Plastic vacuum forming is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, particularly in India, where it has become a go-to process for producing everything from food packaging to automotive components. This technique, which involves heating a plastic sheet and using a vacuum to shape it over a mold, offers a unique combination of affordability, flexibility, and speed. Whether you're a manufacturer looking to optimize production or a designer seeking cost-effective prototyping solutions, understanding vacuum forming is essential.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll take you through the top 10 plastic vacuum forming factories in India1 factories in India, each recognized for their expertise and contributions to the industry. We'll also delve into the nuts and bolts of the procédé de formage sous vide2, from its basic principles to its technical intricacies, and provide practical tools to help you make informed decisions about when and how to use this technology.
Vacuum forming is only suitable for small-scale production.Faux
While it's often used for prototyping and small runs, vacuum forming can also be scaled for medium to large production volumes, especially with multi-station setups.
- 1. Top 10 Plastic Vacuum Forming Factories in India
- 2. What is Plastic Vacuum Forming?
- 3. What are the Typical Applications of Vacuum Forming?
- 4. What are the Pros and Cons of Vacuum Forming Compared to Other Technologies?
- 5. Quelles sont les étapes du processus de formage sous vide ?
- 6. What Materials are Commonly Used in Vacuum Forming?
- 7. How to Design for Vacuum Forming?
- 8. When Should You Choose Vacuum Forming?
- 9. What are the Related Technologies to Vacuum Forming?
- 10. Conclusion
Top 10 Plastic Vacuum Forming Factories in India
Based on a 2022 ranking by The Industry Outlook, here are the leading plastic vacuum forming (thermoforming) manufacturers in India, known for their market presence, innovation, and industry impact:
| Company Name | Location | Description | Website |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oracle Group (Oracle Polyplast) | Thane, Maharashtra | Specializes in food packaging3 with a global network. | oraclepolyplast.in |
| Acros | Mumbai, Maharashtra | Known for polycarbonate roofing and large thermoforming capabilities. | acros.com |
| AVI Global Plast | Ahmedabad, Gujarat | Focuses on rigid packaging for food, medical, and industrial sectors. | avigloplast.com |
| DM Thermoformer | Chennai, Tamil Nadu | Offers cost-effective solutions for rigid packaging. | - |
| Genesis PacAssist | Ahmedabad, Gujarat | Serves agriculture, automotive, and food packaging industries. | - |
| Indu Thermoformers | Ahmedabad, Gujarat | Provides thermoformed products for various industries. | - |
| J V Packs | Pune, Maharashtra | Innovates in plastic packaging materials. | jvpack.com |
| Machinecraft Thermoforming | Mumbai, Maharashtra | Offers comprehensive thermoforming solutions. | - |
| Therm O Pack | Chennai, Tamil Nadu | Known for vacuum-formed trays and automotive components. | - |
| USK Balaji Plast | Mumbai, Maharashtra | Specializes in medical packaging and thermoformed products. | - |
These companies are at the forefront of vacuum forming in India, each bringing unique strengths to the table, from innovative packaging solutions to advanced automotive components.
All top vacuum forming factories in India are located in Maharashtra.Faux
While Maharashtra hosts several leading factories, others are based in Gujarat and Tamil Nadu, reflecting the industry's geographic diversity.
What is Plastic Vacuum Forming?
Plastic vacuum forming, also known as vacuum thermoforming4, is a manufacturing process5 where a feuille thermoplastique6 is heated to a pliable state, stretched over a mold, and shaped using vacuum pressure. The core principle involves three main steps: heating the plastic sheet, applying a vacuum to form it over the mold, and cooling it to set the shape.

Core Principles:
-
Chauffage: The plastic must be heated to a specific temperature where it becomes flexible but not melted.
-
Application du vide: A vacuum removes air between the sheet and the mold, ensuring precise conformation.
-
Refroidissement: Rapid cooling sets the plastic in its new shape, preventing deformation.
Vacuum forming can be used with any type of plastic.Faux
Only thermoplastics that can be heated to a pliable state without degrading are suitable for vacuum forming. Thermosets are not compatible.
Classification of Vacuum Forming
-
Par processus:
- Single-Station Vacuum Forming: Manual or semi-automatic, ideal for low-volume production or prototyping.
- Multi-Station Vacuum Forming: Automated, used for high-volume production with faster cycle times.
-
Par matériel:
- Polystyrène à haut impact (HIPS): Cost-effective for packaging and signage.
- Acrylonitrile Butadiène Styrène (ABS): Durable for automotive and consumer goods.

