai 190-210 ° C. Tekanan dan kecepatan sekrup memastikan aliran material yang lancar melalui cetakan.
4. Pembentukan dan Pendinginan:
PVC cair dibentuk dan didinginkan untuk membentuk profil yang diinginkan.
① Desain Cetakan: PVC dipaksa melalui cetakan ekstrusi, yang membentuk material menjadi profil akhirnya. Cetakan ekstrusi dibuat khusus untuk setiap profil tertentu, baik untuk bingkai jendela, pipa, atau produk lainnya.
② Sistem Pendinginan: Setelah keluar dari cetakan, profil didinginkan dengan cepat menggunakan sistem pendingin air atau udara. Pendinginan air biasanya lebih efektif untuk pemadatan yang cepat dan stabilitas dimensi. Laju pendinginan sangat penting karena berdampak pada sifat mekanis profil dan mencegah lengkungan atau keretakan. Sistem pendinginan yang terkendali memastikan bahwa profil mempertahankan bentuknya saat mengeras.
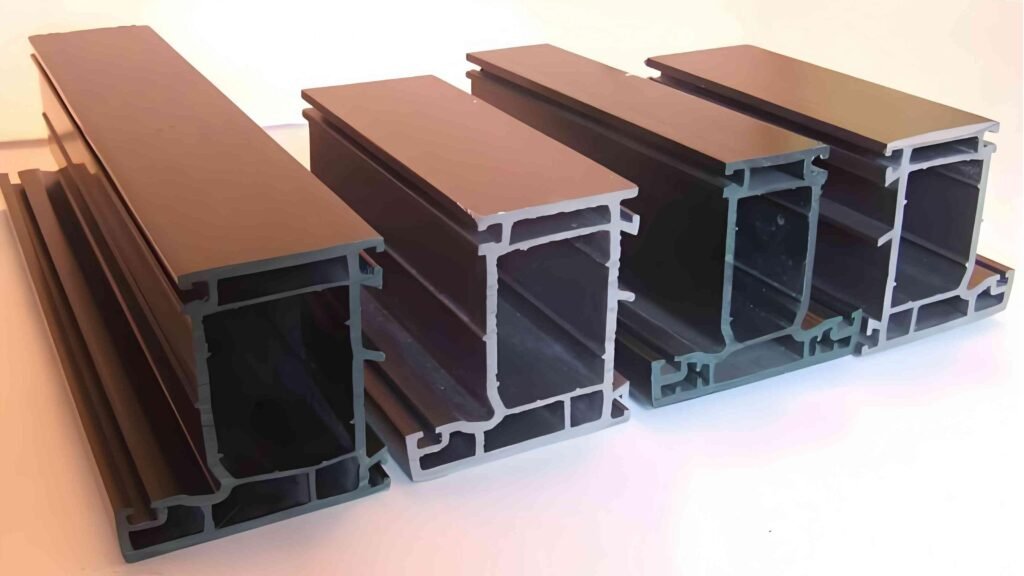

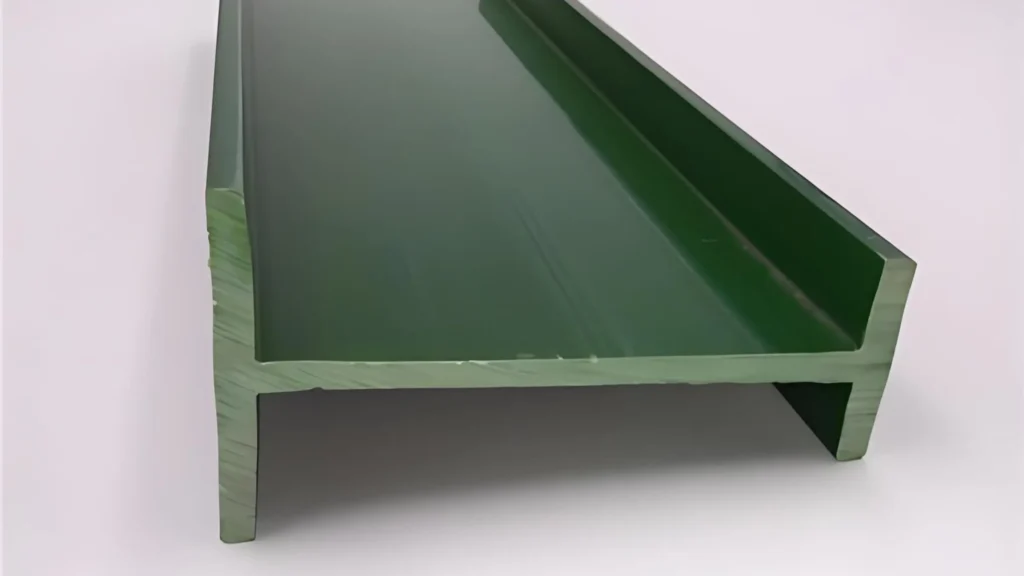
5. Pengangkutan, Pemotongan, dan Penyelesaian:
Setelah profil mendingin, profil ditarik dan dipotong sesuai panjang yang diperlukan.
① Sistem Pengangkutan: Profil ditarik oleh unit pengangkut, yang menyinkronkan kecepatan gerakan profil dengan laju ekstrusi untuk menghindari deformasi.
② Pemotongan: Setelah profil mencapai panjang yang tepat, profil dipotong menggunakan gergaji presisi atau mesin pemotong. Hal ini memastikan bahwa setiap profil dibuat dengan spesifikasi yang tepat yang diperlukan untuk penggunaan akhirnya.
③ Perawatan Permukaan: Beberapa profil dapat menjalani perawatan permukaan tambahan seperti pengamplasan, pencetakan, atau pengembosan. Contohnya, sebagian profil dekoratif mungkin diembos untuk memberikan tekstur yang meniru bahan alami seperti kayu. Dalam beberapa kasus, profil juga dilapisi dengan lapisan tahan UV untuk meningkatkan daya tahan.
6. Kontrol Kualitas:
Kontrol kualitas sangat penting pada setiap tahap untuk memastikan produk akhir memenuhi standar yang ketat.
① Pemeriksaan Dimensi: Profil diperiksa untuk memastikan bahwa dimensinya-seperti ketebalan, lebar, dan panjang-berada dalam toleransi yang ditentukan. Contohnya, profil jendela mungkin memiliki toleransi ketebalan ±0,2 mm.
② Pengujian Sifat Mekanis: Untuk memastikan daya tahan dan kinerja, pengujian mekanis seperti ketahanan benturan, kekuatan tarik, dan modulus lentur dilakukan. Pengujian ini memverifikasi bahwa profil akan bekerja dengan baik dalam aplikasi yang dimaksudkan.
Inspeksi Visual: Profil diperiksa dengan cermat untuk mengetahui adanya cacat permukaan seperti gelembung, goresan, atau perubahan warna. Profil yang cacat akan dikerjakan ulang atau dibuang.
7. Pengemasan dan Pengiriman:
Setelah profil lolos kontrol kualitas, profil dikemas dan dikirim ke pelanggan.
① Pengemasan: Profil yang sudah jadi dikemas dengan cara yang mencegah kerusakan selama pengiriman. Hal ini dapat dilakukan dengan membungkusnya dengan plastik pelindung atau menggunakan kotak khusus untuk produk yang mudah pecah.
Pengiriman: Profil yang telah dikemas kemudian disiapkan untuk dikirim ke pelanggan. Tergantung pada pesanan, profil dapat dikirim ke distributor atau langsung ke produsen untuk dirakit menjadi produk akhir seperti jendela, pintu, atau furnitur.
Apa Saja Keuntungan dari Profil PVC?
Profil PVC banyak digunakan dalam konstruksi, manufaktur, dan industri lainnya karena berbagai keunggulannya. Melalui proses ekstrusi plastik, PVC diubah menjadi profil serbaguna yang menawarkan berbagai manfaat. Di bawah ini adalah ikhtisar komprehensif tentang keunggulan utama:
1. Daya Tahan dan Umur Panjang:
(1) Kekuatan dan Kekakuan Tinggi: Profil PVC dikenal dengan kekuatan dan kekakuannya yang luar biasa, sehingga mampu mempertahankan integritas struktural bahkan di bawah beban berat. Hal ini menjadikannya ideal untuk aplikasi seperti kusen jendela, pintu, dan komponen struktural lainnya yang membutuhkan stabilitas.
② Tahan terhadap cuaca: Salah satu manfaat paling signifikan dari profil PVC adalah kemampuannya untuk bertahan dalam kondisi lingkungan yang keras. Mereka tahan terhadap sinar UV, hujan, salju, dan fluktuasi suhu yang ekstrem. PVC tidak membusuk seperti kayu atau berkarat seperti logam, sehingga menjamin penampilan dan performa yang tahan lama. Hal ini menjadikannya pilihan populer untuk penggunaan di luar ruangan, seperti pada pelapis dinding, atap, dan bingkai jendela.
③ Ketahanan terhadap bahan kimia: Profil PVC memiliki ketahanan yang sangat baik terhadap banyak bahan kimia, termasuk asam, basa, dan pelarut, sehingga ideal untuk lingkungan yang terpapar zat korosif. Profil ini juga lembam terhadap air, minyak, dan zat umum lainnya, memastikan stabilitas jangka panjang dan ketahanan terhadap degradasi.
2. Perawatan Rendah dan Efektivitas Biaya:
(1) Perawatan Minimal: Tidak seperti bahan seperti kayu, yang membutuhkan penyegelan dan pengecatan secara teratur, profil PVC membutuhkan perawatan yang minimal. Mereka tidak memerlukan perawatan terhadap karat atau pembusukan dan dapat dibersihkan dengan sabun dan air sederhana. Hal ini menurunkan biaya dan upaya pemeliharaan jangka panjang.
② Hemat Biaya: PVC adalah bahan yang relatif murah dibandingkan dengan bahan alternatif seperti aluminium, kayu, atau logam. Proses ekstrusi plastik sangat hemat biaya untuk produksi bervolume tinggi, yang mengurangi biaya unit. Selain itu, umur panjang profil PVC lebih lanjut berkontribusi pada efektivitas biaya dengan mengurangi frekuensi penggantian.
3. Efisiensi Energi:
(1) Isolasi Termal: Profil PVC memiliki konduktivitas termal yang rendah, yang membantu mengurangi perpindahan panas. Sifat ini menjadikannya isolator yang sangat baik saat digunakan pada jendela dan pintu, membantu menjaga suhu dalam ruangan yang nyaman dan meningkatkan efisiensi energi dengan mengurangi biaya pemanasan dan pendinginan.
② Insulasi Suara: Selain sifat termal, profil PVC juga memberikan insulasi suara yang baik, sehingga bermanfaat untuk mengurangi kebisingan di dalam bangunan. Sifat ini sangat menguntungkan di lingkungan yang bising atau untuk aplikasi yang membutuhkan kedap suara, seperti pada bangunan tempat tinggal, kantor, dan fasilitas industri.
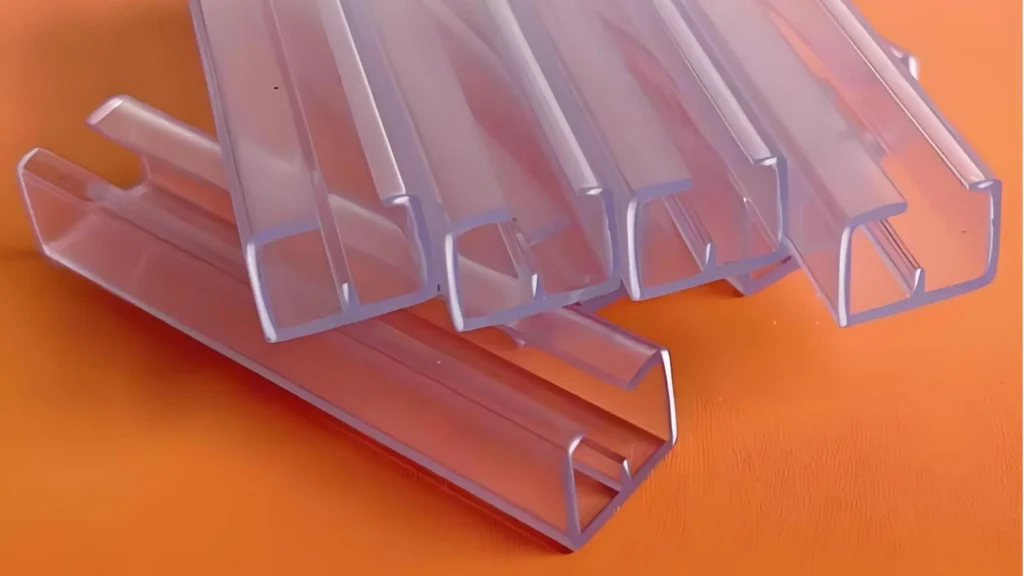
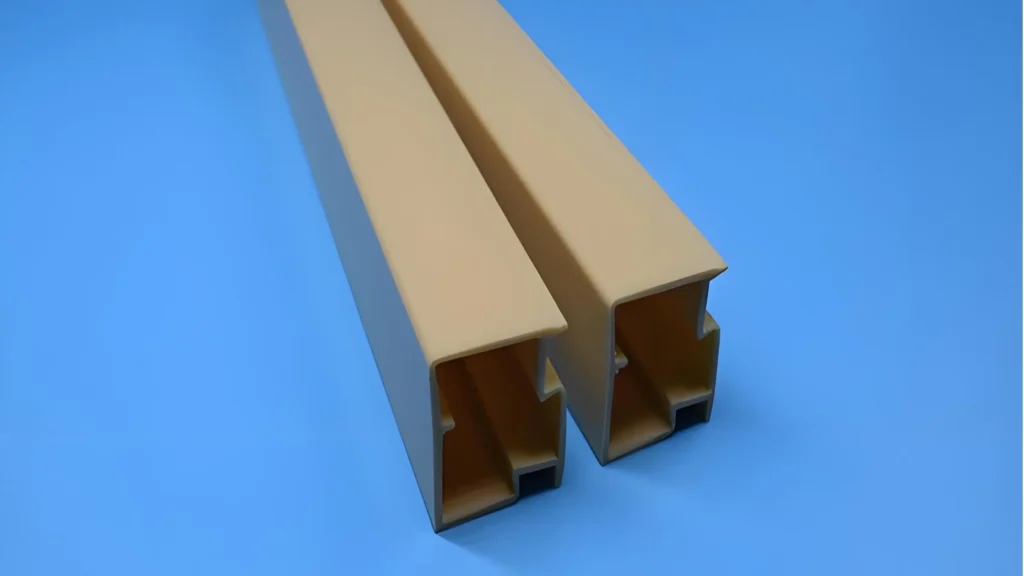

