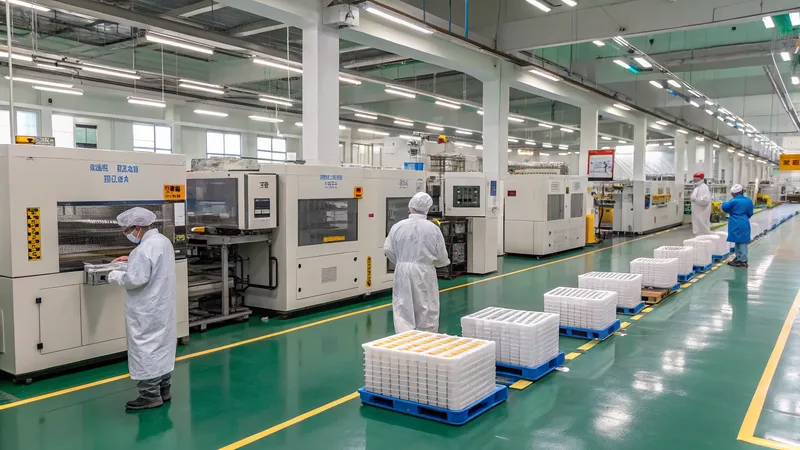
Plastic vacuum forming, also known as thermoformage1, is a versatile manufacturing process that shapes heated plastic sheets2 using vacuum pressure to create a wide range of products, from packaging materials to automotive components. In Indonesia, this technique plays a crucial role in the manufacturing sector, supporting industries such as food packaging, automotive, consumer goods, and more. While identifying the definitive top 10 vacuum forming factories in Indonesia is challenging due to limited public data, we’ve compiled a list of prominent manufacturers based on available information.
Plastic vacuum forming uses heated thermoplastic sheets shaped by vacuum pressure, commonly applied in packaging, automotive, and consumer goods for cost-effective, large-scale production.
Understanding the process, materials, and applications of formage sous vide3 can help businesses make informed decisions about their manufacturing needs. This guide explores the top factories, the materials they use, the vacuum forming process, and its advantages over other technologies.
Vacuum forming is ideal for producing large, complex parts.Vrai
The process allows for the creation of large components with relatively simple tooling, making it cost-effective for large-scale production.
Vacuum forming is only used for low-volume production.Faux
While it’s excellent for prototyping and small runs, vacuum forming is also widely used for medium to large production volumes, especially for larger parts.
- 1. Top 10 Plastic Vacuum Forming Factories in Indonesia
- 2. Quels sont les matériaux couramment utilisés dans le formage sous vide ?
- 3. Quelles sont les étapes du processus de formage sous vide ?
- 4. Quels sont les facteurs clés du processus de formage sous vide ?
- 5. Quelles sont les applications du formage sous vide ?
- 6. What are the Differences Between Vacuum Forming and Injection Molding?
- 7. Conclusion
Top 10 Plastic Vacuum Forming Factories in Indonesia
Below is a list of 10 notable plastic vacuum forming factories4 in Indonesia, each contributing significantly to the country’s manufacturing landscape. These factories specialize in various applications, from packaging to automotive parts, and utilize a range of matériaux thermoplastiques5.
| Factory Name | Location | Produits clés | Materials Used | Certifications/Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PT. FLN | Bekasi, Jawa Barat | Automotive accessories, plastic products | Various thermoplastics | ISO 9001:2015, IATF 16949:2016, over 10 years experience |
| PT. Vacpack Indonesia | Bogor | Blister packs, food trays, electronic trays | PET, PVC, PP, HIPS | High-speed vacuum forming machines, millions capacity |
| PT Granada Mitra Bersama | Karawang, Bekasi | Blister packaging, plastic trays | PVC, PP, PET | Custom design, modern machinery, in-house molds |
| PT. Surya Indo Plastic | Sidoarjo | Recycled PET food packaging (trays, cups, lids) | Recycled PET (rPET) | ISO 9001, HACCP, FSSC 22000, sustainability focus |
| PT. Prima Plastindo | Tangerang | Packaging for electronics and consumer goods | HIPS, PET, PVC | Specializes in custom packaging solutions6 |
| PT. Indovac | Jakarta | Trays and containers for food and medical applications | PET, PP, HIPS | Focus on hygiene and safety standards |
| PT. Mitra Plastik Indonesia | Surabaya | Custom vacuum forming for various industries | ABS, HIPS, PET | Offers design and prototyping services |
| PT. Sinar Jaya Plastik | Bandung | Automotive parts and consumer products | ABS, HIPS, PVC | Experienced in automotive industry standards |
| PT. Wahana Makmur Sejati | Semarang | Signage and display items | HIPS, PET, PVC | Creative designs for retail and advertising |
| PT. Plastikindo | Medan | Packaging solutions | PET, PP, HIPS | Serves local and regional markets |
These factories represent the diversity and capability of Indonesia’s vacuum forming industry, offering solutions for both local and international markets.
Quels sont les matériaux couramment utilisés dans le formage sous vide ?
Vacuum forming relies on thermoplastic materials that can be heated, shaped, and cooled to form durable products. Each material has unique properties suited for specific applications.

