Choosing the right manufacturing process for plastic products1 is a pivotal decision that affects cost, production efficiency, and product quality. Two popular methods, thermoforming and injection molding, often come into consideration. But can thermoformage2 serve as a viable alternative to injection molding? This article provides an in-depth analysis, exploring definitions, applications, pros and cons, workflows, material compatibility, design considerations, and related technologies to help you decide.
Thermoforming shapes heated plastic sheets over molds using vacuum or pressure, while moulage par injection3 injects molten plastic into molds under high pressure for precise, high-volume production.
Both processes have unique strengths, and understanding them is key to making an informed choice. Let’s dive into the details.
Le thermoformage est toujours moins cher que le moulage par injection.Faux
Thermoforming often has lower tooling costs, but injection molding can be more cost-effective for high-volume production due to faster cycle times.
Injection molding is only suitable for small parts.Faux
Injection molding can produce both small and large parts, though it excels in high-precision, complex designs.
- 1. What Are Thermoforming and Injection Molding?
- 2. When Should You Use Thermoforming Instead of Injection Molding?
- 3. What Are the Pros and Cons of Thermoforming vs. Injection Molding?
- 4. How Do Thermoforming and Injection Molding Processes Work?
- 5. What Materials Are Compatible with Thermoforming and Injection Molding?
- 6. What Design Considerations Apply to Thermoforming?
- 7. How Do You Decide Between Thermoforming and Injection Molding?
- 8. What Related Technologies Complement These Processes?
- 9. Conclusion
What Are Thermoforming and Injection Molding?
To evaluate whether thermoforming can replace injection molding, we first need to define each process clearly.

Thermoforming heats a plastic sheet and forms it over a mold using vacuum or pressure, while injection molding melts plastic pellets and injects them into a mold under high pressure.
| Processus | Définition | Common Aliases |
|---|---|---|
| Thermoformage | Heating a plastic sheet and shaping it over a mold using vacuum or pressure. | Vacuum forming, pressure forming |
| Moulage par injection | Fusion granulés de plastique4 and injecting them into a mold under high pressure. | Plastic injection molding |
Thermoformage
Thermoforming begins with a flat thermoplastic sheet, which is heated until pliable. The sheet is then stretched over a single-sided mold, and vacuum suction or air pressure shapes it into the desired form. Once cooled, the part is trimmed and finished. This method is widely used for large, thin-walled items like packaging trays, automotive panels, and medical device housings.
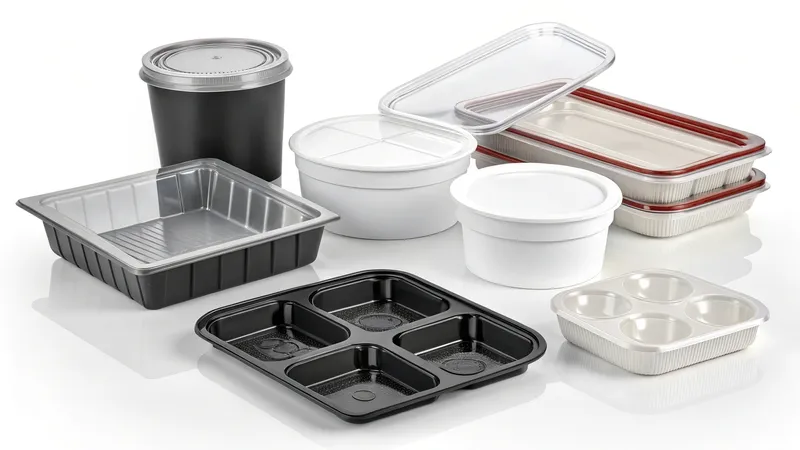

