Plastic vacuum forming is a versatile and cost-effective manufacturing process1 that transforms flat plastic sheets into three-dimensional shapes. Whether you're in packaging, automotive, or product design, understanding vacuum forming can open up new possibilities for your projects. This guide will walk you through the process, applications, and key considerations of formage sous vide2, helping you decide if it's the right fit for your needs.
Vacuum forming heats a plastic sheet, molds it using a vacuum, and cools it to create custom shapes3 for industries like packaging, automotive, and medical devices, offering cost-effective production for small to medium runs.
Le formage sous vide est idéal pour la production de grands volumes.Faux
While cost-effective for small to medium runs, vacuum forming may not be the best choice for very high volumes due to slower cycle times compared to injection molding.
Vacuum forming can produce complex, detailed parts.Faux
Vacuum forming is best suited for simpler designs; intricate details may require additional processes or alternative methods like pressure forming.
- 1. What is Plastic Vacuum Forming?
- 2. How Does the Vacuum Forming Process Work?
- 3. What Materials Are Used in Vacuum Forming?
- 4. What Are the Applications of Vacuum Forming?
- 5. How Does Vacuum Forming Compare to Other Technologies?
- 6. What Are the Key Design Considerations for Vacuum Forming?
- 7. What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Vacuum Forming?
- 8. Conclusion
What is Plastic Vacuum Forming?
Plastic vacuum forming4, also known as thermoforming, is a manufacturing process where a plastic sheet is heated until pliable, stretched over a mold, and shaped using a vacuum. Once cooled, the plastic retains the mold's shape, creating a three-dimensional object. This method is widely used for its simplicity, low tooling costs, and ability to produce large parts quickly.

Key Definitions
-
Formage sous vide: A type of thermoforming where a vacuum is used to pull a heated plastic sheet against a mold.
-
Thermoformage5: A broader term encompassing various methods of heating and shaping plastic sheets, including vacuum forming and pressure forming.
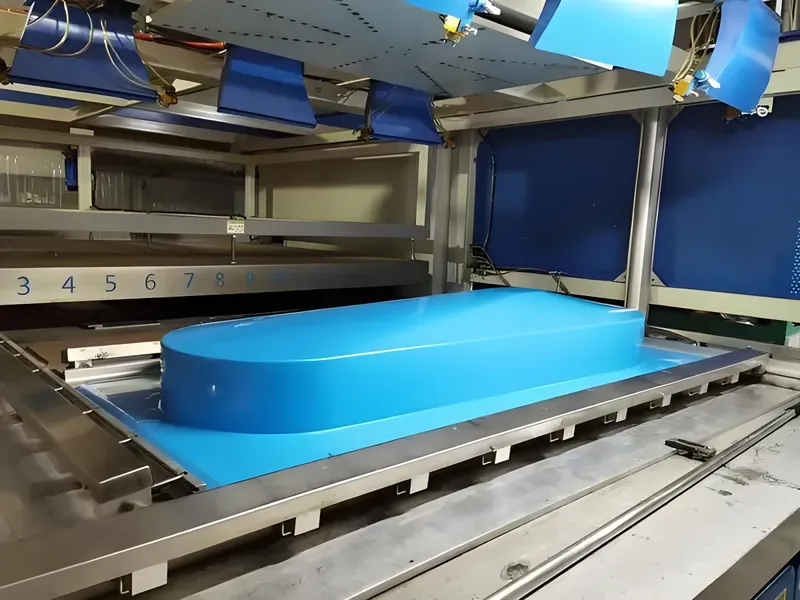
- Thermoplastiques6: Plastics that become pliable when heated and solidify upon cooling, making them ideal for vacuum forming.
Classification of Vacuum Forming
-
Par processus: Vacuum forming is a subset of thermoforming, distinct from pressure forming (which uses positive pressure) and twin-sheet forming (which bonds two sheets together).
-
Par les matériaux: Common thermoplastics used include:

- Polystyrène à haut impact (HIPS)
- Acrylonitrile Butadiène Styrène (ABS)
- Polyéthylène téréphtalate glycol (PETG)
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- Par applications: Used in industries like packaging, automotive, medical, and consumer goods for creating trays, enclosures, and panels.
Vacuum forming is only used for simple shapes.Faux
While best for simpler designs, vacuum forming can produce moderately complex shapes with proper mold design and material selection.
How Does the Vacuum Forming Process Work?
The vacuum forming process involves several key steps, each critical to achieving the desired shape and quality. Here's a breakdown:
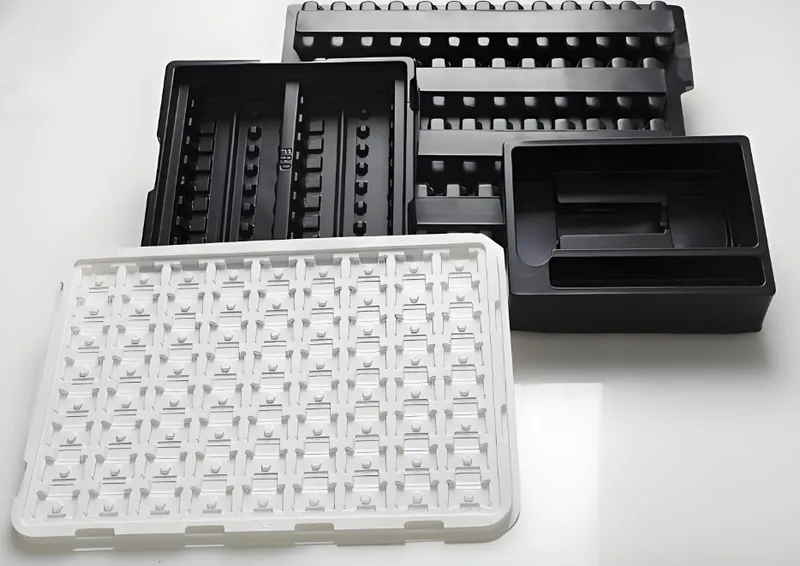

1. Mold Creation
- Molds can be made from materials like wood, aluminum, or resin, depending on the production volume and required durability.
- Aluminum molds are ideal for higher volumes due to their longevity.
2. Heating the Plastic Sheet
- The plastic sheet is clamped into a frame and heated using infrared heaters until it reaches a pliable state.
- Temperature control is crucial to ensure even heating and prevent material degradation.

3. Forming the Shape
- The heated sheet is placed over the mold, and a vacuum is applied to pull the plastic tightly against the mold's surface.
- The vacuum must be strong enough to ensure the plastic conforms to all details of the mold.
4. Cooling and Trimming
- The formed part is cooled using fans or water mist to solidify the plastic.
- Excess material is trimmed, and additional finishing (e.g., drilling, sanding) may be applied.
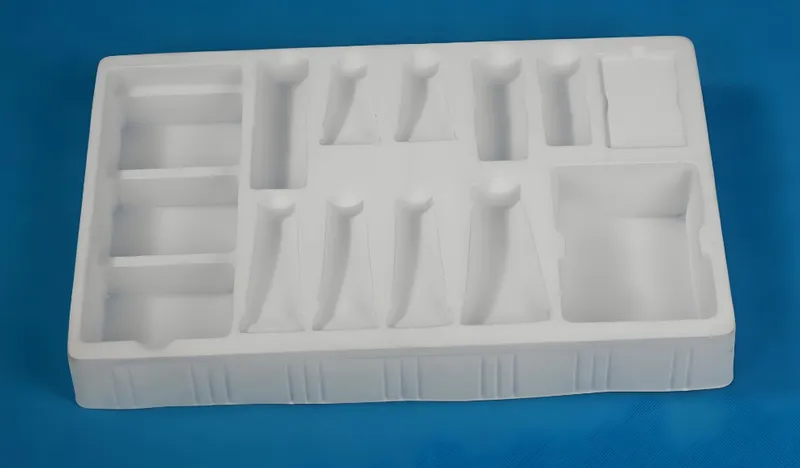

Paramètres du processus
- Temps de chauffage: Varies based on material thickness and type.
- Pression du vide: Typically around 27" of mercury for optimal forming.
- Temps de refroidissement: Must be sufficient to prevent warping or deformation.
Vacuum forming requires expensive molds.Faux
Molds can be made from low-cost materials like wood for prototyping, making it affordable for small runs.
What Materials Are Used in Vacuum Forming?
Choosing the right material is essential for successful vacuum forming. Here's a look at common materials and their properties:
| Matériau | Propriétés | Applications courantes |
|---|---|---|
| HIPS7 | Rentable, facile à former | Packaging trays, displays |
| ABS8 | Durable, résistant aux chocs | Pièces automobiles, boîtiers |
| PETG9 | Transparent, food-safe | Medical trays, packaging |
| PC | High strength, heat-resistant | Aerospace, safety equipment |
Considérations matérielles
- Épaisseur: Thicker sheets require longer heating times and may limit detail.