Common vacuum forming materials include HIPS7, ABS8, PET9, PVC, and PP, chosen for their formability, durability, and cost-effectiveness in packaging, automotive, and consumer goods.
| Type de matériau | Recommended Max Thickness | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| HIPS | 3 - 4 mm | Rentable, facile à former |
| ABS | Up to 6 mm | Higher impact resistance |
| PET | 1 - 2 mm | Clear, rigid, food-safe |
| PVC | 2 - 3 mm | Flexible, cost-effective |
| PP | 2 - 4 mm | Recyclable, good for food contact |
Polystyrène à haut impact (HIPS)
HIPS is a cost-effective, easy-to-form material ideal for low-impact products like packaging trays and disposable items. Its affordability and versatility make it a popular choice in the packaging industry.
Acrylonitrile Butadiène Styrène (ABS)
ABS offers higher impact resistance and durability, making it suitable for automotive parts, consumer goods, and other applications requiring strength and longevity.

Polyéthylène téréphtalate (PET)
PET is clear, rigid, and commonly used for food packaging and blister packs due to its excellent barrier properties and recyclability.
Chlorure de polyvinyle (PVC)
PVC is flexible and cost-effective, often used for blister packaging. However, environmental concerns due to its chlorine content have led to a shift toward more sustainable materials.

Polypropylène (PP)
PP is recyclable and suitable for food contact, making it ideal for food trays and containers. It offers good chemical resistance but may have lower clarity compared to PET.
HIPS is the most commonly used material in vacuum forming.Vrai
HIPS is widely used due to its affordability, ease of forming, and suitability for a broad range of applications.
All vacuum forming materials are equally suitable for food packaging.Faux
Materials like PET and PP are food-safe, while others like PVC may not meet food safety standards due to potential chemical leaching.
Quelles sont les étapes du processus de formage sous vide ?
The vacuum forming process is a straightforward yet precise method for shaping plastic sheets into functional products. Each step must be carefully controlled to ensure high-quality results.
The vacuum forming process involves clamping, heating, forming, cooling, trimming, and finishing plastic sheets to create shaped products for various industries.
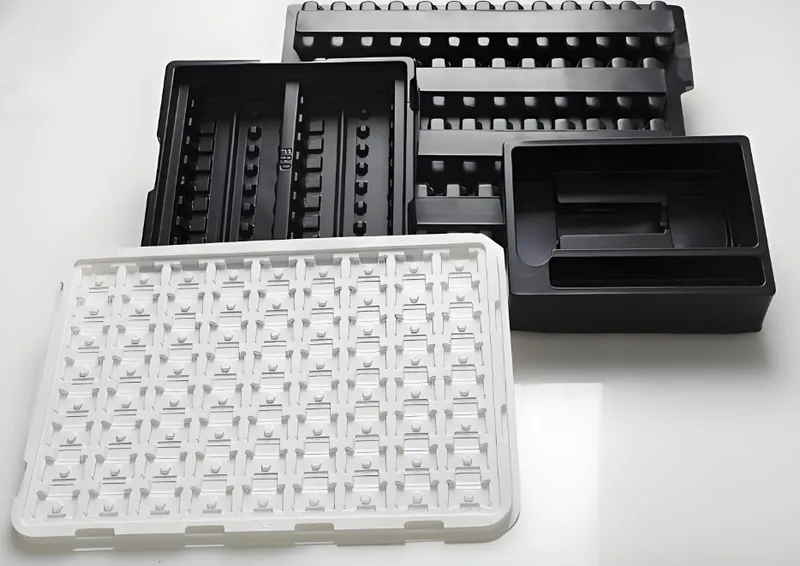