Moulage par injection
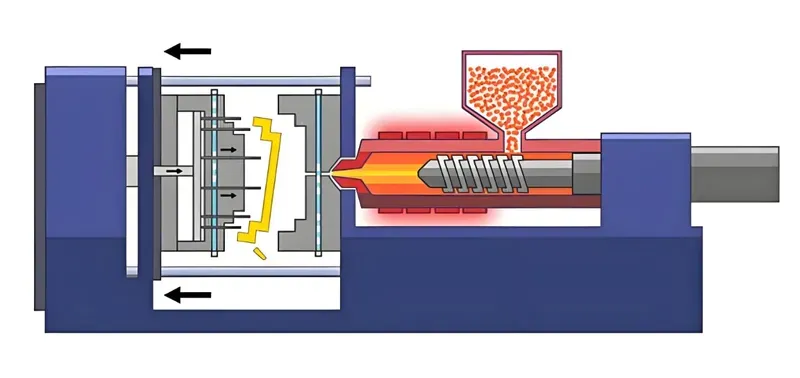
Injection molding involves feeding plastic pellets into a heated barrel, where they melt into a viscous liquid. This molten plastic is then injected into a double-sided mold under high pressure. After cooling, the mold opens, and the solidified part is ejected. It’s ideal for producing intricate, high-precision components such as gears, bottle caps, and electronic enclosures, especially in large quantities.
Thermoforming is primarily used for large parts.Vrai
Thermoforming excels at producing large, thin-walled parts due to its ability to handle sheets up to 10’ x 18’.
Injection molding cannot produce large parts.Faux
While less common for very large parts, injection molding can handle sizable components, though at higher tooling costs.
When Should You Use Thermoforming Instead of Injection Molding?
The suitability of thermoforming as an alternative to injection molding depends on your project’s specific needs, such as volume de production5, part size, and design complexity.

Thermoforming is ideal for large parts, small to medium production runs (250–5,000 parts), and rapid prototyping, while injection molding shines in high-volume, complex, small-part production.
| Facteur | Thermoformage | Moulage par injection |
|---|---|---|
| Volume de production | Best for 250–5,000 parts annually | Best for 3,000+ parts annually |
| Taille de la pièce | Suited for large parts (up to 10’ x 18’) | Best for small to medium parts |
| Complexité de la conception | Handles simple geometries with larger tolerances | Excels at complex designs with tight tolerances |
| Coût de l'outillage | Lower (aluminum or composite molds) | Higher (steel molds) |
| Délai d'exécution | Shorter (0–8 weeks for tooling) | Longer (12–16 weeks for tooling) |
Scénarios d'application
-
Thermoformage:
-
Large items like refrigerator liners, bathtubs, and signage.
-
Small to medium runs (250–5,000 parts annually).
-
Quick prototyping due to faster tooling development.
-

-
Moulage par injection:
-
Small, detailed parts like connectors, toys, and medical devices.
-
High-volume production (3,000+ parts annually) with rapid cycle times.
-
Applications needing precise, intricate designs.
-
Thermoforming is faster for prototyping than injection molding.Vrai
Thermoforming’s simpler tooling process allows for quicker setup and prototyping.
Injection molding cannot handle large parts.Faux
Injection molding can produce large parts, though it’s less cost-effective than thermoforming for very large items.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Thermoforming vs. Injection Molding?
A side-by-side comparison of advantages and limitations reveals when thermoforming can substitute for injection molding.

Thermoforming offers lower tooling costs and faster lead times but lacks in design complexity, while injection molding provides precision and scalability at a higher initial investment.
| Aspect | Thermoformage | Moulage par injection |
|---|---|---|
| Coûts d'outillage6 | Lower (aluminum or composite molds) | Higher (steel molds) |
| Délai d'exécution | Shorter (0–8 weeks) | Longer (12–16 weeks) |
| Volume de production | Cost-effective for 250–5,000 parts | Cost-effective for 3,000+ parts |
| Géométrie des pièces | Suited for large, simple designs with uniform thickness | Ideal for complex, detailed parts with variable thickness |
| Déchets matériels | Higher waste (recyclable) | Minimal waste per part |
| Précision | Larger tolerances (±0.020 inches) | Tight tolerances (±0.005 inches) |
Les pros du thermoformage
- Cost-Effective Tooling: Uses affordable aluminum or composite molds.

