Thermoforming is a widely used manufacturing process that transforms plastic sheets into a variety of products, from packaging trays to automotive components. A common question arises: Can different colors be used in this process? The answer is a resounding yes—thermoforming supports a spectrum of colors, enhancing both the functionality and visual appeal of the final product. Let’s dive into how color is integrated into thermoforming, the materials involved, and the key considerations for achieving stunning, consistent results.
Thermoforming employs pre-colored plastic sheets1 to produce vibrant, uniform parts, offering design flexibility for industries like packaging, automotive, and signage where aesthetics and branding matter.
Whether you’re exploring thermoforming for a project or simply curious about the process, understanding how color plays a role can unlock new possibilities. Read on to learn about the materials, steps, applications, and practical tips for using color in thermoforming.
Different colors can be used in thermoforming.True
Materials like ABS and PET are available in various colors, and custom coloring is possible through pre-colored sheets or post-processing.
Color choice affects the thermoforming process itself.False
Color is typically embedded in the plastic sheet before forming and does not significantly alter the process, though some pigments may subtly influence material behavior.
- 1. What Are the Common Materials Used in Thermoforming?
- 2. What Are the Steps in the Thermoforming Process?
- 3. What Are the Considerations When Using Colored Materials in Thermoforming?
- 4. What Are the Applications of Colored Thermoformed Products?
- 5. What Factors Affect Color Consistency in Thermoforming?
- 6. Practical Tips for Using Colored Materials in Thermoforming
- 7. Conclusion
What Are the Common Materials Used in Thermoforming?
Thermoforming relies on thermoplastic materials2 that can be heated and reshaped repeatedly. Many of these materials come in a variety of colors or can be custom-colored, making them ideal for applications where appearance is as important as performance.

Common thermoforming materials include ABS, PET, HDPE, HIPS, acrylic, TPO, and vinyl, offering a range of color options for diverse industries3 like packaging, automotive, and consumer goods.
| Material Type | Color Availability | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| ABS4 | Wide range, custom colors | Great for automotive parts |
| PET5 | Clear, tinted, or colored | Popular in packaging |
| HDPE | Limited, mostly opaque | Used in industrial applications |
| HIPS6 | Wide range | Cost-effective for signage |
| Acrylic (PMMA) | Clear, colored, or frosted | Known for optical clarity |
| TPO | Custom colors possible | Durable for automotive use |
| Vinyl | Wide range, flexible | Common in medical packaging |
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
ABS is a standout in thermoforming7 due to its strength and versatility. Available in a wide array of colors, ABS can also be custom-colored to meet specific design needs. This makes it a favorite for automotive interiors and consumer electronics where precise color matching enhances branding.
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
PET shines in packaging, thanks to its clarity and recyclability8. While often used clear, it can be tinted or colored to align with brand identities—think vibrant trays for premium food products that catch the eye on store shelves.

High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
HDPE offers durability and chemical resistance9, commonly seen in industrial products like storage bins. Its color options are more limited, typically opaque shades, but it still serves functional roles where aesthetics matter less.
High-Impact Polystyrene (HIPS)
HIPS is a budget-friendly option frequently used in signage and displays. With a broad color palette, it’s perfect for creating eye-catching visuals without breaking the bank.
ABS is the most commonly used material in thermoforming.False
While ABS is popular, PET and HIPS are also widely used, especially in packaging and signage, due to their specific advantages.
All thermoforming materials can be custom-colored.False
Materials like HDPE have fewer color options due to their composition, limiting customization compared to ABS or HIPS.
What Are the Steps in the Thermoforming Process?
Thermoforming involves heating a plastic sheet and molding it into shape, with color typically introduced via pre-colored sheets. This ensures uniformity without complicating the process.
The thermoforming process includes material selection, sheet preparation, heating, forming, cooling, trimming, and finishing, with color integrated into the plastic sheet from the start.