- Chlorure de polyvinyle (PVC): Flexible for blister packs and medical use.
- Polyéthylène (PE): Weather-resistant for outdoor applications.
- Polypropylène (PP): Chemical-resistant for food packaging.
- Acrylique (PMMA): High clarity for displays and lighting.
- Par application:
- Emballage: Blister packs, trays, clamshells.
- Automobile: Dashboards, interior trim, light housings.
- Médical: Surgical trays, device packaging.
- Biens de consommation: Toys, electronics housings.
- Industrial: Machine guards, signage, custom fixtures.
Vacuum forming is primarily used for packaging.Faux
Although packaging is a major application, vacuum forming is also widely used in automotive, medical, and industrial sectors for a variety of products.
What are the Typical Applications of Vacuum Forming?
Vacuum forming's versatility makes it a preferred choice across multiple industries, offering cost-effective solutions7 for both small and large-scale production.
Vacuum forming is used in packaging, automotive, medical, and industrial sectors for its ability to produce lightweight, cost-effective parts with quick turnaround times8.

Emballage
Factories like Oracle Polyplast specialize in producing food packaging solutions such as PET containers, which are lightweight, durable, and ideal for protecting products during transit.
Automobile
Companies like Therm O Pack manufacture interior components like dashboards and trim parts, leveraging materials like ABS for their strength and impact resistance.

Médical
USK Balaji Plast focuses on medical packaging, ensuring products meet stringent sterility and protection standards required for surgical trays and device enclosures.
Biens de consommation
Vacuum forming is used to create protective cases for electronics, toys, and other consumer products, offering design flexibility and rapid prototyping capabilities.
Industrial
Large, lightweight parts9 like machine guards, signage, and custom fixtures are efficiently produced through vacuum forming, catering to various industrial needs.
Vacuum forming is only suitable for simple shapes.Faux
While it's ideal for simple to moderate geometries, vacuum forming can also handle complex shapes with undercuts when combined with techniques like pressure forming.
What are the Pros and Cons of Vacuum Forming Compared to Other Technologies?
Understanding the advantages and limitations of vacuum forming helps in deciding when it's the best manufacturing choice.
Vacuum forming offers lower tooling costs and faster setup than injection molding but is less precise and not suitable for high-volume production of complex parts.

Formage sous vide et moulage par injection
-
Pour:
- Lower tooling costs: Molds cost $1,000-$10,000 vs. $50,000+ for injection molding.
- Faster setup and prototyping: Ideal for small to medium runs (100-10,000 units).
- Suitable for large parts: Can produce parts up to several feet in size.
-
Cons:
- Less precision: Not ideal for tight tolerances.
- Limited to thinner walls: Typically 0.5mm to 10mm.
- May require secondary operations: Such as trimming or finishing.
Le formage sous vide est toujours moins cher que le moulage par injection.Faux
While vacuum forming has lower tooling costs, for very high production volumes, injection molding may be more cost-effective due to faster cycle times and less material waste.
Formage sous vide et moulage par soufflage
-
Pour:
- Better for complex shapes: Can handle undercuts and intricate designs.
- No parting lines: Results in smoother finishes.
-
Cons:
- Not suitable for hollow parts: Unlike blow molding.
- Higher material waste: Due to trimming excess plastic.
Quelles sont les étapes du processus de formage sous vide ?
The vacuum forming process is straightforward but requires precise control over key parameters to achieve high-quality results.
The vacuum forming process involves clamping, heating, forming, cooling, trimming, and finishing, with critical control over temperature and vacuum pressure.