-
Vitesse: Faster tooling lead times make it great for quick turnarounds.
-
Large Parts: Easily handles oversized components.
Thermoformage Cons
-
Limited Complexity: Struggles with intricate details or variable thicknesses.
-
Déchets: Produces more scrap material, though it’s recyclable.
-
Lower Precision: Less suited for parts requiring tight tolerances.
Les pros du moulage par injection
-
High Precision: Achieves tight tolerances for detailed designs.
-
Efficiency at Scale: Lower per-part costs in high volumes.
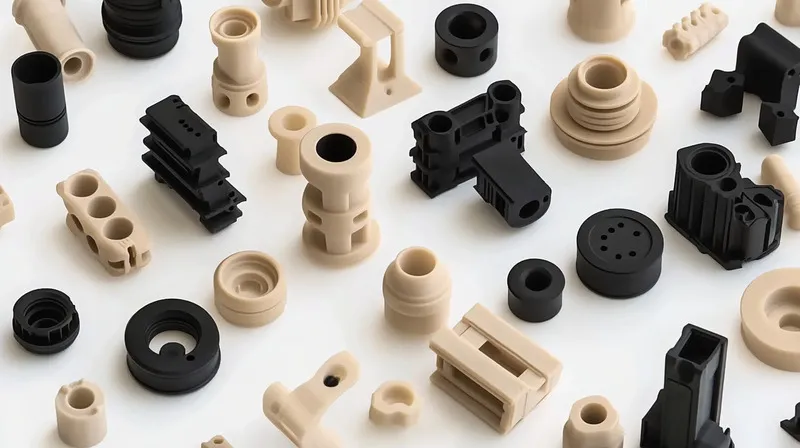

- Material Savings: Minimal waste during production.
Moulage par injection - Conséquences
-
High Upfront Costs: Expensive steel molds increase initial investment.
-
Longer Lead Times: Tooling takes longer to produce.
-
Size Constraints: Less practical for very large parts.
Thermoforming is always better for large parts.Vrai
For very large parts, thermoforming is typically more practical and cost-effective.
Injection molding is never used for prototyping.Faux
Injection molding can be used for prototyping, especially for high-volume products, though it’s less common.
How Do Thermoforming and Injection Molding Processes Work?
Understanding the workflows of each method highlights their operational differences.
Thermoforming heats a plastic sheet and forms it over a mold, while injection molding melts plastic pellets and injects them into a mold under high pressure.

Thermoforming Workflow
-
Chauffage: A thermoplastic sheet is heated until pliable.
-
Formation: The sheet is stretched over a mold using vacuum or pressure.