Material Selection
Choosing the right thermoplastic sets the stage for both performance and color. Materials like ABS offer extensive color choices, while others like HDPE may have constraints.
Sheet Preparation
The pre-colored plastic sheet is cut to size and prepped. Using pre-colored sheets guarantees consistent color throughout the part, eliminating the need for additional coloring steps.
Heating
The sheet is heated to its forming temperature in an oven. Color generally doesn’t affect this step, though darker pigments might absorb heat slightly faster.
Forming
The softened sheet is shaped over a mold using vacuum or pressure. The embedded color remains stable, ensuring the final product matches the intended design.
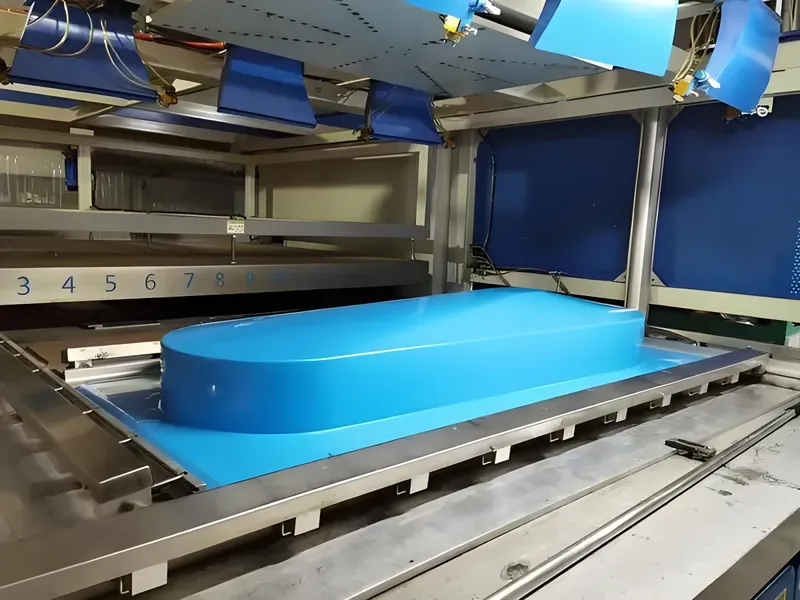
Cooling
The part cools to solidify its shape. Colored materials perform similarly to uncolored ones here, maintaining their hue.
Trimming
Excess material is removed, often with dies or CNC tools. The uniform color ensures trimmed edges blend seamlessly with the rest of the part.
Finishing
Some parts may get extra touches like painting or printing for logos, but pre-colored sheets typically deliver the final look straight from the mold.
Color is applied after the thermoforming process.False
Color is usually part of the plastic sheet before forming, ensuring uniformity without post-processing.
The thermoforming process can alter the color of the plastic.False
The color stays consistent during heating and forming, as it’s inherent to the material.
What Are the Considerations When Using Colored Materials in Thermoforming?
Using colored materials in thermoforming is straightforward, but a few factors can influence the outcome.
Key considerations for colored thermoforming include pigment stability10, material compatibility11, and minor processing adjustments12 to ensure quality and consistency.
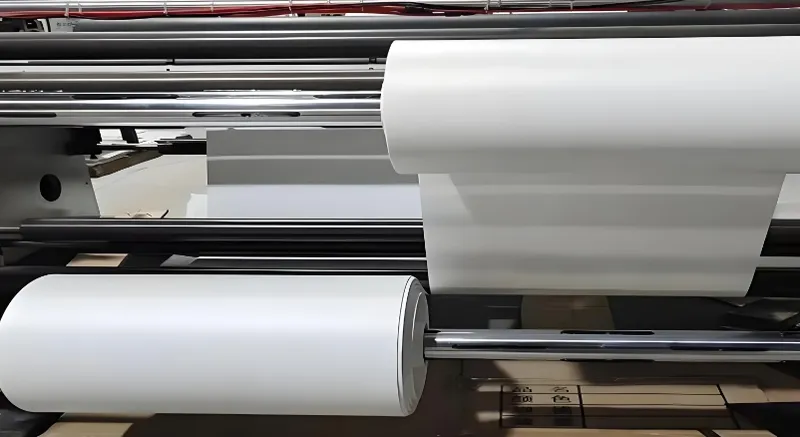

Pigment Stability
Some pigments may fade or shift at high temperatures if they’re not suited to the forming process. Selecting heat-stable pigments is critical for maintaining the desired color.
Material Compatibility
Not all plastics take to coloring equally. PET might need specific dyes for bright hues, while ABS accepts a broader range of pigments with ease.