4. Estetika dan Fleksibilitas Desain:
① Kustomisasi: Profil PVC sangat dapat disesuaikan dalam hal bentuk, ukuran, warna, dan tekstur. Proses ekstrusi plastik memungkinkan produsen untuk membuat profil dengan dimensi dan hasil akhir yang presisi, sehingga cocok untuk berbagai persyaratan desain. Profil PVC dapat meniru tampilan bahan lain, seperti kayu atau logam, menawarkan fleksibilitas desain yang lebih besar.
② Permukaan Halus dan Hasil Akhir yang Menarik: Profil PVC memiliki permukaan yang halus dan seragam yang memberikan tampilan yang estetis. Profil ini tersedia dalam berbagai warna dan sentuhan akhir, yang dapat dipilih agar sesuai dengan gaya arsitektur atau desain interior proyek.
5. Ringan dan Mudah Ditangani:
Ringan: Salah satu manfaat utama dari profil PVC adalah kepadatannya yang rendah, membuatnya jauh lebih ringan daripada bahan seperti logam atau kayu. Fitur ini menyederhanakan penanganan, transportasi, dan pemasangan, mengurangi biaya tenaga kerja dan membuat profil PVC lebih nyaman untuk proyek konstruksi berskala besar.
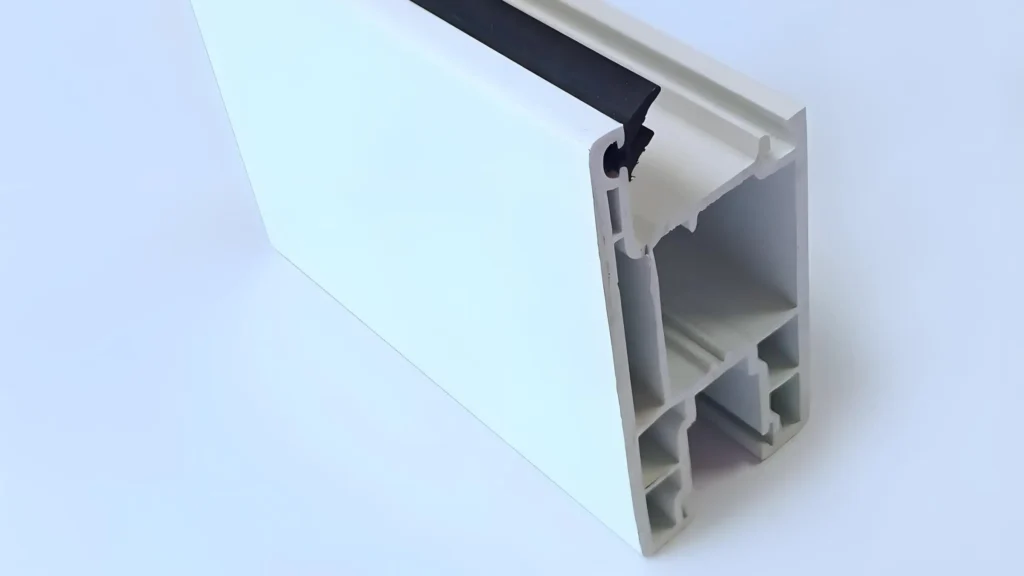

