Heavy gauge thermoforming is a manufacturing process that transforms thick plastic sheets into durable, lightweight components by heating and shaping them over molds. In passenger buses1, this technology is pivotal for crafting both interior and exterior parts that boost comfort, safety, and efficiency. From ceiling panels to seating elements, heavy gauge thermoforming delivers cost-effective, versatile solutions that meet the demands of modern bus manufacturing.
Heavy gauge thermoforming shapes thick plastic sheets into durable, lightweight parts for passenger buses, enhancing comfort, safety, and efficiency in interior and exterior applications.
This blog post dives into the applications, benefits, and technical details of heavy gauge thermoforming2 in passenger buses, offering insights for manufacturers and enthusiasts alike. Let’s explore how this process stands out in the mass transit industry.
Heavy gauge thermoforming reduces weight in passenger buses.True
By using lightweight plastics instead of heavier materials like metal, it contributes to overall weight reduction, improving fuel efficiency.
Heavy gauge thermoforming is only used for interior bus parts.False
While commonly used for interiors, it can also be applied to some exterior components for weather resistance and weight reduction.
- 1. What is Heavy Gauge Thermoforming?
- 2. What are the Applications of Heavy Gauge Thermoforming in Passenger Buses?
- 3. How Does Heavy Gauge Thermoforming Compare to Other Technologies?
- 4. What Materials are Used in Heavy Gauge Thermoforming for Buses?
- 5. What are the Design and Manufacturing Considerations for Heavy Gauge Thermoforming?
- 6. Conclusion
What is Heavy Gauge Thermoforming?
Heavy gauge thermoforming involves heating plastic sheets thicker than 0.06 inches (1.5 mm) until they’re pliable, then forming them over a mold using vacuum or pressure. This technique excels at producing large, sturdy parts with complex shapes, making it a go-to choice for industries like automotive and mass transit.
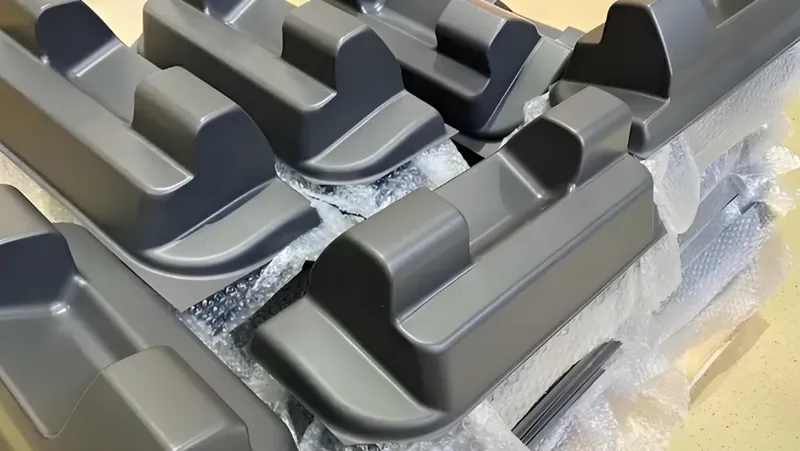

In passenger buses, it’s used to create components that balance strength and weight savings—think interior panels, seating parts, and even some exterior elements. Its appeal lies in its cost-effectiveness, rapid production, and ability to deliver smooth, visually appealing finishes.
How Does Heavy Gauge Thermoforming Work?
The process unfolds in a series of straightforward steps:
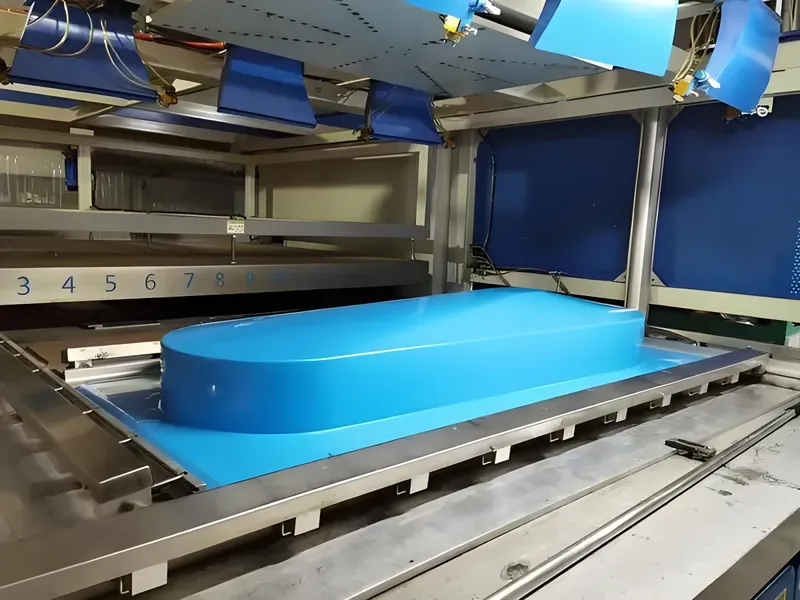
-
Material Selection: Pick a thermoplastic3 (e.g., ABS, HDPE, polycarbonate) tailored to the part’s needs.
-
Sheet Preparation: Cut the plastic sheet to fit the mold.
-
Heating: Warm the sheet until it’s flexible but not melted.
-
Forming: Shape the sheet over a mold using vacuum or pressure.
-
Cooling: Let the part cool to lock in its shape.
-
Trimming: Trim excess material for a finished edge.
-
Finishing: Add paint, texture, or assembly as required.
This streamlined process is fast and economical, especially for large parts, making it a perfect fit for bus manufacturing.
Heavy gauge thermoforming is more expensive than metal fabrication for bus parts.False
Actually, it is often more cost-effective due to lower material and production costs, especially for medium to low volume production.
What are the Applications of Heavy Gauge Thermoforming in Passenger Buses?
Heavy gauge thermoforming shines in passenger buses, producing a range of components that prioritize durability, weight savings, and design flexibility.