Processing Adjustments
Darker colors can absorb heat faster, potentially requiring slight tweaks to heating times. These changes are minor and easily managed with proper oversight.
Cost Considerations
Custom colors can increase material costs, especially for small runs. Balancing aesthetics with budget is key for cost-sensitive projects.
Colored materials require significant changes to the thermoforming process.False
The process remains largely unchanged, with only minor adjustments needed for some colored materials.
All pigments are stable at thermoforming temperatures.False
Certain pigments may degrade if temperatures exceed their stability range, requiring careful selection.
What Are the Applications of Colored Thermoformed Products?
Colored thermoformed products are everywhere, serving both practical and aesthetic purposes across multiple sectors.
Colored thermoformed products enhance packaging, automotive, signage, and consumer goods, where color boosts branding, visibility, and appeal.
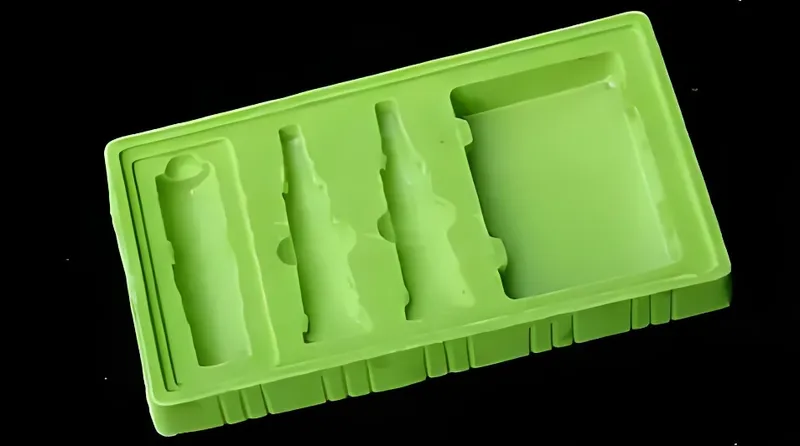

Packaging
In packaging, color differentiates products and reinforces branding. Colored PET trays, for instance, make food items pop on shelves, signaling quality or freshness.
Automotive
Automotive parts like dashboards or panels often use colored ABS or TPO to match vehicle interiors, blending style with durability.

Signage and Displays
HIPS shines in signage, where bold colors grab attention for retail displays or promotional signs, all at a low cost.
Consumer Goods
From toy casings to electronics housings, colored thermoformed parts combine functionality with eye-catching design.
Color is purely aesthetic in thermoformed products.False
Beyond aesthetics, color can indicate product type or improve visibility, adding functional value.
Thermoforming is the only process for colored plastic products.False
Injection molding and other methods also produce colored plastics, but thermoforming excels for large, flat parts.
What Factors Affect Color Consistency in Thermoforming?
Achieving uniform color in thermoformed parts requires attention to detail throughout the process.
Color consistency in thermoforming depends on material batch quality, pigment dispersion, and process control during heating and forming.