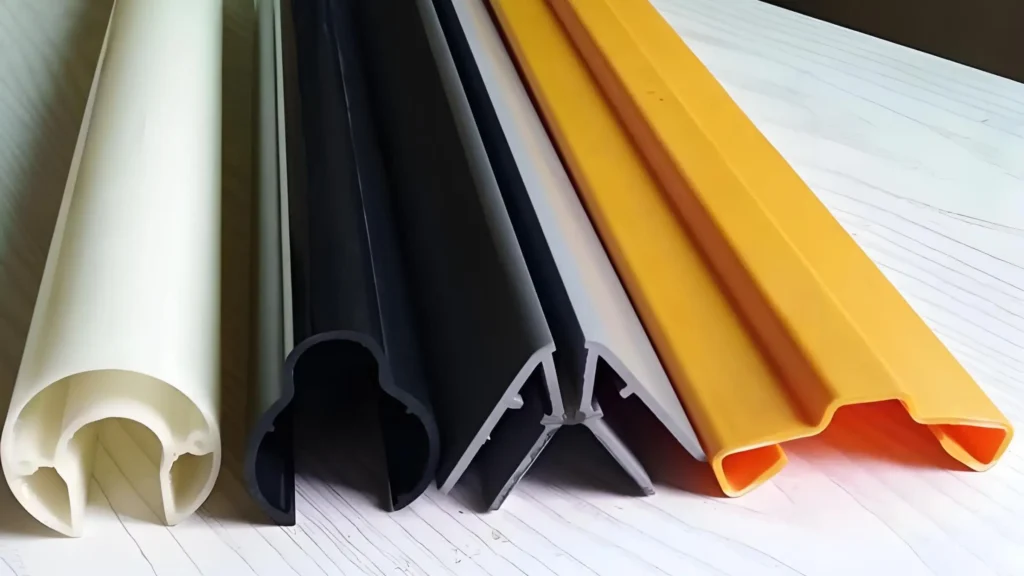
6. Tahan Api:
(1) Pemadaman Sendiri: PVC adalah bahan yang dapat memadamkan diri sendiri, yang berarti bahan ini akan berhenti terbakar setelah sumber api dihilangkan. Sifat tahan api ini menjadikannya pilihan ideal untuk bahan bangunan, karena meningkatkan keamanan kebakaran dengan mengurangi risiko penyebaran api.
② Penyebaran Api Rendah: Profil PVC menghasilkan penyebaran api dan asap yang lebih rendah dibandingkan dengan bahan lainnya, yang membantu menunda penyebaran api dan memungkinkan lebih banyak waktu untuk evakuasi, sehingga meningkatkan keselamatan secara keseluruhan.
7. Ramah Lingkungan:
Dapat didaur ulang: Profil PVC dapat didaur ulang, yang menambahkan aspek ramah lingkungan pada produksi dan penggunaannya. Dengan mendaur ulang profil yang sudah tua atau rusak, produsen dapat mengurangi limbah dan ketergantungan pada bahan baku. Selain itu, efisiensi energi dan masa pakai yang lama dari PVC berkontribusi pada keberlanjutan secara keseluruhan, menjadikannya pilihan yang bertanggung jawab terhadap lingkungan dalam konstruksi.
8. Keserbagunaan dalam Aplikasi:
(1) Pembentukan Khusus: Proses ekstrusi plastik memungkinkan pembuatan profil khusus dengan berbagai bentuk, ukuran, dan spesifikasi. Fleksibilitas ini membuat profil PVC cocok untuk berbagai aplikasi, mulai dari produk bangunan perumahan dan komersial seperti kusen jendela dan pintu hingga komponen industri seperti pipa, gasket, dan seal.
② Resistensi terhadap Hama: Tidak seperti kayu, profil PVC tidak rentan terhadap hama atau serangga, sehingga menjadikannya pilihan yang tepat untuk lingkungan yang membutuhkan ketahanan terhadap hama.
9. Produksi Volume Tinggi:
Proses ekstrusi plastik memungkinkan produsen untuk memproduksi profil PVC dalam jumlah besar dengan cepat dan efisien. Kecepatan produksi yang tinggi dan tingkat limbah yang rendah membuat PVC menjadi pilihan yang menarik bagi industri yang membutuhkan produksi skala besar, seperti di sektor konstruksi, otomotif, dan manufaktur.
10. Stabilitas Jangka Panjang:
Profil PVC mempertahankan sifat fisik dan mekaniknya dari waktu ke waktu, bahkan ketika terpapar faktor lingkungan seperti kelembapan, perubahan suhu, atau radiasi UV. Stabilitas jangka panjangnya memastikan bahwa mereka tetap menjadi pilihan material yang andal dan tahan lama selama bertahun-tahun, dengan keausan yang minimal.
Apa Saja Aplikasi dari Profil PVC?
Profil PVC (Polivinil Klorida) sangat serbaguna dan banyak digunakan di banyak industri karena daya tahan, ketahanan kimia, kemudahan fabrikasi, dan biaya rendah. Berkat proses ekstrusi plastik, PVC dapat dicetak menjadi bentuk dan ukuran yang tepat untuk berbagai aplikasi. Di bawah ini adalah tampilan rinci tentang beberapa aplikasi profil PVC yang paling umum:
1. Industri Konstruksi:
Kusen Jendela dan Pintu:
Profil PVC banyak digunakan untuk membuat kusen jendela dan pintu yang hemat energi dan tahan lama. Profil ini memberikan insulasi yang sangat baik, mengurangi biaya energi dengan meminimalkan perpindahan panas. Struktur multi-biliknya meningkatkan insulasi termal, sementara ketahanan materialnya terhadap pelapukan memastikan daya tahan jangka panjang. Kusen jendela dan pintu PVC tidak melengkung atau berkarat, bahkan saat terkena hujan, sinar matahari, dan fluktuasi suhu.
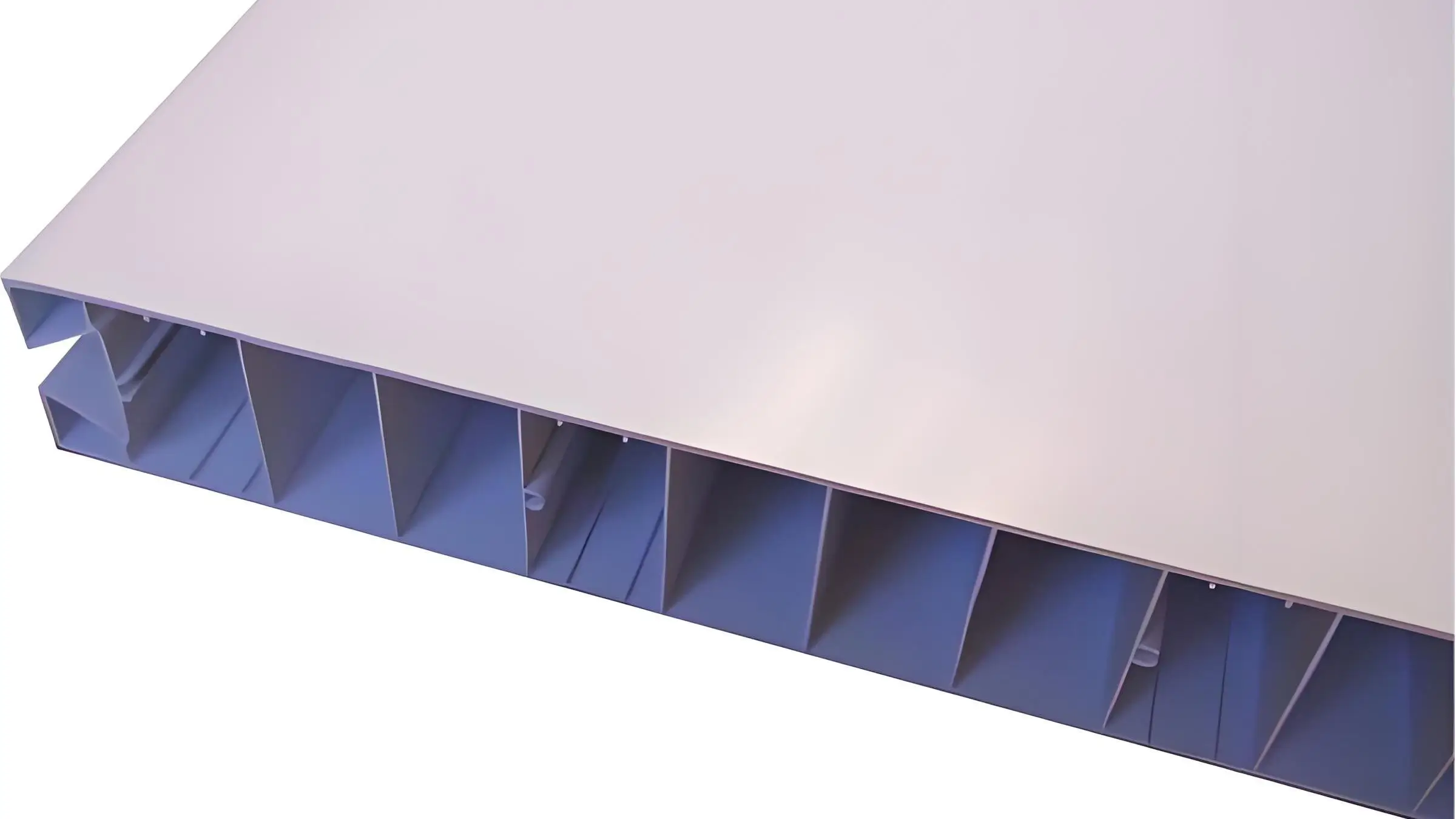