-
Refroidissement: The part cools to retain its shape.
-
Parage: Excess material is removed, and finishing is applied.
Key factors include heating temperature, vacuum strength, and cooling duration7, which depend on the material and design.
Processus de moulage par injection
-
Fusion: Plastic pellets are melted in a barrel.
-
Injection: Molten plastic is injected into a mold under high pressure.
-
Refroidissement: The mold cools to solidify the part.
-
Ejection: The finished part is ejected from the mold.
Critical parameters include injection pressure, mold temperature, and cooling time, adjusted for material and part requirements.
Thermoforming requires less energy than injection molding.Faux
Injection molding often demands more energy due to high pressures and temperatures.
Both processes can use the same types of plastics.Vrai
Both can utilize thermoplastics like ABS and PP, though in different forms (sheets vs. pellets).
What Materials Are Compatible with Thermoforming and Injection Molding?
Material choice significantly impacts the feasibility of each process.
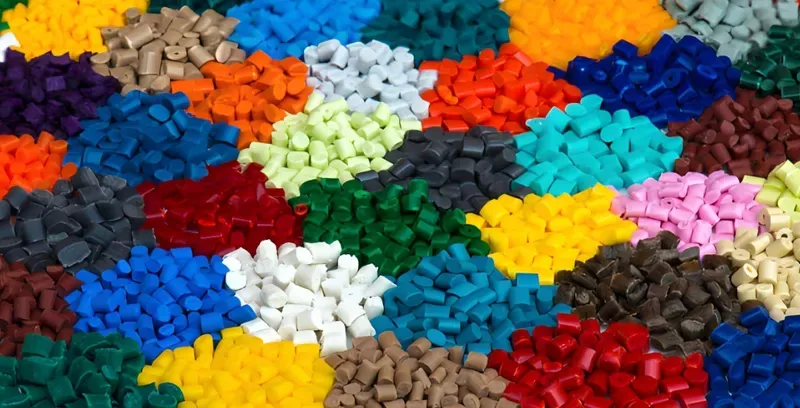

Thermoforming uses feuilles thermoplastiques8 like PET, PVC, and ABS, while injection molding uses pellets of thermoplastics and thermosets like ABS, PC, and PE.
| Processus | Matériaux communs | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Thermoformage | PET, PVC, ABS, PP, PS (sheets) | Affects formability and strength |
| Moulage par injection | ABS, PC, PE, PP, PS (pellets) | Includes plastiques techniques9 |
Matériaux de thermoformage
-
PET: Excellent for clear packaging.
-
PVC: Offers chemical resistance.
-
ABS: Strong and impact-resistant.
-
PP: Flexible and durable.
-
PS: Cost-effective for simple shapes.

Matériaux de moulage par injection
-
ABS: Tough and versatile.
-
PC: High strength and transparency.
-
PE: Flexible and resilient.
-
PP: Chemically resistant and versatile.
-
PS: Rigid and easy to mold.
Thermoforming can use the same materials as injection molding.Vrai
Both processes handle similar thermoplastics, though in sheet vs. pellet form.
Thermosetting plastics are commonly used in thermoforming.Faux
Thermoforming uses thermoplastics, while injection molding can also process thermosets.
What Design Considerations Apply to Thermoforming?
Switching to thermoforming requires adapting to its design constraints.
Thermoforming demands épaisseur uniforme de la paroi10, angles de dépouille11, and planning for trimming as key design considerations.
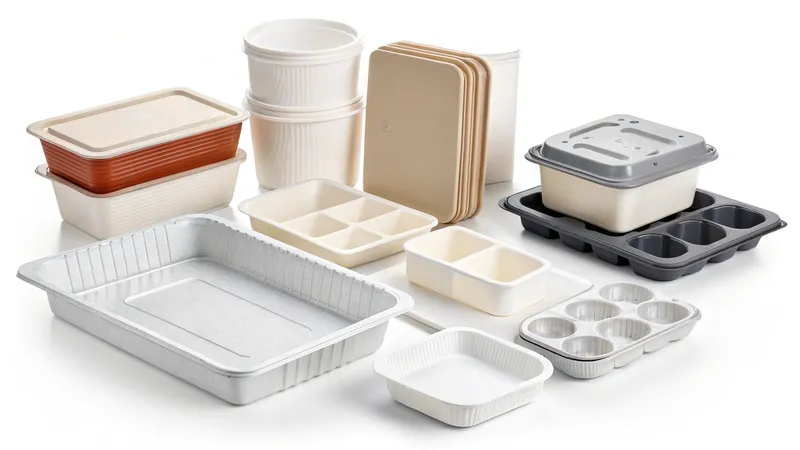