Clamping
The plastic sheet is secured in a frame to prevent movement during heating and forming. The frame must be robust enough to handle the sheet’s thickness, typically ranging from 1 to 10 mm.
Chauffage
The sheet is heated using infrared or radiant heaters to a pliable temperature, typically between 120°C and 180°C, depending on the material. Proper temperature control is crucial to avoid overheating or underheating.
Formation
The heated sheet is stretched over a mold, and vacuum pressure (typically 28-30 inches of mercury) is applied to draw the plastic tightly against the mold, ensuring accurate shaping.
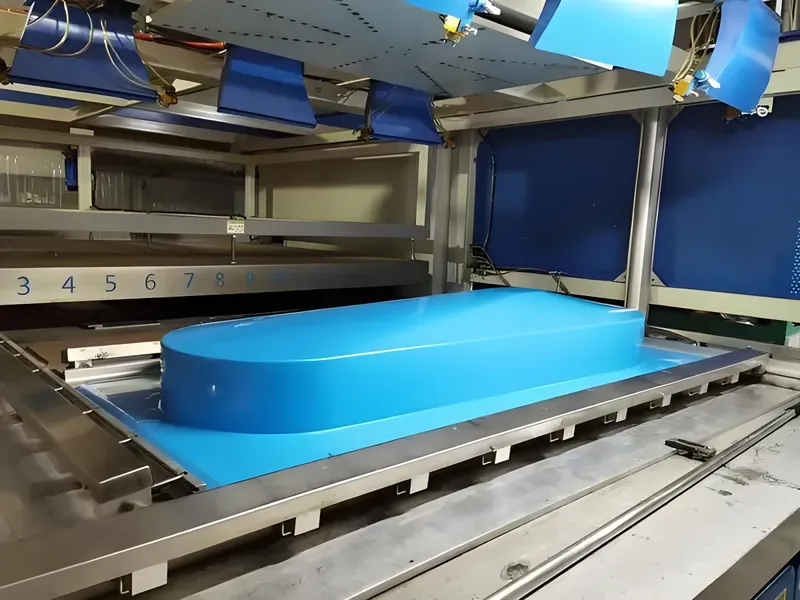
Refroidissement
The formed part is cooled using fans or ambient air to solidify the plastic and retain its shape. Cooling time varies based on material thickness and mold design.
Parage
Excess material (flash) is removed using cutting tools or CNC machines to achieve the final part dimensions. Precision in trimming is essential for part quality.
Finition
Additional operations like printing, assembly, or secondary machining may be applied to meet specific product requirements, such as branding or functionality.
Vacuum forming can only produce simple shapes.Faux
While best suited for relatively simple geometries, vacuum forming can create complex shapes with proper mold design and process control.
The vacuum forming process is fully automated.Faux
While many steps can be automated, some aspects, like mold changes and trimming, often require manual intervention.
Quels sont les facteurs clés du processus de formage sous vide ?
Several factors influence the quality and efficiency of the vacuum forming process. Understanding these can help optimize production and ensure consistent results.
Key factors in vacuum forming include temperature control, vacuum pressure, and material thickness, which directly affect the part’s quality, detail, and strength.

Contrôle de la température
Proper heating ensures the plastic is pliable enough to form without overheating, which can cause material degradation or poor surface finish. Each material has an optimal forming temperature range.
Pression du vide
Sufficient vacuum pressure is necessary to draw the plastic tightly against the mold. Inadequate pressure can lead to incomplete forming, while excessive pressure may cause defects like webbing or thinning.