-
Rétrécissement: Some materials shrink more than others, affecting final dimensions.
-
Finition: Materials like acrylic offer a glossy finish, while others may need post-processing.
All thermoplastics can be used in vacuum forming.Faux
Only thermoplastics that become pliable when heated are suitable; thermosets cannot be reformed once set.
What Are the Applications of Vacuum Forming?
Vacuum forming is used across various industries due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness. Here are some typical applications:

1. Packaging
- Blister packs, clamshells, and trays for food, electronics, and medical devices.
- Lightweight and customizable for branding.
2. Automotive
- Interior panels, dashboards, and trim pieces.
- Ideal for prototyping and small production runs.

3. Medical
- Equipment enclosures, trays, and protective covers.
- Sterilizable materials like PETG are often used.
4. Consumer Goods
- Point-of-sale displays, toys, and cosmetic packaging.
- Allows for creative designs at a low cost.
Vacuum forming is only suitable for disposable products.Faux
Durable materials like ABS and PC make vacuum-formed parts suitable for long-term use in industries like automotive and medical.
How Does Vacuum Forming Compare to Other Technologies?
Understanding how vacuum forming stacks up against alternatives can help you make informed decisions.

Formage sous vide et moulage par injection
-
Coût de l'outillage: Vacuum forming has lower tooling costs, especially for small runs.
-
Vitesse de production: Injection molding is faster for high volumes but slower for setup.
-
Détail: Injection molding can achieve finer details and tighter tolerances.
Formage sous vide et formage sous pression
- Détail: Pressure forming offers better detail and sharper edges.
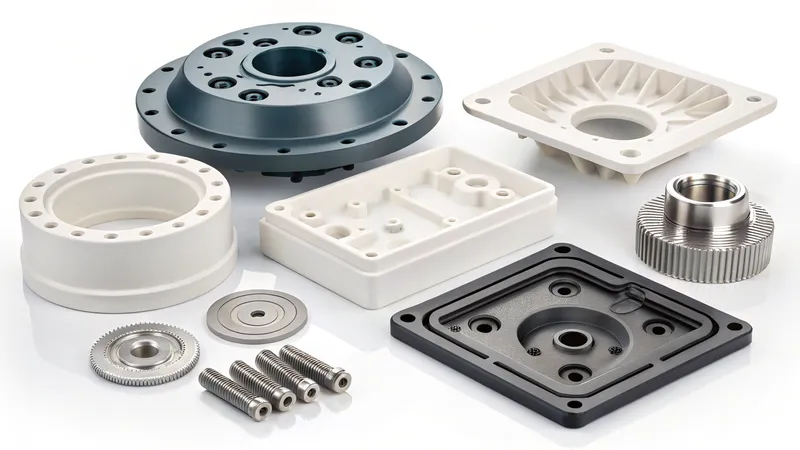