1. Clamping
The plastic sheet is securely clamped in a frame to prevent movement during heating and forming.
2. Chauffage
The sheet is heated using infrared or radiant heaters to its forming temperature (e.g., 220-240°F for ABS).
3. Formation
The heated sheet is stretched over the mold, and a vacuum (10-20 inHg) is applied to pull it tightly against the mold.
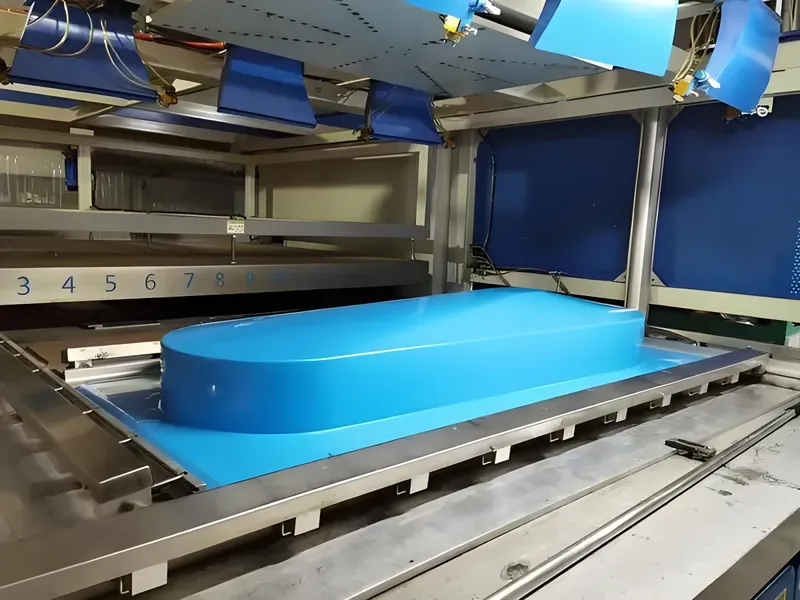
4. Refroidissement
The part is cooled using air blowers or water mist to set its shape.
5. Parage
Excess material is removed using cutting tools or CNC machines.
6. Finishing
Secondary operations like drilling, painting, or assembly are performed as needed.
Paramètres clés:
-
Température: Critical for material pliability.
-
Pression du vide: Ensures even forming.
-
Temps de refroidissement: Affects cycle time and part quality.
-
Material Thickness: Impacts strength and forming ease.
Vacuum forming can produce parts with consistent wall thickness.Faux
Wall thickness can vary, especially in deeper draws, requiring careful design and process control.
What Materials are Commonly Used in Vacuum Forming?
Material selection is crucial in vacuum forming, as it affects the process parameters and the final product's properties.

Common vacuum forming materials include HIPS, ABS, PVC, PE, PP, and acrylic, each offering unique properties for specific applications.
| Type de matériau | Température de formage | Applications | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| HIPS | 200-220°F | Emballage, signalétique | Rentable, facile à former |
| ABS | 220-240°F | Automobile, biens de consommation | Durable, high impact resistance |
| PVC | 180-200°F | Medical, blister packs | Flexible, résistant aux produits chimiques |
| PE | 200-220°F | Outdoor applications | Weather-resistant |
| PP | 220-240°F | Food packaging | Chemical-resistant |
| Acrylique (PMMA) | 260-300°F | Displays, lighting | High clarity, strong |
Material Impacts
- Température de formage: Higher temperatures increase energy costs and cycle times.

-
Rétrécissement: Materials like ABS shrink more (0.5-0.8%), requiring mold adjustments.
-
La force: Thicker sheets enhance durability but are harder to form.
All thermoplastics can be used in vacuum forming.Faux
Only thermoplastics that soften when heated and can be reshaped are suitable. Materials like thermosets cannot be reformed once cured.
How to Design for Vacuum Forming?
Designing for vacuum forming requires attention to specific guidelines to ensure successful part production.
Key design considerations for vacuum forming include draft angles, material thickness, and planning for trimming and finishing operations.
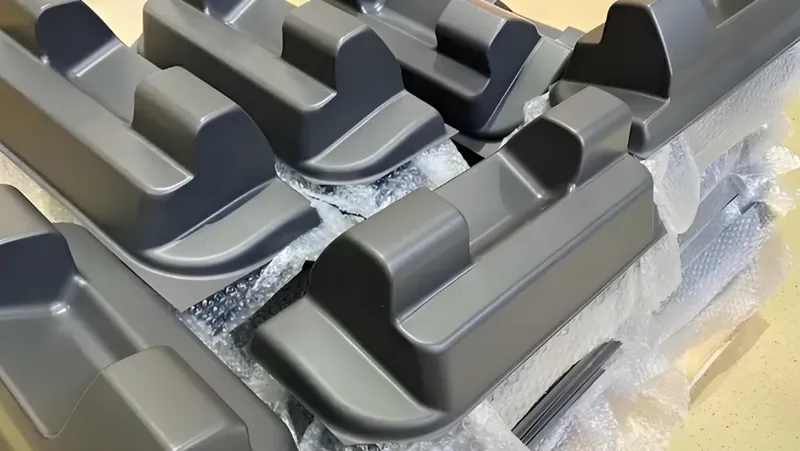