Partisi dan Panel Dinding:
Profil PVC ideal untuk membuat partisi internal di kantor, ruang pameran, dan bangunan industri. Mereka ringan dan mudah dipasang atau dikonfigurasi ulang. Selain itu, panel dinding PVC bersifat dekoratif, tahan lembab, dan dapat disesuaikan dalam berbagai tekstur dan warna untuk meniru bahan seperti kayu atau batu. Hal ini membuatnya cocok untuk estetika dan daya tahan, terutama di lingkungan dengan kelembaban tinggi seperti kamar mandi atau dapur.
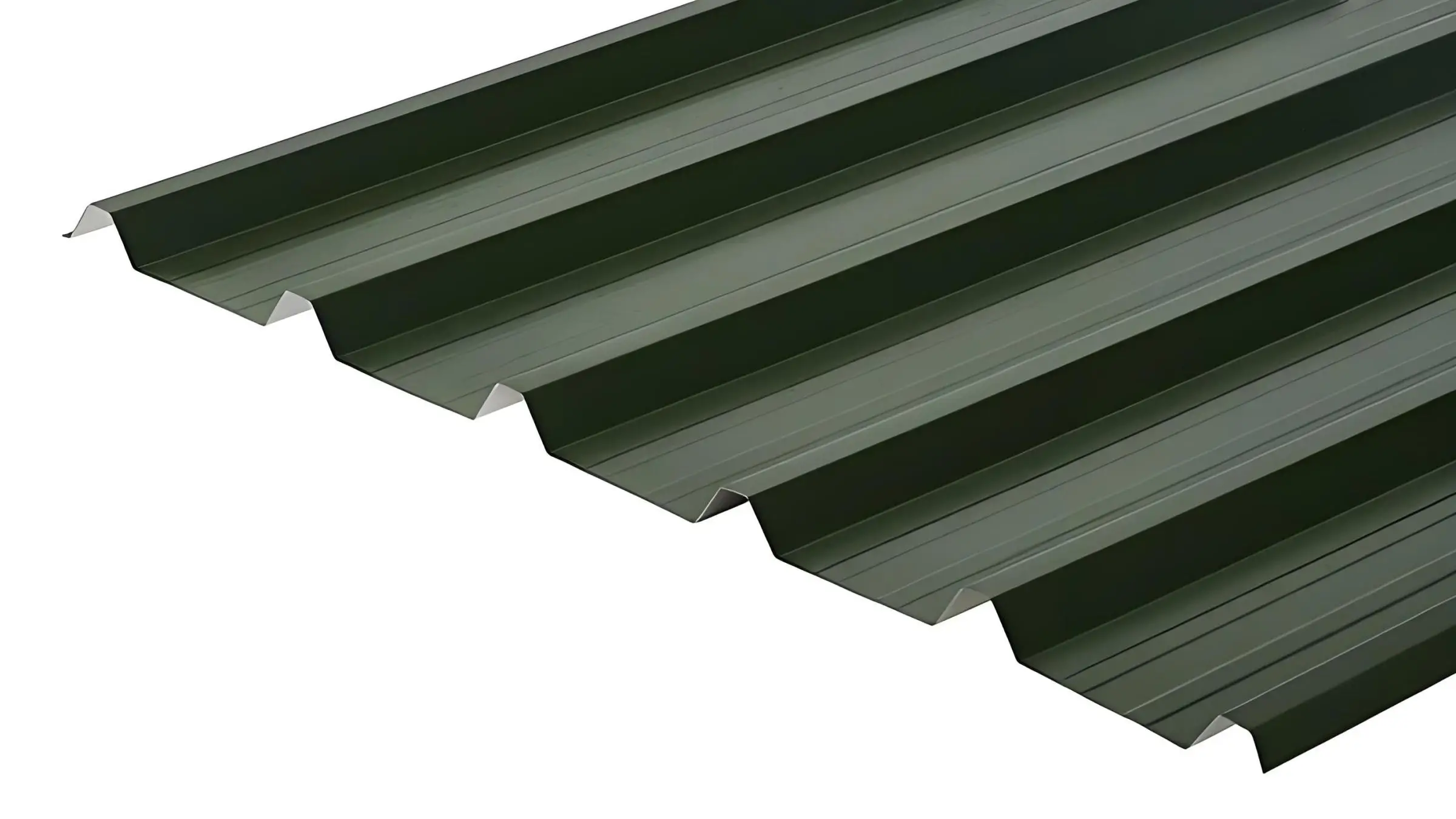
Atap dan Penutup Atap:
Profil PVC digunakan pada sistem atap dan kelongsong karena sifatnya yang tahan air, ringan, dan mudah dipasang. Profil ini melindungi struktur dari kondisi cuaca yang keras dan memberikan insulasi termal yang efektif, sehingga ideal untuk solusi bangunan yang tahan lama.

Pagar dan Pagar:
PVC banyak digunakan untuk pagar dan pagar luar ruangan karena ketahanannya terhadap cuaca. Tidak seperti kayu atau logam, PVC tidak akan membusuk, berkarat, atau rusak saat terkena elemen-elemennya, sehingga menjadikannya pilihan yang minim perawatan dan tahan lama baik untuk lingkungan perumahan maupun komersial.
2. Industri Furnitur:
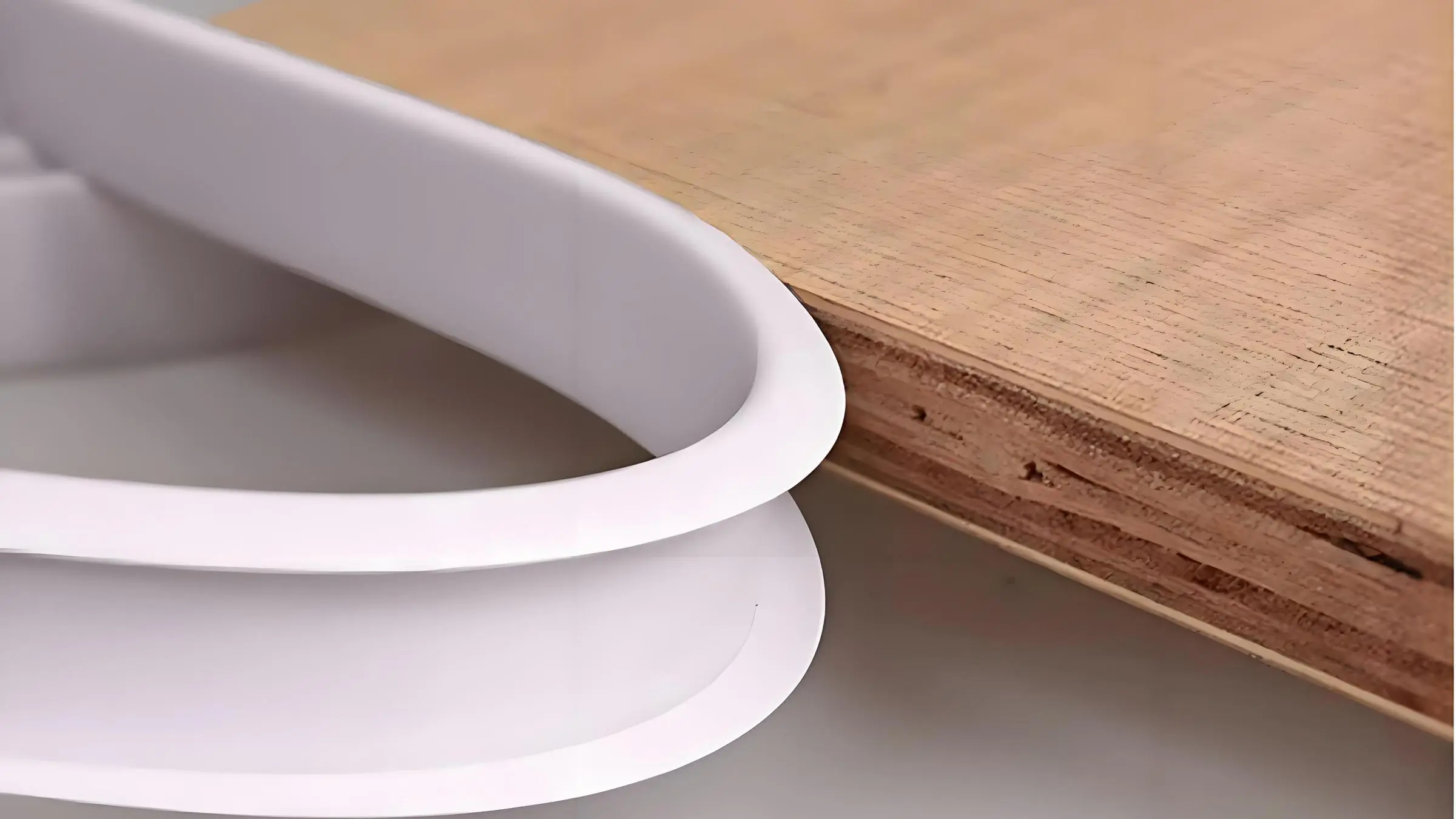