-
Coût: Vacuum forming is generally cheaper and faster.
-
Applications10: Pressure forming11 is used for high-end packaging and displays.
| Aspect | Formage sous vide | Moulage par injection | Formage sous pression |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coût de l'outillage | Faible | Haut | Moyen |
| Volume de production | Faible à moyen | Haut | Faible à moyen |
| Detail Level | Modéré | Haut | Haut |
Le formage sous vide est toujours moins cher que le moulage par injection.Faux
For very high volumes, injection molding may be more cost-effective due to faster cycle times.
What Are the Key Design Considerations for Vacuum Forming?
Designing for vacuum forming requires attention to specific details to ensure success. Here's a checklist to guide you:
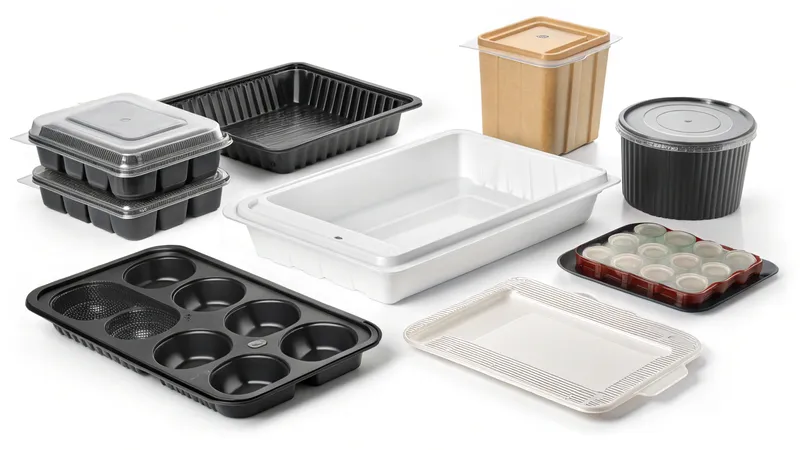

Liste de contrôle pour la conception
-
Angles d'ébauche: Use at least 3° for male molds and 5° for female molds to ease part removal.
-
Corner Radii: Rounded corners prevent thinning and improve mold release.
-
Taux de tirage: Keep the depth-to-width ratio low to avoid excessive thinning.
-
Vent Holes: Place in deep cavities to ensure complete forming.
-
Sous-coupes: Avoid or minimize to reduce mold complexity and cost.
Process Selection Tips
- Choose Vacuum Forming If:

- You need low to medium volumes (250–3000 units/year).
- Your design is relatively simple.
- You require fast turnaround for prototyping.
- Consider Alternatives If:
- You need high volumes or intricate details.
- Your part requires uniform wall thickness.
Le formage sous vide permet d'atteindre le même niveau de détail que le moulage par injection.Faux
While vacuum forming can produce detailed parts, it cannot match the precision of injection molding for complex geometries.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Vacuum Forming?
Like any manufacturing process, vacuum forming has its strengths and limitations.

Avantages
-
Faibles coûts d'outillage: Molds can be made from inexpensive materials like wood or resin.
-
Fast Prototyping: Quick setup and production make it ideal for testing designs.
-
Capacité de production de grandes pièces: Can produce parts up to several feet in size.
-
Variété de matériaux: Works with a wide range of thermoplastics.

Inconvénients
-
Limited Detail: Struggles with sharp corners and fine features.
-
Variation de l'épaisseur: Material thins in deeper areas, affecting strength.
-
Finishing Required: Parts often need trimming and post-processing.
Vacuum forming is environmentally friendly.Vrai
It produces less waste than other processes and uses recyclable materials, making it a sustainable choice.
Conclusion
Plastic vacuum forming is a powerful tool for creating custom parts quickly and affordably. Whether you're designing packaging, automotive components, or consumer products, understanding the process can help you make informed decisions. By considering material selection, design constraints, and production needs, you can leverage vacuum forming to bring your ideas to life efficiently.
-
Discover insights on cost-effective manufacturing processes that can enhance your production efficiency and reduce costs. ↩
-
Explore this link to gain a deeper understanding of vacuum forming, its applications, and benefits in various industries. ↩
-
Learn about the techniques used to create custom shapes in manufacturing, which can inspire your design projects. ↩
-
Explore this resource to understand the versatility and applications of plastic vacuum forming in various industries. ↩
-
Learn about the various thermoforming processes and how they differ, enhancing your knowledge of plastic manufacturing techniques. ↩
-
Discover the types of thermoplastics and their properties, crucial for understanding material selection in manufacturing. ↩
-
Explore the unique properties of HIPS to understand its advantages in vacuum forming applications. ↩
-
Learn about ABS's durability and impact resistance, making it ideal for various applications in vacuum forming. ↩
-
Discover why PETG is favored for its transparency and food safety, especially in medical packaging. ↩
-
Discover the various industries and uses for Pressure and Vacuum forming techniques. ↩
-
Explore the advantages of Pressure forming for high-quality production and design. ↩