Thermoforming Design Checklist
-
Épaisseur uniforme de la paroi: Maintain consistency to prevent thinning.
-
Angles d'ébauche: Use 1–5 degrees for easy mold release.
-
Taille de la pièce: Ensure compatibility with equipment (up to 10’ x 18’).
-
Opérations secondaires: Account for trimming and finishing needs.
Thermoforming allows for variable wall thickness.Faux
Uniform thickness is critical to avoid defects in thermoforming.
Les angles de dépouille ne sont pas nécessaires pour le thermoformage.Faux
Draft angles facilitate part removal from the mold.
How Do You Decide Between Thermoforming and Injection Molding?
A systematic approach can guide your choice between these processes.
Opt for thermoforming for large parts, small to medium runs, and prototyping; choose injection molding for high-volume, complex, small-part production.

Cadre décisionnel
-
Volume de production:
-
250–5,000 parts: Thermoforming.
-
3,000+ parts: Injection molding.
-
-
Taille de la pièce:
-
Large (>10’ x 18’): Thermoforming.
-
Small to medium: Injection molding.
-
-
Complexité de la conception:
-
Simple, larger tolerances: Thermoforming.
-
Complex, tight tolerances: Injection molding.
-
-
Coût:
-
Low volume (<5,000): Thermoforming is cheaper.
-
High volume: Injection molding reduces per-part cost.
-
Thermoforming is always best for low-volume production.Faux
For very low volumes, alternatives like 3D printing may be more economical.
Injection molding is never suitable for large parts.Faux
It can produce large parts, though less Ladder-efficiently than thermoforming.
What Related Technologies Complement These Processes?
Exploring related technologies provides context for integrating thermoforming or injection molding into your workflow.
Key related technologies include extrusion de feuilles12 for thermoforming and mold making for injection molding, alongside finishing processes13.

-
En amont:
-
Sheet extrusion (thermoforming).
-
Pellet production (injection molding).
-
-
En aval:
-
Assembly (e.g., attaching fittings).
-
Finishing (e.g., painting).
-
-
Alternatives:
-
Blow molding (hollow parts).
-
Rotational molding (large hollow items).
-
Thermoforming and injection molding are the only plastic manufacturing methods.Faux
Alternatives like blow molding and compression molding serve specific needs.
Conclusion
Thermoforming can indeed replace injection molding for plastic products in certain scenarios, particularly for large parts, small to medium production runs (250–5,000 parts), and prototypage rapide14. Its lower tooling costs and faster lead times make it attractive, though it falls short in design complexity and precision compared to injection molding. Injection molding, with its scalability and accuracy, is better suited for high-volume, intricate parts. Your choice hinges on balancing production goals, design needs, and budget.
-
Discover essential factors that influence the choice of manufacturing processes, ensuring optimal production outcomes. ↩
-
Explore the benefits of thermoforming to understand how it can be a cost-effective and efficient alternative to injection molding. ↩
-
Learn about injection molding's unique features and advantages compared to other methods, enhancing your decision-making process. ↩
-
Discover the role of plastic pellets in manufacturing to understand their significance in processes like Injection Molding. ↩
-
Understanding production volume can help you choose the right manufacturing method for your project, ensuring efficiency and cost-effectiveness. ↩
-
Learn about the cost implications of tooling in both processes to better budget your manufacturing projects. ↩
-
Learn about the critical factors influencing cooling duration and how they impact the quality of plastic products. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand the various applications and benefits of thermoplastic sheets in manufacturing processes. ↩
-
Learn about engineering plastics, their properties, and how they are utilized in various industries for enhanced performance. ↩
-
Understanding uniform wall thickness is crucial for ensuring product quality and preventing defects in thermoforming processes. ↩
-
Exploring draft angles can help you optimize mold design for easier part release and better production efficiency. ↩
-
Understanding sheet extrusion is crucial for optimizing your thermoforming processes and improving product quality. ↩
-
Learning about finishing processes can enhance the final quality of your products and customer satisfaction. ↩
-
Discover the concept of rapid prototyping and its significance in modern manufacturing processes. ↩