Tepi Furnitur:
Profil PVC banyak digunakan untuk melapisi bagian tepi furnitur seperti meja, kursi, dan lemari. Profil PVC memberikan tampilan akhir yang halus sekaligus melindungi tepi dari keausan. Tepian PVC tersedia dalam berbagai warna dan sentuhan akhir, menambahkan elemen dekoratif pada furnitur sekaligus memastikan daya tahan.
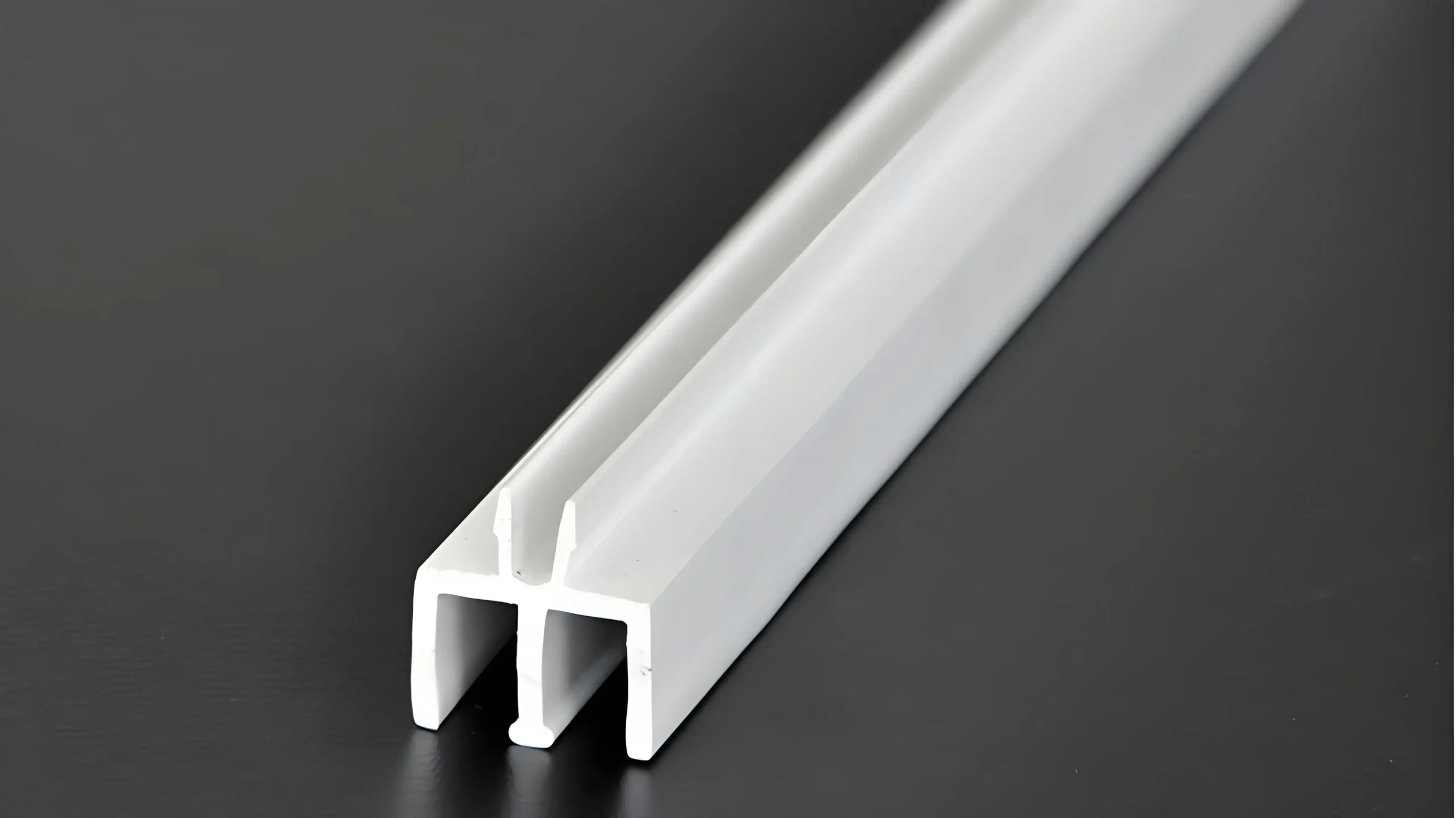

Pemandu dan Rel Laci:
Profil PVC digunakan dalam membuat pemandu laci dan rel. Profil ini memastikan pengoperasian laci yang mulus, memberikan permukaan gesekan rendah yang tahan terhadap keausan dan beban berat. Daya tahan PVC menjamin bahwa komponen ini tetap berfungsi untuk waktu yang lama.
3. Industri Otomotif:
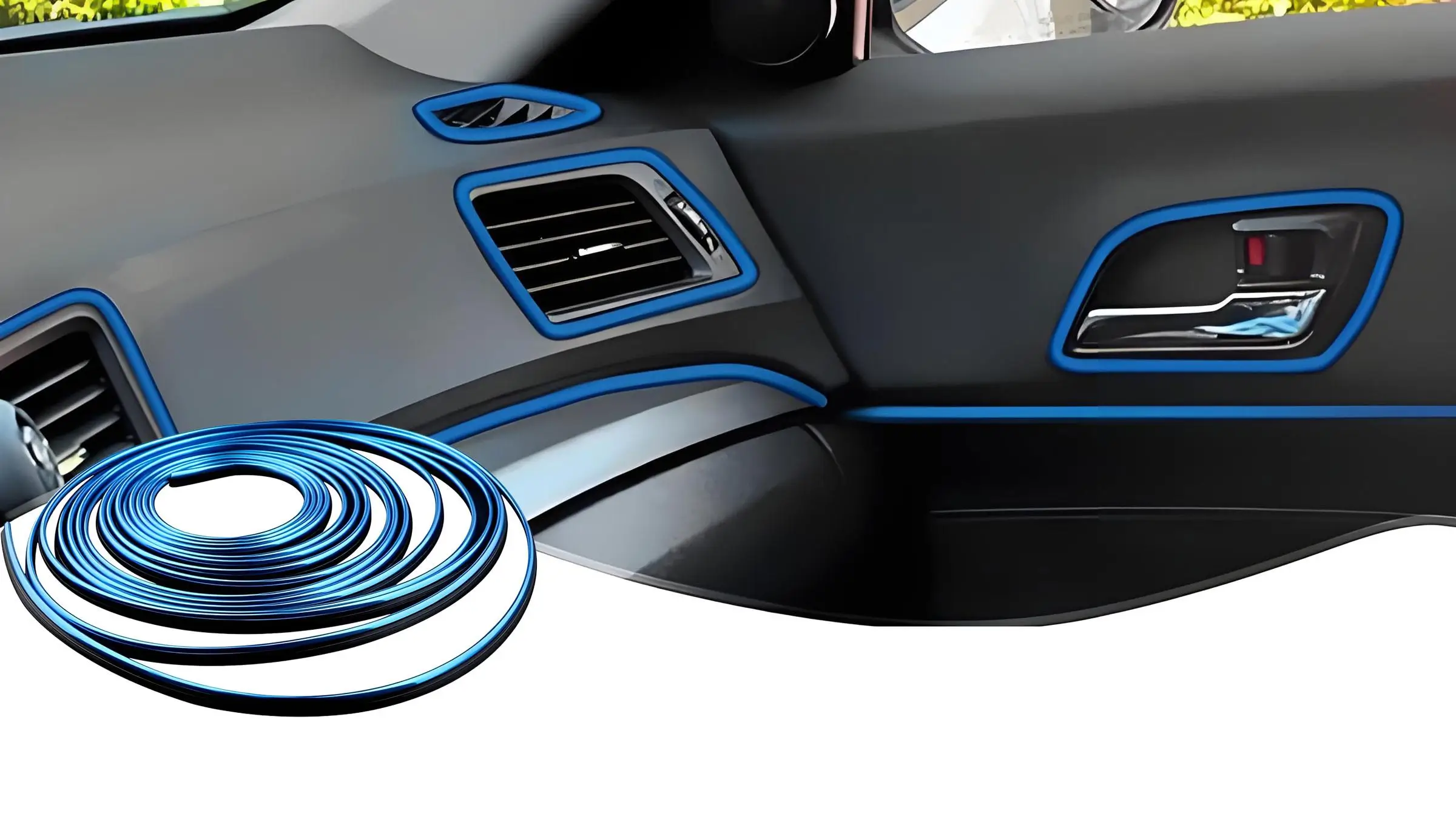