In passenger buses, heavy gauge thermoforming is used for interior panels4, seating components5, storage units, window surrounds, and some exterior parts, enhancing durability and reducing weight.
| Application | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Interior Paneling | Ceiling, wall, and floor panels | Durable, lightweight, aesthetically pleasing |
| Seating Components | Seat backs, armrests, and other parts | Strong, comfortable, impact-resistant |
| Storage Units | Luggage racks and compartments | Withstands heavy use, lightweight |
| Window Surrounds | Frames around windows | Impact-resistant, enhances safety |
| Exterior Parts | Some body parts or fascias | Weather-resistant, reduces weight |
Interior Paneling
Ceiling, wall, and floor panels in buses are often made with heavy gauge thermoforming. These parts endure daily wear while keeping weight low to boost fuel efficiency, all with a polished look that elevates the passenger experience.
Seating Components
Seat backs, armrests, and other seating parts rely on thermoformed plastics for strength and comfort. These components are built to handle constant use and provide impact resistance for safety.
Window Surrounds
Window frames need to be impact-resistant6 to protect passengers. Thermoformed plastics like polycarbonate deliver the strength and clarity required.

Storage Units
Luggage racks and compartments benefit from the process’s ability to create large, rigid structures that are lightweight yet tough enough for heavy loads.
Exterior Parts
Though less common, some exterior parts—like body panels or fascias—use heavy gauge thermoforming for weather resistance and corrosion-free durability, cutting maintenance costs.
Heavy gauge thermoforming is unsuitable for exterior bus parts.False
It can be used for exterior components, offering weather resistance and weight reduction compared to metal.
How Does Heavy Gauge Thermoforming Compare to Other Technologies?
Heavy gauge thermoforming holds its own against alternatives like metal fabrication, fiberglass, and injection molding, especially for large, lightweight parts.

Heavy gauge thermoforming is cost-effective, quick to produce, and lightweight compared to metal fabrication, fiberglass, and injection molding, though it may lack strength for high-stress applications.
| Technology | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Heavy Gauge Thermoforming | Cost-effective, quick production, lightweight, corrosion-resistant | May lack strength for high-stress applications, temperature sensitivity |
| Metal Fabrication | High strength, heat resistance | Heavier, more expensive, prone to corrosion |
| Fiberglass | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Can be more expensive, less strong for complex shapes |
| Injection Molding | High precision, suitable for complex shapes | High initial tool costs, not ideal for large parts |
Comparison with Metal Fabrication
Metal offers unmatched strength and heat resistance but weighs more, costs more, and rusts over time. Thermoforming wins for lighter, cheaper, corrosion-resistant7 bus parts.
Comparison with Fiberglass
Fiberglass matches thermoforming’s lightweight and corrosion-resistant traits but struggles with complex shapes and higher costs. Thermoforming provides better flexibility and speed.
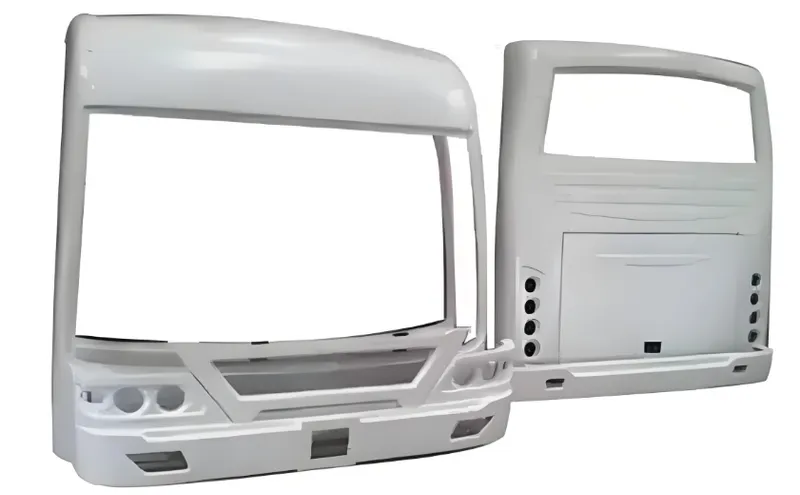