Liste de contrôle pour la conception
-
Include draft angles (min. 3°) for easy demolding.
-
Avoid deep draws without pre-stretching to prevent tearing.
-
Select material thickness based on strength needs (e.g., 1-3mm for packaging).
-
Plan for trimming and secondary operations like drilling or painting.
-
Verify material compatibility with application requirements (e.g., PET for food safety).
Le formage sous vide permet d'atteindre le même niveau de détail que le moulage par injection.Faux
While vacuum forming can produce detailed parts, it generally cannot match the precision and fine features of injection molding.
When Should You Choose Vacuum Forming?
Vacuum forming is ideal for specific scenarios, but it's important to know when other processes might be more suitable.
Choose vacuum forming for low to medium production volumes, large parts, or when tooling costs need to be minimized.

Processus Sélection Prise de décision
-
Step 1: Is your production volume less than 10,000 units? → If yes, consider vacuum forming.
-
Step 2: Are your parts large (over 12 inches) or have simple to moderate geometries? → If yes, vacuum forming is suitable.
-
Step 3: Is your tooling budget under $10,000? → If yes, vacuum forming offers cost advantages.
-
Step 4: Do you need hollow parts? → If yes, explore blow molding instead.
Vacuum forming is the best choice for high-volume production.Faux
For very high volumes, injection molding is often more efficient due to faster cycle times and lower per-part costs.
What are the Related Technologies to Vacuum Forming?
Understanding related technologies helps in seeing where vacuum forming fits within the broader manufacturing landscape.
Related technologies include plastic sheet extrusion, mold making, pressure forming, and rotational molding, each serving complementary roles.

-
Technologies en amont:
- Extrusion de feuilles de plastique: Produces raw thermoplastic sheets.
- Mold Making: Creates molds via CNC machining or 3D printing.
-
Technologies en aval:
- Parage et finition: Includes CNC cutting and painting.
- Assemblée: Integrates parts into larger products.
-
Processus connexes:
- Formage sous pression: Uses air pressure for sharper details.
- Formage de feuilles jumelées: Bonds two sheets for hollow parts.
- Moulage par rotation: Produces large, hollow plastic parts.
Conclusion
Plastic vacuum forming is a vital manufacturing process in India, supported by top factories like Oracle Polyplast, Acros, and AVI Global Plast. By understanding its applications, technical aspects, and decision-making criteria, you can leverage this technology effectively for your projects. Whether you're producing packaging solutions, automotive components, or custom industrial parts, vacuum forming offers a cost-effective and efficient path to bringing your designs to life.
-
Explore the advantages of plastic vacuum forming to understand its impact on manufacturing efficiency and cost-effectiveness. ↩
-
Learn about the vacuum forming process to grasp its technical intricacies and applications in various industries. ↩
-
Explore this link to discover innovative trends in food packaging that can enhance product appeal and sustainability. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand the intricacies of vacuum thermoforming, its applications, and benefits in manufacturing. ↩
-
Discover the various manufacturing processes, including vacuum forming, and how they impact production efficiency and product quality. ↩
-
Learn about the various applications of thermoplastic sheets in manufacturing processes, including their advantages and versatility. ↩
-
Exploring this resource will provide insights into how cost-effective solutions can enhance production efficiency and profitability. ↩
-
Discover why quick turnaround times are crucial for maintaining competitiveness and meeting market demands in manufacturing. ↩
-
This link will help you understand the advantages of lightweight parts in improving performance and reducing costs across sectors. ↩