Trim Interior:
Pada mobil, profil PVC digunakan untuk komponen seperti segel pintu, saluran jendela, dan bagian dasbor. PVC dihargai karena kemampuannya untuk memberikan pengoperasian yang tenang dan estetika yang halus, meningkatkan kenyamanan dan tampilan interior kendaraan. Segel pintu PVC membantu menjaga interior bebas dari debu dan air, sementara saluran jendela memastikan pengoperasian jendela yang mulus dan melindungi mekanisme jendela dari kerusakan seiring waktu.
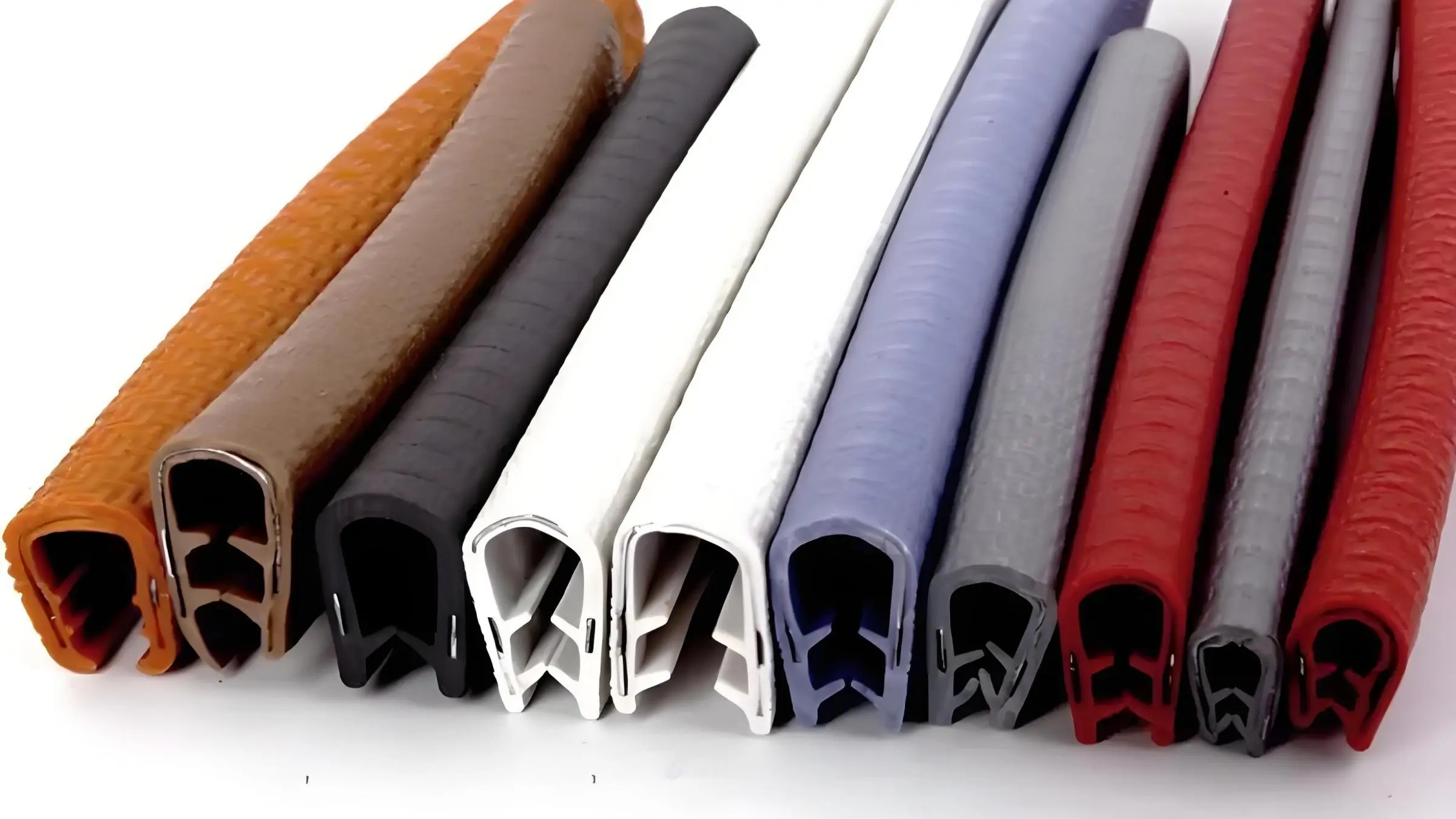

Trim Eksterior:
Profil PVC biasanya digunakan pada bagian trim otomotif eksterior seperti cetakan samping, bumper, dan fender liner. Bagian-bagian ini tidak hanya meningkatkan penampilan kendaraan tetapi juga memberikan perlindungan terhadap benturan dan goresan ringan. Mereka berkontribusi terhadap daya tahan kendaraan secara keseluruhan dengan menawarkan solusi tahan lama dan tahan cuaca yang mempertahankan daya tarik estetika dan integritas struktural kendaraan dari waktu ke waktu.
4. Manajemen Listrik dan Kabel:
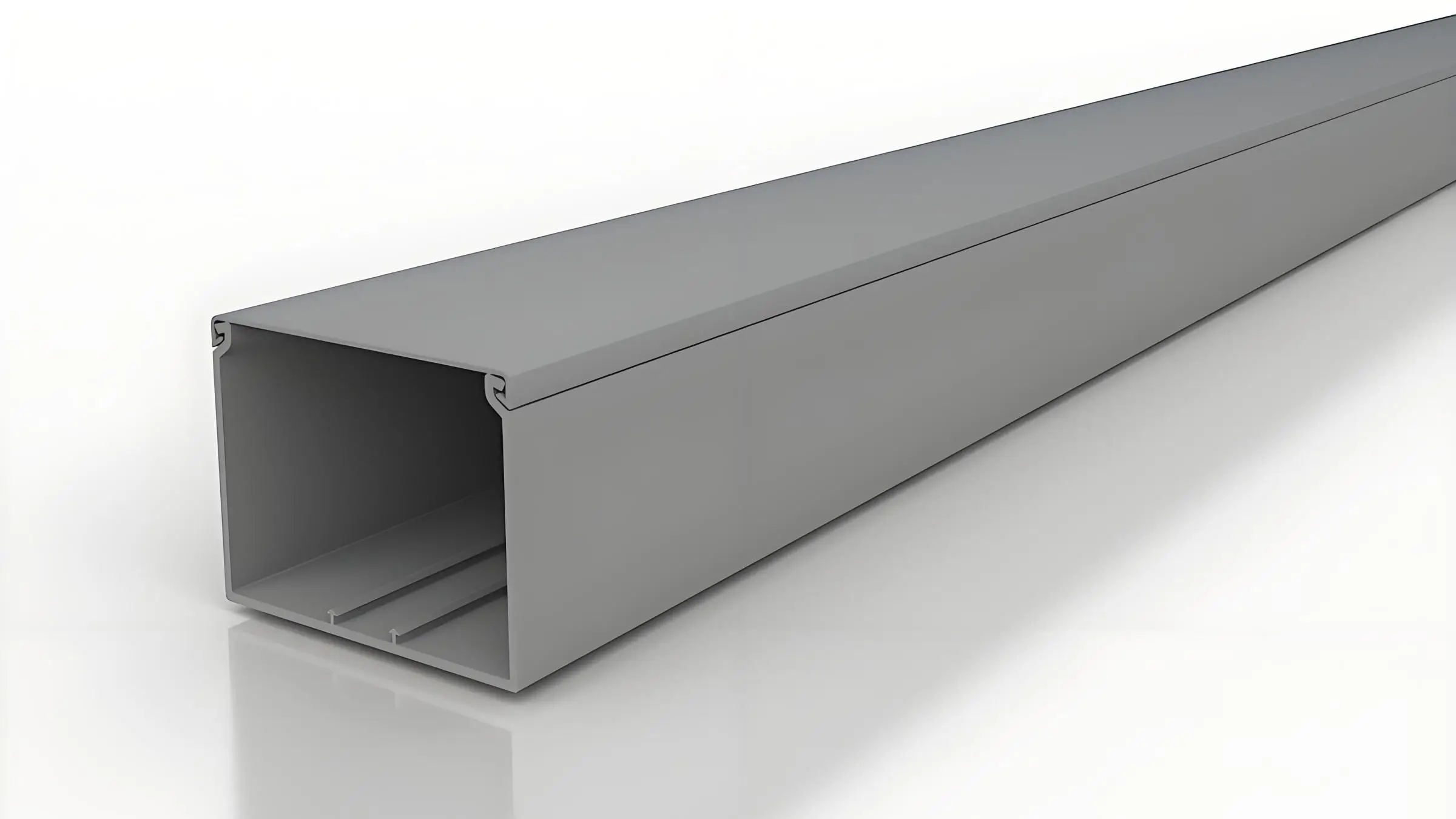