Material Thickness
Thicker sheets require longer heating times and may limit the complexity of shapes that can be formed. Thinner sheets are more suitable for intricate details but may lack strength for certain applications.
Higher vacuum pressure always results in better part quality.Faux
While adequate vacuum pressure is necessary, excessive pressure can cause defects like webbing or thinning in the part.
Material thickness has no impact on the vacuum forming process.Faux
Thicker materials require more heat and time to form, and they may not capture fine details as well as thinner sheets.
Quelles sont les applications du formage sous vide ?
Vacuum forming is used across a wide range of industries due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness. It is particularly valuable for producing large, lightweight parts with relatively low tooling costs.
Vacuum forming is applied in packaging, automotive, consumer goods, signage, and medical industries for creating lightweight, durable, and cost-effective products.

Industrie de l'emballage
Vacuum forming is ideal for producing blister packs, clamshells, and trays used in food, electronics, and pharmaceutical packaging. It offers excellent product visibility and protection.
Automotive Sector
The process is used to create interior components like dashboards, door panels, and trim parts, providing a cost-effective solution for large, complex shapes.

Biens de consommation
Vacuum forming is used for appliance housings, furniture components, and toys, offering lightweight and customizable options for manufacturers.
Signalisation et affichage
The process is applied in creating dimensional signs and retail displays, leveraging its ability to produce aesthetically pleasing and functional designs.

Medical Applications
Vacuum forming creates trays for medical devices and packaging for pharmaceuticals, ensuring hygiene, tamper-resistance, and ease of use.
Le formage sous vide est principalement utilisé pour le prototypage.Faux
While useful for prototyping due to low tooling costs, vacuum forming is also widely used for production runs, especially for large parts or lower volumes.
Vacuum forming is unsuitable for high-precision applications.Vrai
The process is less precise than injection molding, making it less suitable for parts requiring tight tolerances or complex geometries.
What are the Differences Between Vacuum Forming and Injection Molding?
Understanding the differences between vacuum forming and other manufacturing processes like injection molding can help businesses choose the right method for their needs.
Vacuum forming offers lower tooling costs and faster setup times compared to injection molding, making it ideal for large parts and prototyping, but it lacks the precision and strength of injection-molded parts.

Tooling Costs and Setup Times
Vacuum forming molds are simpler and cheaper to produce than injection molding tools, making it more cost-effective for small to medium production runs and prototyping.
Part Complexity and Precision
Injection molding allows for higher precision and more complex geometries, while vacuum forming is better suited for simpler, larger parts.

Sélection des matériaux
Injection molding can use a wider range of materials, including thermosets, while vacuum forming is limited to thermoplastics.
Volume de production
Injection molding is more efficient for high-volume production due to faster cycle times and automation, whereas vacuum forming is better for lower volumes or larger parts.
Vacuum forming is less expensive than injection molding for all applications.Faux
While vacuum forming has lower tooling costs, injection molding can be more cost-effective for high-volume production due to faster cycle times and automation.
Le formage sous vide permet de produire des pièces avec le même niveau de détail que le moulage par injection.Faux
Injection molding offers greater precision and detail, especially for small, intricate parts, whereas vacuum forming is better for larger, simpler shapes.
Conclusion
Plastic vacuum forming is a versatile and cost-effective manufacturing process widely used in Indonesia for producing a variety of products across industries. Factories like PT. FLN, PT. Vacpack Indonesia, and PT. Surya Indo Plastic are leading the way in providing high-quality vacuum-formed products, from packaging solutions to automotive components. By understanding the materials, process steps, key factors, and applications of vacuum forming, businesses can leverage this technology to meet their manufacturing needs efficiently.
-
Discover the advantages of thermoforming, a key process in plastic manufacturing, and how it can benefit your production needs. ↩
-
Learn about the different types of plastic sheets used in vacuum forming, which can help you choose the right materials for your projects. ↩
-
Explore this link to gain a deeper understanding of vacuum forming, its applications, and benefits in various industries. ↩
-
Explore this link to discover the leading vacuum forming factories in Indonesia and their contributions to the manufacturing sector. ↩
-
Learn about the various thermoplastic materials used in vacuum forming, which are crucial for understanding the manufacturing processes. ↩
-
Find out about innovative packaging solutions in the vacuum forming industry that can enhance product safety and presentation. ↩
-
Explore the unique properties of HIPS and its applications in packaging and disposable items, making it a versatile choice. ↩
-
Learn about ABS's impact resistance and durability, essential for automotive and consumer applications. ↩
-
Discover PET's excellent barrier properties and recyclability, crucial for safe food packaging solutions. ↩