Comparison with Injection Molding
Injection molding excels at precision and complexity but falters with large parts due to pricey tooling. Heavy gauge thermoforming is more practical for big bus components.
Heavy gauge thermoforming offers the same precision as injection molding.False
While it can produce complex shapes, it may not match the fine detail and precision of injection molding.
What Materials are Used in Heavy Gauge Thermoforming for Buses?
Material choice in heavy gauge thermoforming hinges on the part’s specific needs—strength, weather resistance, or aesthetics.

Common materials include ABS for impact resistance, HDPE for moisture resistance, and polycarbonate for high strength, each selected based on the part’s functional needs.
| Material | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| ABS | Good impact resistance, easy to form | Interior panels, seating components |
| HDPE | Strong, moisture-resistant | Exterior parts, storage units |
| Polycarbonate | High impact resistance, clarity | Window surrounds, safety-critical parts |
| PETG | Clear, impact-resistant | Displays, signage |
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
ABS is a staple for interior parts like panels and seats, thanks to its impact resistance and formability.
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene)
HDPE’s strength and moisture resistance make it ideal for exterior parts or components facing tough conditions.

Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate’s toughness and clarity suit it for safety-critical uses like window surrounds.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol)
PETG offers clarity and impact resistance for aesthetic parts like signage or displays.
All thermoplastics are suitable for heavy gauge thermoforming in buses.False
Material selection depends on specific properties like strength, temperature resistance, and application requirements.
What are the Design and Manufacturing Considerations for Heavy Gauge Thermoforming?
Choosing heavy gauge thermoforming involves weighing part size, production volume, complexity, and cost.

Heavy gauge thermoforming is ideal for large, lightweight parts in medium to low volumes, offering cost advantages and design flexibility, but may not be suitable for high-precision or high-stress applications.
Part Size and Complexity
It’s perfect for big parts like bus panels, where injection molding falls short, though it sacrifices some precision.
Production Volume
With lower tooling costs, it’s cost-effective for medium to low volumes—high-volume runs might favor other methods.

Material and Tooling Costs
Thermoforming keeps material and tooling costs down compared to metal fabrication or injection molding.
Design Constraints
Designs need draft angles and radii for mold release, with sheet thickness typically between 0.06 and 0.5 inches.
Heavy gauge thermoforming is the best choice for all bus components.False
While versatile, it may not be suitable for parts requiring extreme strength or precision, where other technologies might be better.
Conclusion
Heavy gauge thermoforming blends cost-effectiveness, design flexibility, and weight reduction, making it a standout choice for passenger bus components. Its role in crafting interior panels, seating, storage, and even exterior parts underscores its value in mass transit. As the industry pushes for efficiency and comfort, this technology’s applications are set to grow.
Heavy gauge thermoforming will replace all other manufacturing methods in bus production.False
While it offers many advantages, other technologies like metal fabrication and injection molding still have their place for specific applications.
-
Discover how thermoforming technology enhances the manufacturing process of passenger buses, improving comfort and safety. ↩
-
Explore the advantages of heavy gauge thermoforming to understand its impact on manufacturing efficiency and product quality. ↩
-
Learn about the different thermoplastics used in heavy gauge thermoforming and their specific applications in manufacturing. ↩
-
Learn about the manufacturing process of interior panels in buses and their impact on passenger experience. ↩
-
Discover the materials and design considerations for seating components that enhance comfort and safety in buses. ↩
-
Learn about impact-resistant materials to enhance safety in vehicle design and manufacturing. ↩
-
Discover the top corrosion-resistant materials to ensure durability and longevity in bus manufacturing. ↩