Baki dan Saluran Kabel:
Profil PVC banyak digunakan dalam sistem manajemen listrik dan kabel. Baki dan saluran kabel yang terbuat dari PVC membantu mengatur dan melindungi kabel listrik di gedung, pabrik, dan pusat data. Sifat non-konduktif PVC memastikan keamanan jika terjadi gangguan listrik. Profil ini juga mudah dipasang dan disesuaikan untuk memenuhi persyaratan perutean tertentu, sehingga memastikan bahwa kabel listrik dikelola dan dapat diakses dengan aman.
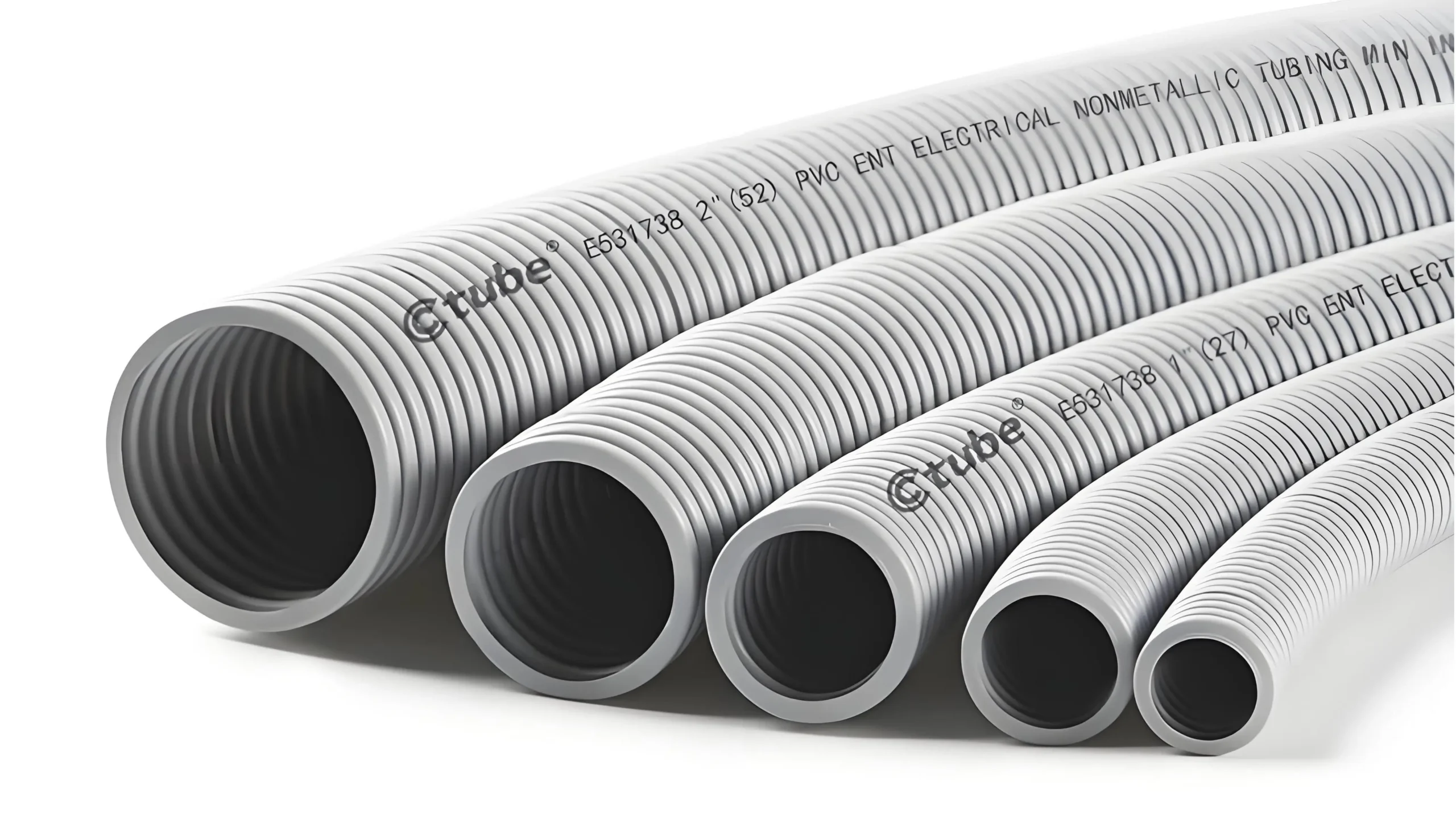

Rumah dan Saluran Kawat:
PVC biasanya digunakan untuk membuat rumah kawat dan saluran yang melindungi kabel listrik dari faktor lingkungan seperti kelembaban, bahan kimia, dan kerusakan fisik. Saluran PVC sering digunakan dalam instalasi listrik di luar ruangan untuk melindungi kabel dari sinar matahari, hujan, dan benturan yang tidak disengaja. Daya tahan bahan memastikan perlindungan jangka panjang, sehingga ideal untuk melindungi sistem kelistrikan dalam berbagai kondisi.
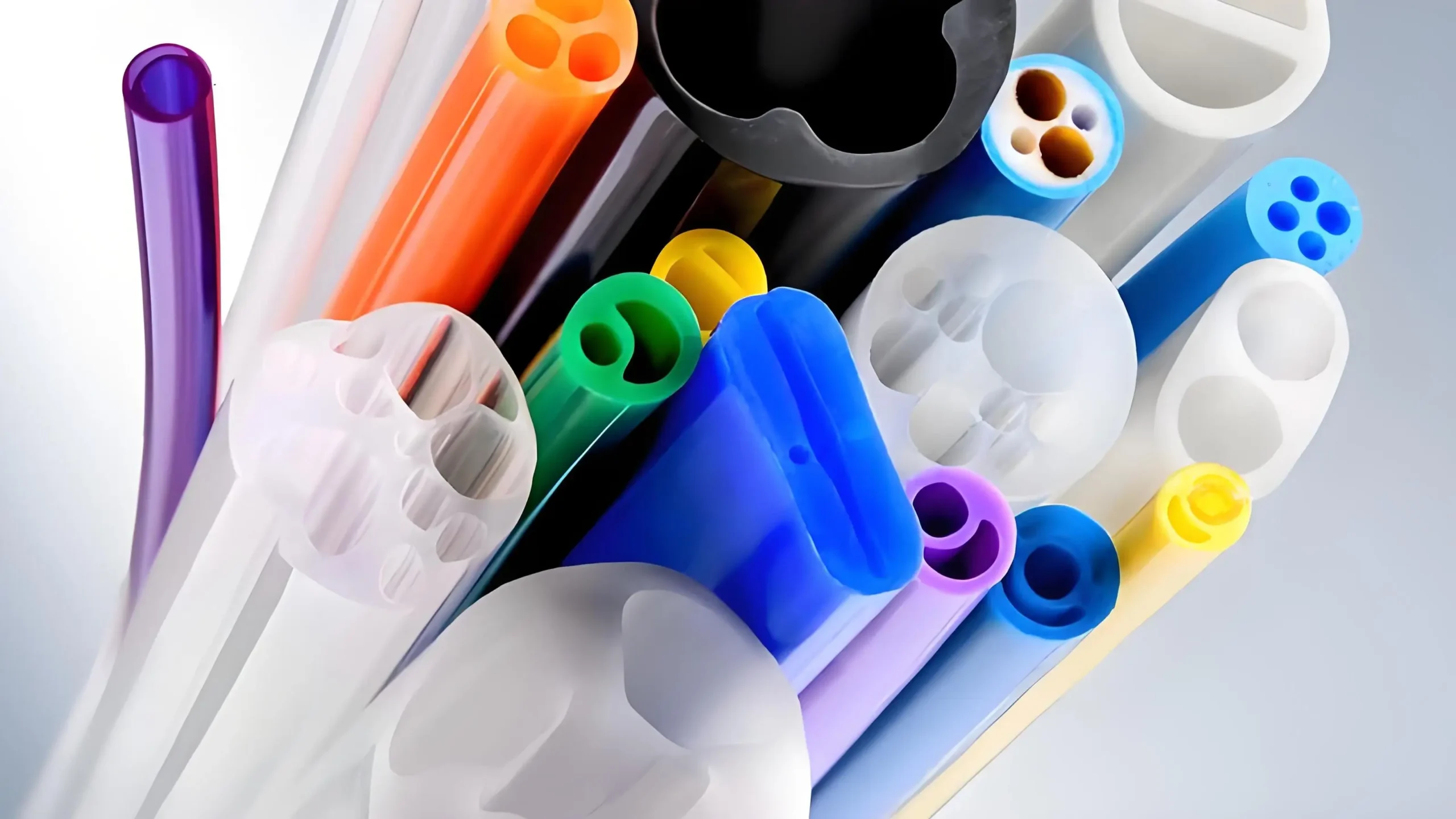
5. Sistem Perpipaan:
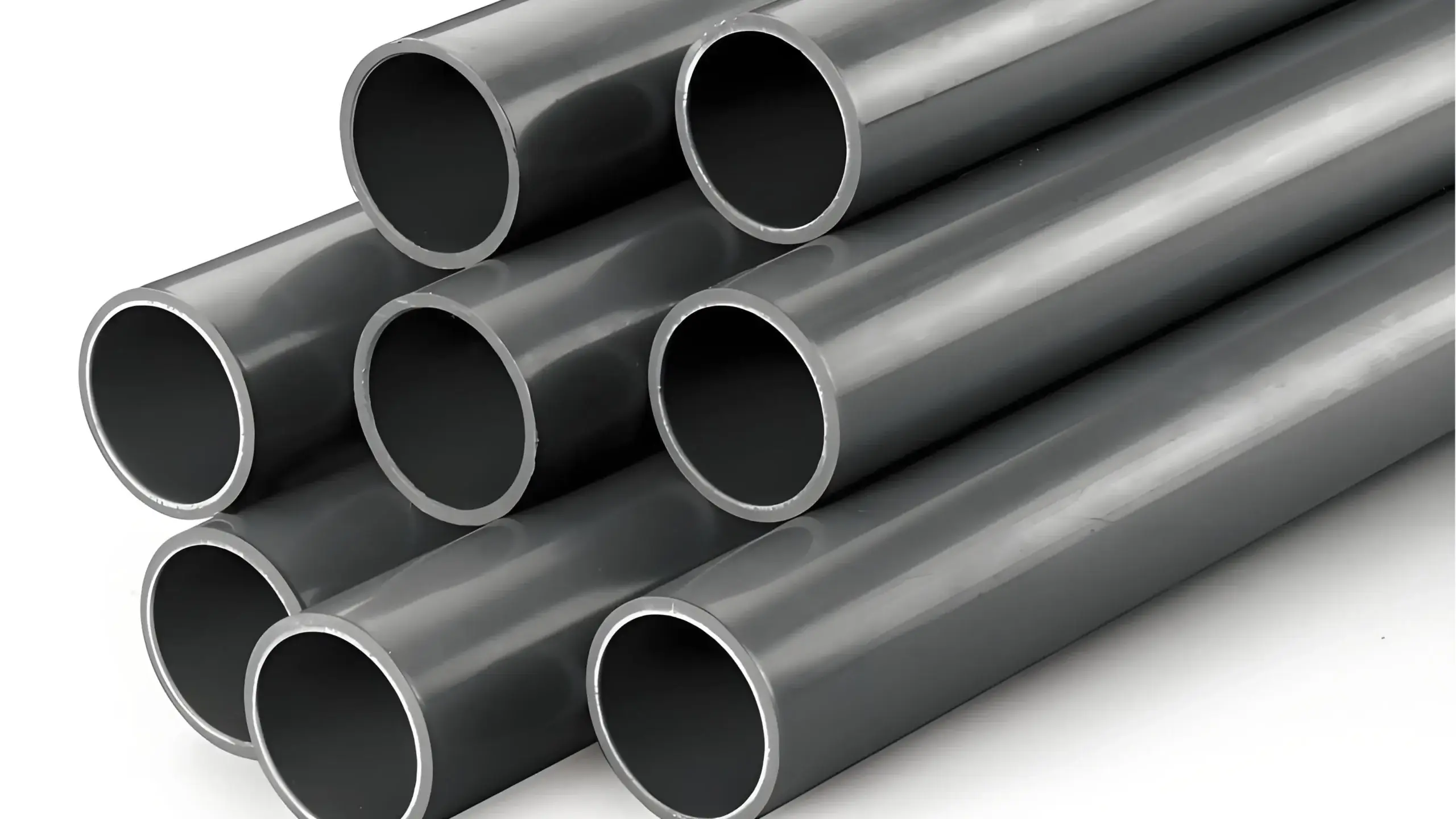