Material Batch Quality
Using sheets from the same batch prevents color variations across a production run, ensuring a cohesive look.
Pigment Dispersion
Even pigment distribution in the sheet avoids streaks or uneven hues, critical for high-quality finishes.
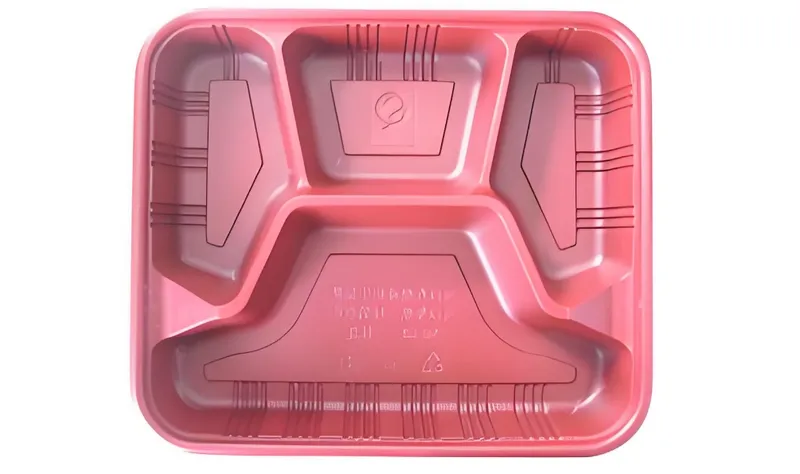

Process Control
Consistent heating and forming conditions keep colors stable, preventing shifts from overheating or uneven cooling.
Mold Design
Stretching during forming can thin the material, lightening the color in some areas. Good mold design minimizes this effect.
Color consistency is guaranteed in thermoforming.False
It’s achievable but requires careful material and process management to prevent variations.
Mold design has no impact on color in thermoformed parts.False
Stretching can alter perceived color, so mold design plays a role in uniformity.
Practical Tips for Using Colored Materials in Thermoforming
Ready to add color to your thermoforming project? Here are some actionable tips to ensure success.
For optimal results with colored thermoforming, use quality pre-colored sheets, test small batches, and monitor process parameters closely.

Choose Quality Materials
Source pre-colored sheets from trusted suppliers for reliable color and performance.
Test Before Scaling
Run small batches to confirm color stability and process fit before full production.
Adjust for Heat Absorption
Darker colors may need shorter heating times—fine-tune settings to avoid overprocessing.

Select Stable Pigments
Work with suppliers to pick pigments that withstand forming temperatures without degrading.
Match Batches
For critical color matching, use material from a single batch to avoid subtle differences.
Pre-colored sheets are the only way to achieve color in thermoforming.False
Post-processing like painting can add color, but pre-colored sheets are most efficient.
Testing is unnecessary for experienced manufacturers.False
Even pros should test new colors or materials to ensure they meet expectations.
Conclusion
Thermoforming opens the door to a colorful world of plastic products, blending practicality with creativity. By leveraging pre-colored sheets, manufacturers can craft vibrant, consistent parts for packaging, automotive, signage, and beyond—all without overhauling the process. Whether you’re aiming to boost brand appeal or simply explore design options, colored thermoforming offers a flexible, effective solution.
This blog post delivers a detailed, reader-friendly exploration of color in thermoforming, complete with practical insights and industry examples, all formatted to match the sample’s professional yet approachable style.
-
Discover how pre-colored plastic sheets enhance design flexibility and aesthetics in thermoforming applications. ↩
-
Learn about the advantages of thermoplastic materials in thermoforming, including their versatility and color options. ↩
-
Explore the various color options available in thermoforming and how they cater to different industry needs. ↩
-
Explore the advantages of ABS, including its strength and versatility, ideal for automotive and electronics applications. ↩
-
Discover the benefits of PET in packaging, including its clarity and recyclability, perfect for brand visibility. ↩
-
Learn why HIPS is cost-effective and widely used in signage, offering a broad color palette for impactful displays. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand the process of thermoforming and its significance in various industries, including automotive and consumer electronics. ↩
-
Learn about the benefits of recyclability in packaging, especially with materials like PET, and its impact on sustainability. ↩
-
Discover the importance of chemical resistance in materials like HDPE and how it impacts industrial applications. ↩
-
Understanding pigment stability is crucial for ensuring the longevity and vibrancy of colors in thermoformed products. Explore this link for in-depth insights. ↩
-
Material compatibility is key to achieving the best coloring results in thermoforming. Discover more about this essential factor. ↩
-
Processing adjustments can significantly impact the quality of colored thermoformed products. Learn more about these adjustments for optimal results. ↩