Pipa dan Perpipaan Industri:
Profil PVC digunakan untuk membuat pipa untuk pasokan air, drainase, dan sistem pembuangan limbah. Pipa PVC tahan terhadap korosi, ringan, dan mudah dipasang, menjadikannya bahan yang ideal untuk sistem perpipaan perumahan, komersial, dan industri.
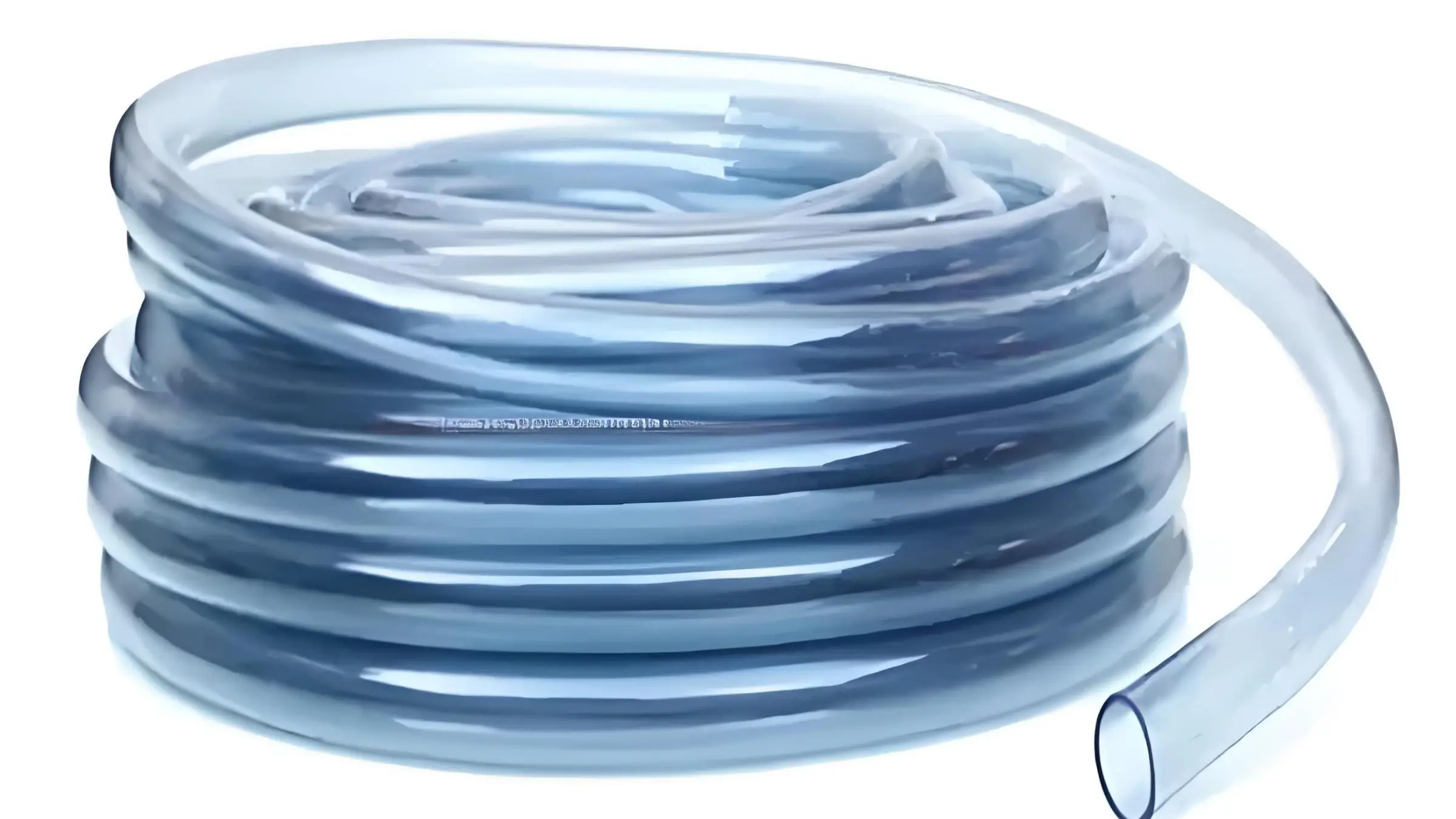

Tabung Industri:
PVC juga digunakan dalam aplikasi industri untuk mengangkut bahan kimia, gas, dan bahan lainnya karena ketahanan dan kekuatannya terhadap bahan kimia. Hal ini menjadikannya pilihan yang cocok untuk digunakan di pabrik kimia, pabrik, dan lingkungan industri lainnya.
6. Barang Konsumsi:

Furnitur, Mainan, dan Peralatan:
Profil PVC umumnya ditemukan dalam produksi barang-barang konsumen seperti mainan, komponen furnitur, dan peralatan rumah tangga. Keserbagunaan dan biaya yang rendah dari PVC membuatnya menjadi bahan yang ideal untuk elemen fungsional dan dekoratif pada produk-produk ini. Sifat PVC yang ringan dan kemudahan kustomisasi memungkinkan terciptanya barang yang tahan lama dan menarik secara estetika, memenuhi permintaan produsen dan konsumen.

Pengemasan:
Profil PVC banyak digunakan dalam industri pengemasan untuk kemasan blister, kemasan kulit kerang, dan jenis kemasan pelindung lainnya. Kemampuan PVC untuk dibentuk menjadi bentuk yang presisi membuatnya ideal untuk menciptakan solusi kemasan khusus yang melindungi produk selama pengangkutan dan pemajangan. Selain itu, kejernihan dan kekuatan PVC meningkatkan daya tarik visual dan keamanan barang yang dikemas, memberikan solusi yang efektif untuk berbagai industri.
7. Aplikasi Medis:
8. Aplikasi Pertanian:

Profil PVC digunakan dalam industri medis untuk membuat berbagai perangkat seperti kateter, stent, dan tabung. PVC bersifat biokompatibel, tahan terhadap bahan kimia, dan dapat dengan mudah disterilkan, sehingga menjadi pilihan yang sangat baik untuk aplikasi medis yang membutuhkan kebersihan dan daya tahan yang ketat.

Profil PVC digunakan dalam lingkungan pertanian untuk membuat struktur seperti rumah kaca, sistem irigasi, dan peralatan pertanian. Ketahanan PVC terhadap sinar UV dan kelembapan membuatnya tahan lama di lingkungan luar ruangan, sehingga berkontribusi pada umur panjang infrastruktur pertanian.
FAQ UNTUK KLIEN
Memulai dengan Uplastech
Ada pertanyaan? Kami punya jawabannya.
Kami mengkhususkan diri dalam ekstrusi, pembentukan vakum, cetakan tiup, dan pembuatan cetakan presisi, menawarkan solusi yang disesuaikan untuk memenuhi beragam kebutuhan manufaktur Anda.
Kami bekerja dengan berbagai industri, termasuk otomotif, elektronik, barang konsumen, dan pengemasan, dengan fokus pada kemitraan B2B dan memberikan solusi di bidang ekstrusi, thermoforming, blow moulding, dan pembuatan cetakan presisi.
Ya, kami menyesuaikan solusi kami agar sesuai dengan kebutuhan unik Anda.
Hubungi
Jangan ragu untuk mengirim email kepada kami atau mengisi formulir di bawah ini untuk mendapatkan penawaran.
Email: uplastech@gmail.com







